Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 70
Question 1
Define an acid.
Solution 1
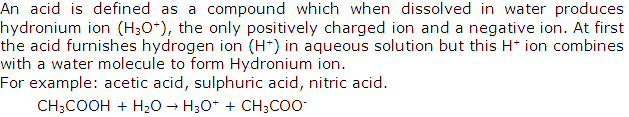
Question 2
Give the name and formula of two
(a) Strong monobasic acids
(b) Weak dibasic acids
(c) Non-volatile acids
(d) Volatile acids
(a) Strong monobasic acids
(b) Weak dibasic acids
(c) Non-volatile acids
(d) Volatile acids
Solution 2
(a) (i) Hydrogen chloride HCl
(ii) Nitric acid HNO3
(b) (i) Carbonic acid H2CO3
(ii) Oxalic acid (COOH)2
(c) (i) Sulphuric acid H2SO4
(ii) Hydrogen chloride HCl
(d) (i) Carbonic acid H2CO3
(ii) Acetic acid
(ii) Nitric acid HNO3
(b) (i) Carbonic acid H2CO3
(ii) Oxalic acid (COOH)2
(c) (i) Sulphuric acid H2SO4
(ii) Hydrogen chloride HCl
(d) (i) Carbonic acid H2CO3
(ii) Acetic acid
Question 3
(a) Define a base.
(b) Explain, all alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
(b) Explain, all alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Solution 3
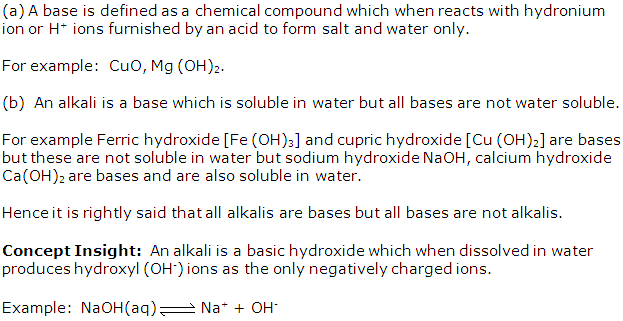
Question 4
(a) Define pH.
(b) State three applications of pH scale.
(b) State three applications of pH scale.
Solution 4
(a) The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydronium ion concentration present in the solution.
pH = -log10 [H3O+]
(b) The three applications of pH scale are:
It is used to determine the acidic or basic nature of the solution.
It is used to determine hydronium ion concentration present in the solution.
It is used to find out neutrality of the solution.
pH = -log10 [H3O+]
(b) The three applications of pH scale are:
It is used to determine the acidic or basic nature of the solution.
It is used to determine hydronium ion concentration present in the solution.
It is used to find out neutrality of the solution.
Question 5
(a) Define an indicator.
(b) Explain, why a universal indicator is preferred to acid-base indicators.
(b) Explain, why a universal indicator is preferred to acid-base indicators.
Solution 5

Question 6
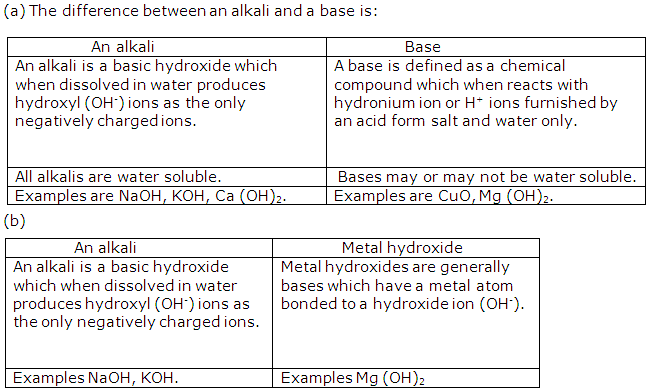
What is the difference between:
(a) An alkali and a base?
(b) An alkali and a metal hydroxide?
(a) An alkali and a base?
(b) An alkali and a metal hydroxide?
Solution 6
Question 7
Name the ions furnished by
(a) Bases in solution
(b) a weak alkali
(c) an acid
(a) Bases in solution
(b) a weak alkali
(c) an acid
Solution 7
(a) Base in solution furnishes the ions:
Hydroxide ion/ oxide ion and a metallic ion.
(b) A weak alkali furnishes the ions:
Hydroxide ion and metallic ion and molecules of weak alkali./
(c) An acid in a solution furnishes the ions:
Hydronium / Hydrogen ion and a negative ion.
Hydroxide ion/ oxide ion and a metallic ion.
(b) A weak alkali furnishes the ions:
Hydroxide ion and metallic ion and molecules of weak alkali./
(c) An acid in a solution furnishes the ions:
Hydronium / Hydrogen ion and a negative ion.
