Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 85
Question 1
Write the colour of the following salts:
(a) Cuprous salts.
(b) Cupric salts.
(c) Aluminium salts.
(d) Ferrous salts.
(e) Ferric salts.
(f) Calcium salts.
(a) Cuprous salts.
(b) Cupric salts.
(c) Aluminium salts.
(d) Ferrous salts.
(e) Ferric salts.
(f) Calcium salts.
Solution 1
(a) Cuprous salts = Colourless
(b) Cupric salts = Blue
(c) Aluminium salts = Colourless
(d) Ferrous salts= Light green
(e) Ferric salts = Yellow
(f) Calcium salts = Colourless
(b) Cupric salts = Blue
(c) Aluminium salts = Colourless
(d) Ferrous salts= Light green
(e) Ferric salts = Yellow
(f) Calcium salts = Colourless
Question 2
Using ammonium hydroxide, how would you distinguish between the following pairs of ions in solution?
(a) Ferrous ion and Ferric ion.
(b) Zinc ion and Lead ion.
(a) Ferrous ion and Ferric ion.
(b) Zinc ion and Lead ion.
Solution 2

Question 3
You are provided with PbCO3, ZnCO3 and CaCO3. How will you identify these cations?
Solution 3

Question 4
Z is a compound. With dilute HCl it gives a gas turning dichromatic solution green. Z gives lilac flame. Name Z.
Solution 4
K2SO4.
Question 5
What do you observe when caustic soda solution is added to the following solution: first a little and then in excess
(a) FeCl3
(b) ZnSO4
(c) Pb(NO3)2
(d) CuSO4
(a) FeCl3
(b) ZnSO4
(c) Pb(NO3)2
(d) CuSO4
Solution 5

Question 6
What is the reaction of freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide with caustic soda solution? Give equation.
Solution 6
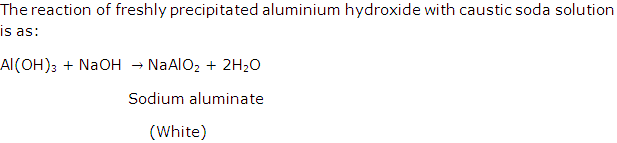
Question 7
What do you understand by amphoteric oxide? Give the balanced equations for the reaction with three different amphoteric oxides with a caustic alkali. Write your observation if any.
Solution 7

Question 8
Name a solution that will separate the components of the following mixtures:
(a) Zn(OH)2 from Pb(OH)2
(b) CaO from PbO
(c) CuO from ZnO
(a) Zn(OH)2 from Pb(OH)2
(b) CaO from PbO
(c) CuO from ZnO
Solution 8

Question 9
Give two examples of amphoteric hydroxides.
Solution 9
Examples of amphoteric hydroxides are: Zn(OH)2, Al(OH)3.
Question 10
A metal whose alloy finds use in the construction of aircrafts in the powdered form is added to sodium hydroxide solution. A colourless gas was evolved and after reaction was over, the solution was colourless.
(a) Name the powdered metal added to sodium hydroxide solution.
(b) Name the gas evolved.
(c) Name the salt present in the colorless solution.
(a) Name the powdered metal added to sodium hydroxide solution.
(b) Name the gas evolved.
(c) Name the salt present in the colorless solution.
Solution 10

Question 11
Name:
(a) A metallic hydroxide soluble in excess of NH4OH
(a) A metallic oxide soluble in excess of caustic soda solution.
(b) A strong alkali
(c) A weak alkali.
(d) Two coloured ions
(e) Two bases which are not alkalis but dissolve in strong alkalis.
(f) A coloured metallic oxide which dissolves in alkalis to yield colourless solutions.
(a) A metallic hydroxide soluble in excess of NH4OH
(a) A metallic oxide soluble in excess of caustic soda solution.
(b) A strong alkali
(c) A weak alkali.
(d) Two coloured ions
(e) Two bases which are not alkalis but dissolve in strong alkalis.
(f) A coloured metallic oxide which dissolves in alkalis to yield colourless solutions.
Solution 11
Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 86
Question 1
What happens when ammonia solution is added
(a) Dropwise and then
(b) In excess to the following solutions:
(i) CuSO4
(ii) ZnSO4
(iii) FeCl3
(c) Write balanced reactions.
(a) Dropwise and then
(b) In excess to the following solutions:
(i) CuSO4
(ii) ZnSO4
(iii) FeCl3
(c) Write balanced reactions.
Solution 1

Question 2
Name the chloride of a metal which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
Solution 2
The chloride of a metal which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide is zinc chloride i.e. ZnCl2.
Question 3
On adding dilute ammonia solution to a colourless solution of a salt, a white gelatinous precipitate appears. This precipitate however dissolves on addition of excess of ammonia solution. Identify (Choose from Na, l, Zn, Pb, Fe)
(a) Which metal salt solution was used?
(b) What is the formula of white gelatinous precipitate obtained?
(a) Which metal salt solution was used?
(b) What is the formula of white gelatinous precipitate obtained?
Solution 3

Question 4
Name
(a) A yellow monoxide that dissolves in hot and concentrated caustic alkali.
(b) A white, insoluble oxide that dissolves when fused with caustic soda or potash.
(c) A compound containing zinc in the anion.
(a) A yellow monoxide that dissolves in hot and concentrated caustic alkali.
(b) A white, insoluble oxide that dissolves when fused with caustic soda or potash.
(c) A compound containing zinc in the anion.
Solution 4
(a) PbO
(b) Al2O3
(c) Na2ZnO2
(b) Al2O3
(c) Na2ZnO2
Question 5
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Salts of ______ [normal / transition] elements are generally coloured. From the ions K1+, Cr3+, Fe2+, Ca2+,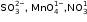 the ions generally coloured are ______.
the ions generally coloured are ______.
(b) The hydroxide which is soluble in excess of NaOH is ______ [Zn(OH)2 / Fe(OH)3 / Fe(OH)2].
(c) The salt which will not react with NH4OH solution ______[ZnCl2, CuCl2 / NH4Cl/ FeCl2]
(d) The substance/s which react with hot conc. NaOH solution and undergoes a neutralization reaction ______ [Al2O3 / Al / Al(OH)3]
(e) To distinguish soluble salts of zinc and lead ______ [NaOH / NH4OH]can be used.
(a) Salts of ______ [normal / transition] elements are generally coloured. From the ions K1+, Cr3+, Fe2+, Ca2+,
(b) The hydroxide which is soluble in excess of NaOH is ______ [Zn(OH)2 / Fe(OH)3 / Fe(OH)2].
(c) The salt which will not react with NH4OH solution ______[ZnCl2, CuCl2 / NH4Cl/ FeCl2]
(d) The substance/s which react with hot conc. NaOH solution and undergoes a neutralization reaction ______ [Al2O3 / Al / Al(OH)3]
(e) To distinguish soluble salts of zinc and lead ______ [NaOH / NH4OH]can be used.
Solution 5
(a) transition, Cr3+, Fe2+, MnO44-.
(b) Zn(OH)2
(c) NH4Cl
(d) Al2O3, Al
(e) NH4OH
(b) Zn(OH)2
(c) NH4Cl
(d) Al2O3, Al
(e) NH4OH
Question 6
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Color of ferrous ion is
(a) Blue
(b) Green
(c) Pink
(d) Light green
(ii) Which one is colourless anion?
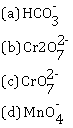
(iii) Sodium zincate (Na2ZnO2)
is
(a) Pale blue ppt