Question 8
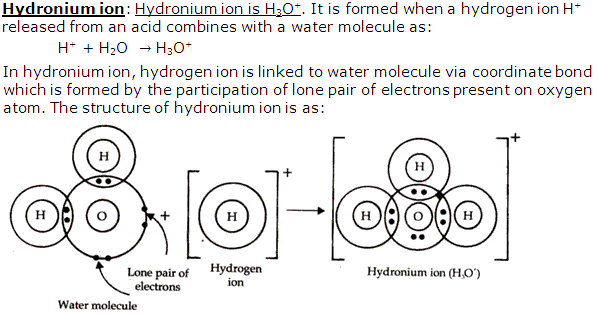
Explain hydronium ion. Write the ionization of sulphuric acid showing the formation of hydronium ion.
Solution 8
Question 9
Give one example in each case:
(a) Basic oxide which is soluble in water
(b) A hydroxide which is highly soluble in water.
(c) A basic oxide which is insoluble in water.
(d) A hydroxide which is insoluble in water.
(e) A weak mineral acid.
(f) A base which is not an alkali.
(g) An oxide which is a base.
(h) A hydrogen containing compound which is not an acid.
(a) Basic oxide which is soluble in water
(b) A hydroxide which is highly soluble in water.
(c) A basic oxide which is insoluble in water.
(d) A hydroxide which is insoluble in water.
(e) A weak mineral acid.
(f) A base which is not an alkali.
(g) An oxide which is a base.
(h) A hydrogen containing compound which is not an acid.
Solution 9
(a) CaO
(b) NaOH
(c) CuO
(d) Cu[(OH)2]
(e) H2CO3
(f) Ferric hydroxide [Fe (OH)3].
(g) CuO
(h) NH3
(b) NaOH
(c) CuO
(d) Cu[(OH)2]
(e) H2CO3
(f) Ferric hydroxide [Fe (OH)3].
(g) CuO
(h) NH3
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 71
Question 1
Anhydrous hydrogen chloride is not an acid but its aqueous solution is a strong acid. Explain.
Solution 1
Anhydrous hydrogen chloride is not an acid but its aqueous solution is a strong acid because anhydrous means without water and we know that the property of acidity is shown by a substance only when it is dissolved in water or its aqueous solution is prepared.
Question 2
Carbonic acid gives an acid salt but hydrochloric acid does not. Explain.
Solution 2

Question 3
What do you understand by the strength of an acid? On what factors does the strength of an acid depend?
Solution 3
Strength of an acid measures the ease with which the acid can ionize to produce hydrogen or hydronium ions when dissolved in water. Those acids which can easily ionize to form hydrogen ions are called strong acids while those which can partially ionize to form hydrogen ions are called weak acids.
Strength of an acid depends upon many factors such as:
Molecular structure of the acid
The temperature
Properties of the solvent
Strength of an acid depends upon many factors such as:
Molecular structure of the acid
The temperature
Properties of the solvent
Question 4
How is an acid prepared from a non metal and a base from a metal? Give equation.
Solution 4

Question 5
Two solutions A and B have pH values of 2 and 9 respectively which one of these two will give a pink colour with phenolphthalein indicator?
Solution 5
Solution B with pH value 9 will give pink colour with phenolphthalein.
Concept Insight: Bases give pink colour with phenolphthalein because a base will abstract two protons from phenolphthalein and the resulting phenolphthalein ion provides pink colour to the solution.
Concept Insight: Bases give pink colour with phenolphthalein because a base will abstract two protons from phenolphthalein and the resulting phenolphthalein ion provides pink colour to the solution.
Question 6
Name two indicators which can identify the presence of an acid?
Solution 6
Two indicators for identification of acid are methyl red and Thymol blue.
Question 7
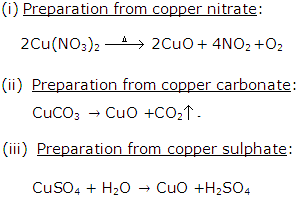
State how would you prepare copper (II) oxide from
(a) Copper nitrate
(b) copper carbonate
(c) copper sulphate
(a) Copper nitrate
(b) copper carbonate
(c) copper sulphate
Solution 7
Question 8
Give four examples of preparation of acids by synthesis.
Solution 8
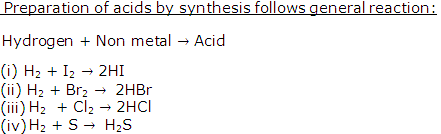
Question 9
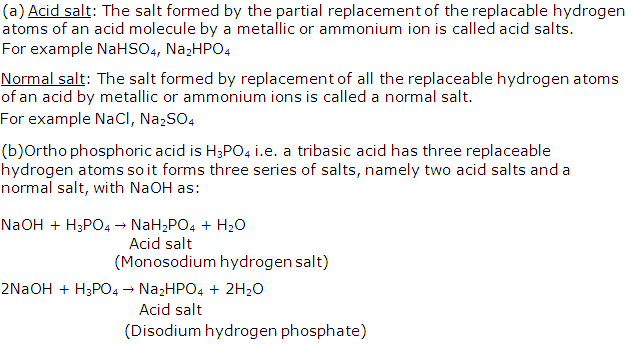
(a) Define an acid salt and a normal salt.
(b) How many salts can be obtained from ortho phosphoric acid? Is there any difference in the salts formed by the acid?
(b) How many salts can be obtained from ortho phosphoric acid? Is there any difference in the salts formed by the acid?
Solution 9
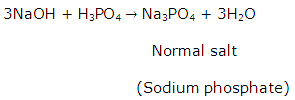
Question 10
Give equations to prepare the following as directed:
(a) MgCO3 from MgCl2
(b) PbCO3 from Pb(NO3)
(c) NaHCO3 from Na2CO3
(a) MgCO3 from MgCl2
(b) PbCO3 from Pb(NO3)
(c) NaHCO3 from Na2CO3
Solution 10
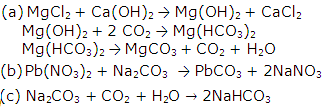
Question 11
Define the following terms:
(i) Efflorescence.
(ii) Hygroscopy.
(iii) Water of crystallization.
(i) Efflorescence.
(ii) Hygroscopy.
(iii) Water of crystallization.
Solution 11
(i) Efflorescence: It is the phenomenon by which hydrated salts on exposure to dry air, lose their water of crystallization and crumble to powder.
(ii) Hygroscopy: It is the phenomenon by which substances absorb moisture from air, but only sufficiently so as to become wet.
(iii) Water of crystallization: It is the fixed amount of water that is present in a crystal as an integral part of its constitution. Hydrated salts are salts having water of crystallisation.
(ii) Hygroscopy: It is the phenomenon by which substances absorb moisture from air, but only sufficiently so as to become wet.
(iii) Water of crystallization: It is the fixed amount of water that is present in a crystal as an integral part of its constitution. Hydrated salts are salts having water of crystallisation.
Question 12
What is deliquescence? What name is given to the compounds exhibiting such property?
Solution 12
Deliquescence is the phenomenon by which certain salts absorb moisture from air, lose their water of crystallization and dissolve in it to form a saturated solution.
The substances which exhibit deliquescence are called deliquescent.
For example Caustic soda NaOH, Caustic potash KOH.
The substances which exhibit deliquescence are called deliquescent.
For example Caustic soda NaOH, Caustic potash KOH.
Question 13
Explain salt hydrolysis. Name two salts which are (a) acidic (b) basic (c) neutral, when dissolved in water.
Solution 13

Question 14
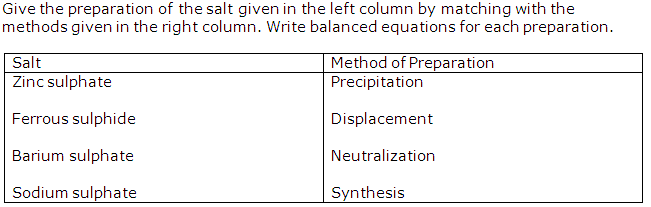
Solution 14

Question 15
(a) Why common salt gets wet during rainy season?
(b) Give four substances which contain water of crystallization and write their common name.
(b) Give four substances which contain water of crystallization and write their common name.
Solution 15
(a) Common salt gets wet during rainy season because the commercially available salt contains impurities, like magnesium chloride, which are deliquescent substances. These absorb moisture from atmosphere and make the table salt wet.
(b) (i) Na2CO3.10H2O = Washing soda
(ii) MgSO4.7H2O = Epsom salt
(iii) CuSO4.5H2O = Blue vitriol
(iv) ZnSO4.7H2O = White vitriol
(b) (i) Na2CO3.10H2O = Washing soda
(ii) MgSO4.7H2O = Epsom salt
(iii) CuSO4.5H2O = Blue vitriol
(iv) ZnSO4.7H2O = White vitriol
Question 16
Write
the reactions of SO2 and oxides of nitrogen which leads to acid
rain formation.
Solution 16
Reactions
of SO2:
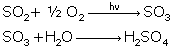
Reactions
of oxides of nitrogen:
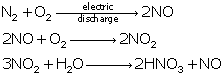
Question 17
Fill
in the blanks
(a) The word acid comes from latin word acidus meaning
_________
(b) Vinegar is the source of ________ acid.
(c) Magnesia is used in making __________.
(d) pH scale was introduced by _________ in 1909.
(e) ___________ is the phenomenon by which
hydrated salts on exposure to dry air, lose their water of crystallization
and crumble to powder.
Solution 17
(a) The word acid comes from the latin word acidus
meaning 'sour'.
(b) Vinegar is the source of acetic acid.
(c) Magnesia is used in making refractory
bricks.
(d) pH scale was introduced by Sorencen
in 1909.
(e) Efflorescence is the phenomenon by which hydrated salts
on exposure to dry air lose their water of crystallisation
and crumble to powder.
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 72
Question 1
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below:
(i) Which of them occurs in solid state?
(a) Citric acid
(b) Formic acid
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(ii) Benzoic acid is used for/in/as
(a) Baking powder
(b) Food preservative
(c) Fertilizers
(d) Explosives
(iii) Which colour with the universal indicator indicates
highly alkaline solution?
(a) Dark red
(b) Yellow
(c) Green
(d) Violet
(iv) Which one is the acidic salt?
(a) KNO3
(b) Sodium acetate
(c) Calcium chloride
(d) Ammonium acetate
Solution 1
(i) Citric acid
(ii) Food preservative
(iii) Violet
(iv) Calcium chloride
Question 2
A solution has a pH of 7. Explain, how you would:
(i) Increase its pH
(ii) Decrease its pH
If a solution changes the color of litmus from red to blue, what can you say about its pH?
(i) Increase its pH
(ii) Decrease its pH
If a solution changes the color of litmus from red to blue, what can you say about its pH?
Solution 2
(i) pH of a solution having pH 7 can be increased by adding a base to it such as NaOH.
(ii) pH can be decreased by adding an acid such as HCl to it.
If a solution changes colour of litmus from red to blue, it shows that its pH is above 7.
(ii) pH can be decreased by adding an acid such as HCl to it.
If a solution changes colour of litmus from red to blue, it shows that its pH is above 7.
Question 3
What can you say about the pH of a solution that liberates carbon dioxide from sodium carbonate?
Solution 3
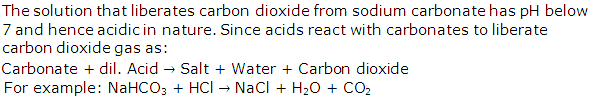
Question 4
From the list of the substances given, name the substances which you would use to prepare each of the following salts:
List of substances: Copper, lead, sodium, zinc, copper oxide, lead carbonate, sodium carbonate solution, dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute nitric acid and dilute sulphuric acid.
Salts: (a) zinc sulphate (b) copper sulphate (c) sodium sulphate (d) lead sulphate.
List of substances: Copper, lead, sodium, zinc, copper oxide, lead carbonate, sodium carbonate solution, dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute nitric acid and dilute sulphuric acid.
Salts: (a) zinc sulphate (b) copper sulphate (c) sodium sulphate (d) lead sulphate.
Solution 4
(a) Zinc sulphate = Zinc and dilute sulphuric acid
(b) Copper sulphate = Copper oxide and dilute sulphuric acid
(c) Sodium sulphate = Sodium carbonate solution and dilute sulphuric acid
(d) Lead sulphate = Lead carbonate and dilute sulphuric acid
(b) Copper sulphate = Copper oxide and dilute sulphuric acid
(c) Sodium sulphate = Sodium carbonate solution and dilute sulphuric acid
(d) Lead sulphate = Lead carbonate and dilute sulphuric acid
Question 5
Define the meaning of the term 'acid salt'.
Solution 5
The term acid salt means the salt formed by partial replacement of the hydrogens present in the acid by metallic or ammonium ions.
For example: NaHCO3
For example: NaHCO3
Question 6
(i) What is the purpose of the pH scale?
(ii) What is the pH of pure water?
(iii) A is a soluble acidic oxide; B is a soluble base. Compared to the pH of pure water, what is the pH of (a) a solution of A (b) a solution of B.
(ii) What is the pH of pure water?
(iii) A is a soluble acidic oxide; B is a soluble base. Compared to the pH of pure water, what is the pH of (a) a solution of A (b) a solution of B.
Solution 6
(i) pH scale is used to express the acidic or basic nature of solution.
(ii) pH of pure water is 7 since it does not have any impurities.
(iii) (a) A soluble oxide of A will have pH less than the pH of pure water i.e. below 7.
(b) A solution of 'B' will have more pH than pure water i.e. above 7.
(ii) pH of pure water is 7 since it does not have any impurities.
(iii) (a) A soluble oxide of A will have pH less than the pH of pure water i.e. below 7.
(b) A solution of 'B' will have more pH than pure water i.e. above 7.
Question 7
Taking sodium carbonate as an example, give the meaning of the following terms:
(i) Water of crystallization.
(ii) Anhydrous.
(i) Water of crystallization.
(ii) Anhydrous.
Solution 7
(i) Water of crystallization: It is the fixed amount of water that is present in a crystal as an integral pat of its constitution. Compounds having water of crystallization are called hydrous salts.
For example: Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 has 10 molecules of water present as water of crystallization Na2CO3.10H2O
(ii) Anhydrous: Hydrous salt on heating lose their water of crystallization, such salts are then called anhydrous.
For example: Na2CO3.10H2O on losing 10 molecules of water forms Na2CO3.
For example: Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 has 10 molecules of water present as water of crystallization Na2CO3.10H2O
(ii) Anhydrous: Hydrous salt on heating lose their water of crystallization, such salts are then called anhydrous.
For example: Na2CO3.10H2O on losing 10 molecules of water forms Na2CO3.
Question 8
Outline the steps required to convert hydrogen chloride to anhydrous iron (III) chloride. Write the equations for the reactions.
Solution 8
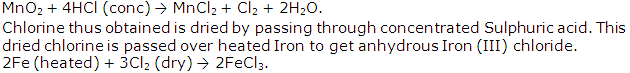
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 73
Question 1
Answer the following questions below, relating your answers only to salts in the following list:
Sodium chloride, anhydrous calcium chloride, copper sulphate-5-water.
(i) What is the name given to the water in the compound copper sulphate-5-water?
(ii) If copper sulphate-5-water is heated, the water is driven off leaving anhydrous copper sulphate. What is the colour of anhydrous copper sulphate?
(iii) By what means, other than heating, you can dehydrate copper sulphate-5-water and obtain anhydrous copper sulphate?
(iv) Which one of the salts in the given list is deliquescent?
Sodium chloride, anhydrous calcium chloride, copper sulphate-5-water.
(i) What is the name given to the water in the compound copper sulphate-5-water?
(ii) If copper sulphate-5-water is heated, the water is driven off leaving anhydrous copper sulphate. What is the colour of anhydrous copper sulphate?
(iii) By what means, other than heating, you can dehydrate copper sulphate-5-water and obtain anhydrous copper sulphate?
(iv) Which one of the salts in the given list is deliquescent?
Solution 1
(i) Water of cystallization.
(ii) White.
(iii) Efflorescence.
(iv) Sodium chloride.
(ii) White.
(iii) Efflorescence.
(iv) Sodium chloride.
Question 2
What is meant by the term weak acid?
Solution 2
Those acids which ionize partially in aqueous solution and thus they contain ions as well as molecules of the acid. Organic acid such as CH3COOH, is a weak acid.
Question 3
Solution P has a pH of 13, solution Q has a pH of 6, and a solution R has a pH of 2. Which solution:
(a) Will liberate ammonia from ammonium sulphate on heating?
(b) Is a strong acid.
(c) Contains molecules as well as ions?
(a) Will liberate ammonia from ammonium sulphate on heating?
(b) Is a strong acid.
(c) Contains molecules as well as ions?
Solution 3
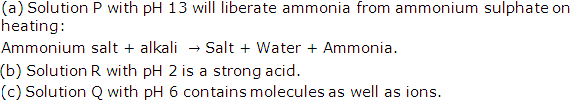
Question 4
Give the name and formula of the acid salt which gives sodium ions and sulphate ions in solution.
Solution 4
The name and formula of the acid salt which gives sodium ions and sulphate ions in solution is Sodium hydrogen sulphate NaHSO4.
Question 5
(a) Define the following terms:
(i) Acid.
(ii) pH scale.
(iii) Neutralisation.
(b) (i) Outline the steps that would be necessary to convert insoluble lead (II) oxide into insoluble chloride.
(ii) Write the balanced equations for the reaction required to convert insoluble lead (II) oxide into insoluble lead chloride.
(iii) If iron reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, what will be the products?
(iv) A solution of iron (III) chloride has a pH less than 7. Is the solution acidic or alkaline?
(i) Acid.
(ii) pH scale.
(iii) Neutralisation.
(b) (i) Outline the steps that would be necessary to convert insoluble lead (II) oxide into insoluble chloride.
(ii) Write the balanced equations for the reaction required to convert insoluble lead (II) oxide into insoluble lead chloride.
(iii) If iron reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, what will be the products?
(iv) A solution of iron (III) chloride has a pH less than 7. Is the solution acidic or alkaline?
Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 74
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
(a) Write the balanced equations for the preparation of the following compounds, starting from iron and using only one other substance:
(i) Iron (II) chloride
(ii) Iron (III) chloride
(iii) Iron (II) sulphate
(iv) Iron (II) sulphide
(b) Write the equations for the laboratory preparation of
(i) sodium sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
(ii) lead sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
(i) Iron (II) chloride
(ii) Iron (III) chloride
(iii) Iron (II) sulphate
(iv) Iron (II) sulphide
(b) Write the equations for the laboratory preparation of
(i) sodium sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
(ii) lead sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
Solution 2
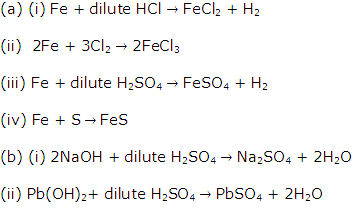
Question 3
Choosing the correct words given in brackets, complete the sentences given below:
(i) An acid is a compound which, when dissolved in water gives ______ ( hydronium / hydroxide) ions as the only ______ (positive/negative) ions.
(ii) A(n) ______ (acid/basic) salt is one in which the hydrogen of an acid has been partially replaced by a ______ (metal/non-metal).
(i) An acid is a compound which, when dissolved in water gives ______ ( hydronium / hydroxide) ions as the only ______ (positive/negative) ions.
(ii) A(n) ______ (acid/basic) salt is one in which the hydrogen of an acid has been partially replaced by a ______ (metal/non-metal).
Solution 3
(i) Hydronium, positive.
(ii) Acid, metal.
(ii) Acid, metal.
Question 4
Write equations for the laboratory preparation of the following salts, using sulphuric acid:
(i) Iron (II) sulphate from the iron.
(ii) Copper sulphate from copper.
(iii) Lead sulphate from lead nitrate.
(iv) Sodium sulphate from sodium carbonate.
(i) Iron (II) sulphate from the iron.
(ii) Copper sulphate from copper.
(iii) Lead sulphate from lead nitrate.
(iv) Sodium sulphate from sodium carbonate.
Solution 4
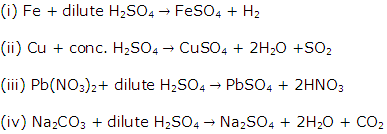
Question 5
Which of the following methods, (a), (b), (c), (d) or (e) is generally used for preparing the chlorides listed below from (i) to (v). Answer by writing down the chloride and the letter pertaining to the corresponding method. Each letter is to be used only once.
(a) Action of an acid on a metal.
(b) Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate.
(c) Direct combination.
(d) Neutralization of an alkali by an acid.
(e) Precipitation (double decomposition).
(i) copper(II) chloride.
(ii) iron(III) chloride.
(iii) iron(II) chloride.
(iv) lead (II) chloride.
(v) sodium chloride.
(a) Action of an acid on a metal.
(b) Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate.
(c) Direct combination.
(d) Neutralization of an alkali by an acid.
(e) Precipitation (double decomposition).
(i) copper(II) chloride.
(ii) iron(III) chloride.
(iii) iron(II) chloride.
(iv) lead (II) chloride.
(v) sodium chloride.
Solution 5
methods for preparation:
(i) Preparation of copper(II) chloride.
Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate
(ii) Preparation of iron(III) chloride.
Direct combination
(iii) Preparation of iron (II) chloride.
Action of an acid on a metal
(iv) Preparation of lead (ii) chloride
Precipitation (double decomposition)
(v) Preparation of sodium chloride
Neutralization of an alkali by an acid.
(i) Preparation of copper(II) chloride.
Action of an acid on an oxide or carbonate
(ii) Preparation of iron(III) chloride.
Direct combination
(iii) Preparation of iron (II) chloride.
Action of an acid on a metal
(iv) Preparation of lead (ii) chloride
Precipitation (double decomposition)
(v) Preparation of sodium chloride
Neutralization of an alkali by an acid.
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 75
Question 1
The preparation of lead sulphate from lead carbonate is a two step process (lead sulphate cannot be prepared by adding dilute sulphuric acid to lead carbonate)
(a) What is the first step that is required to prepare lead sulphate from lead carbonate?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction that will take place when this first step is carried out.
(c) Why is the direct addition of dilute sulphuric acid to lead carbonate an impractical method of preparing lead sulphate?
(a) What is the first step that is required to prepare lead sulphate from lead carbonate?
(b) Write the equation for the reaction that will take place when this first step is carried out.
(c) Why is the direct addition of dilute sulphuric acid to lead carbonate an impractical method of preparing lead sulphate?
Solution 1
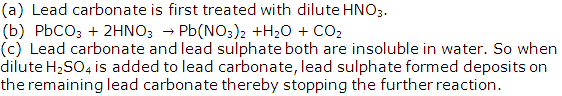
Question 2
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the only ______ ions.
A base is a compound which if soluble in water contains ______ ions. A base reacts with an acid to form ______ and water only. This type of reaction is known as ______.
An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water forms hydronium ions as the only ______ ions.
A base is a compound which if soluble in water contains ______ ions. A base reacts with an acid to form ______ and water only. This type of reaction is known as ______.
Solution 2
Positive, hydroxyl, Salt, Neutralization.
Question 3
What is observed when neutral litmus solution is added to sodium hydrogen carbonate solution?
Solution 3
When neutral litmus solution is added to sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, litmus solution turns red
Question 4
Mention the colour changes observed when the following indicators are added to acids:
(a) Alkaline phenolphthalein solution.
(b) Methyl orange solution.
(c) Neutral litmus solution.
(a) Alkaline phenolphthalein solution.
(b) Methyl orange solution.
(c) Neutral litmus solution.
Solution 4
(a) From pink to colourless.
(b) From orange to pink.
(c) From colourless to red.
(b) From orange to pink.
(c) From colourless to red.
Question 5
From the list given below. Select the word(s) required to correctly complete the blanks (i) to (v) in the following passage:
Ammonia, Ammonium, Carbonate, Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen, Hydronium,
A solution 'X' turns blue litmus red so it must contain (i) ______ ions; another solution 'Y' turns red litmus blue and therefore must contain(ii) ______ ions. When solutions X and Y are mixed together, the products will be a (iii) ______ and ______ (iv) ______. If a piece of magnesium was put into solution X, (v) ______ gas would be evolved.
Ammonia, Ammonium, Carbonate, Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen, Hydronium,
A solution 'X' turns blue litmus red so it must contain (i) ______ ions; another solution 'Y' turns red litmus blue and therefore must contain(ii) ______ ions. When solutions X and Y are mixed together, the products will be a (iii) ______ and ______ (iv) ______. If a piece of magnesium was put into solution X, (v) ______ gas would be evolved.
Solution 5
(i) Hydronium
(ii) Hydroxide
(iii) Salt
(iv) Water
(v) Hydrogen
(ii) Hydroxide
(iii) Salt
(iv) Water
(v) Hydrogen
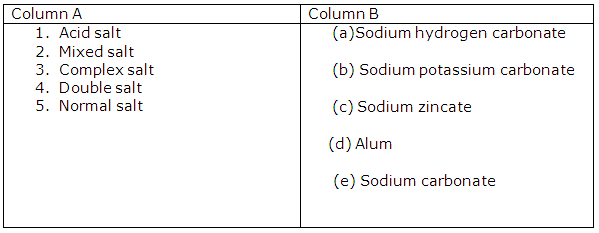
Question 6
Solution 6
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 76
Question 1
What are the terms defined in (i) and (ii) below?
(i) A salt containing a metal ion surrounded by other ions or molecules.
(ii) A base which is soluble in water.
(i) A salt containing a metal ion surrounded by other ions or molecules.
(ii) A base which is soluble in water.
Solution 1
(i) Complex salt.
(ii) Alkali.
(ii) Alkali.
Question 2
Choose the correct answer:
Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide gas can be distinguished by using:
(a) Moist blue litmus paper.
(b) Lime water
(c) Acidified potassium dichromate paper
(d) None of the above.
Carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide gas can be distinguished by using:
(a) Moist blue litmus paper.
(b) Lime water
(c) Acidified potassium dichromate paper
(d) None of the above.
Solution 2
Acidified potassium dichromate paper
Question 3
Solution A is a strong acid.
Solution B is a weak acid.
Solution C is a strong alkali.
(i) Which solution contains solute molecules in addition to water molecules?
(ii) Which solution will give a gelatinous white precipitate with zinc sulphate solution? The precipitate disappears when an excess of the solution is added.
(iii) Which solution could be a solution of glacial acetic acid?
(iv) Give an example of a solution which is a weak alkali.
Solution B is a weak acid.
Solution C is a strong alkali.
(i) Which solution contains solute molecules in addition to water molecules?
(ii) Which solution will give a gelatinous white precipitate with zinc sulphate solution? The precipitate disappears when an excess of the solution is added.
(iii) Which solution could be a solution of glacial acetic acid?
(iv) Give an example of a solution which is a weak alkali.
Solution 3
(i) Solution B.
(ii) Solution A.
(iii) Solution B
(iv) Solution of ammonium hydroxide NH4OH is a weak alkali.
(ii) Solution A.
(iii) Solution B
(iv) Solution of ammonium hydroxide NH4OH is a weak alkali.
Question 4
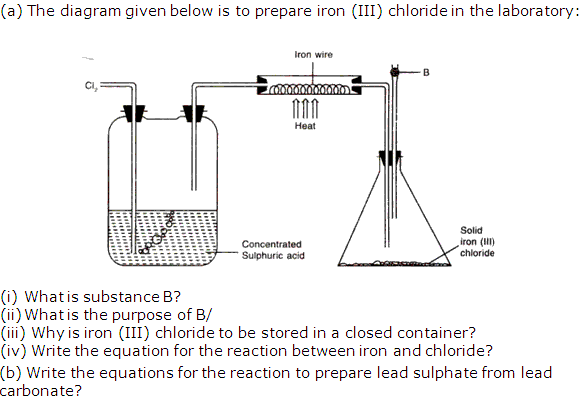
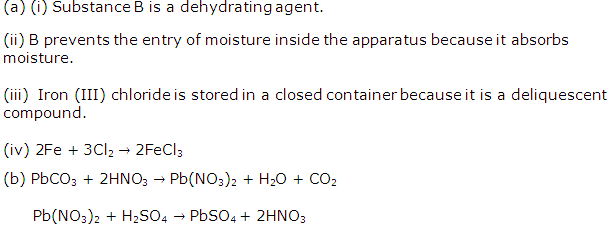
Solution 4
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 77
Question 1
Select
the correct answer from the choices a,b,c
and d which are given.
Write
only the letter corresponding to the correct answer.
(i) A particular solution contains molecules and ions of
the solute so it is a
(a) Weak acid
(b) Strong acid
(c) Strong base
(d) Salt solution
(ii) An organic weak acid is
(a) Formic acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Sulphuric base
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(iii) An example of a complex salt is
(a) Zinc sulphate
(b) Solution hydrogen sulphate
(c) Iron(II) ammonium sulphate
(d) Tetramine copper (II) sulphate
Solution 1
(i) A
(ii) A
(iii) D
Question 2
Write
the equation for the following reaction:
Magnesium
sulphate solution is mixed with barium chloride solution.
Solution 2
Question 3
Give
the equation for the preparation of each of the following salts from the
starting material given.
(i) Copper sulphate from copper (II) oxide
(ii) Iron (III) Chloride from Iron
(iii) Potassium sulphate from potassium hydroxide solution
(iv) Lead chloride from lead carbonate (two equations)
Solution 3
(i) 
(ii) 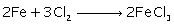
(iii) 
(iv) 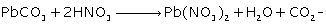
Question 4
Solution
A is a sodium hydroxide solution. Solution B is a weak acid. Solution C is
dilute sulphuric acid. Which solution will.
(i) Liberate sulphur dioxide from sodium sulphite
(ii) Give a white precipitate with zinc sulphate solution,
(iii) Contain solute molecules and ions?
Solution 4
(i) C = Dilute sulphuric acid
(ii) A = Sodium hydroxide
(iii) B = Weak acid
Question 5
What
happen to the crystals of washing soda when exposed to air? Name the
phenomenon exhibited.
Solution 5
When
crystals of washing soda are exposed to air, it loses its water of crystallisation and the phenomenon is known as
efflorescence.
Question 6
Name
the method used for preparation of the following salts from the list given
below:
(i) Sodium nitrate
(ii) Iron (III) chloride
(iii) Lead chloride
(iv) Zinc sulphate
(v) Sodium hydrogen sulphate
List
:
(a) Simple displacement
(b) Neutralization
(c) Decomposition by acid
(d) Double decomposition
(e) Direct synthesis
Solution 6
(i) (B) Neutralisation
(ii) (E) Direct synthesis
(iii) (D) Double decomposition
(iv) (A) Simple displacement
(v) (C) Decomposition by acid
Question 7
From
the list given below, select the word(s) required to correctly complete
blanks (i) to (v) in the following passage. The
words from the list are to be used only once. Write the answers as (a) (i), (ii) (iii) and so on. Do not copy the passage
Ammonia,
ammonium, carbonate, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, hydronium,hydroxide,precipitate,salt,water
(a) A solution M turns blue litmus red, so it
must contain (i) _______ ions; another, solution O
turns red litmus blue and hence, must contain (ii)__________ ions
(b) When Solutions M and O are mixed together,
the products will be (iii) ________ and (iv) ________
(c) If a piece of magnesium was put into a solution M.(v)
_________________Gas would be evolved
Solution 7
(i) Hydronium
(ii) Hydroxide
(iii) Salt
(iv) Water
(v) Hydrogen
Chapter 3 - Study Of Acids, Bases and Salts Exercise 78
Question 1
State
what would you observe when :
(a) Washing soda crystals are exposed to the
atmosphere.
(b) The salt ferric chloride is exposed to the
atmosphere.
Solution 1
(a) When washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O)
is exposed to air, it loses 9 molecules of water to form a monohydrate.
(b) It absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and
becomes moist and ultimately dissolves in the absorbed water, forming a
saturated solution.
Question 2
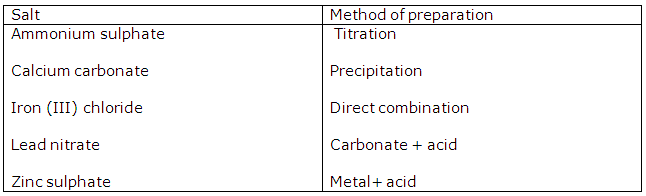
Match
the salts given in Column I with their method of preparation given in Column
II:
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) P(NO3)2 from PbO
(ii) MgCl2 from Mg
(iii) FeCl3 from Fe
(iv) NaNO3 from NaOH
(v) ZnCO3 from ZnSO4
|
(A) Simple displacement
(B) Titration
(C) Neutralisation
(D) Precipitation
(E) Combination
|
Solution 2
Column I
|
Column II
|
(i) P(NO3)2 from PbO
(ii) MgCl2 from Mg
(iii) FeCl3 from Fe
(iv) NaNO3 from NaOH
(v) ZnCO3 from ZnSO4
|
(A) Precipitation
(F) Simple displacement
(B) Combination
(G) Neutralisation
(H) Titration
|
Question 3
Fill
in the blank from the choices given in bracket:
(a) When a metallic oxide is dissolved in
water, the solution formed has a high concentration of ___________ ions. (H+,H3O+,OH-)
Solution 3
(a) When a metallic oxide is dissolved in
water, the solution formed has a high concentration of OH⁻
ions.
Question 4
To
increase the pH value of neutral solution, we should add
(a) An
acid
(b) An acid salt
(c) An alkali
(d) A salt
Solution 4
(b) (c) An alkali

0 comments:
Post a Comment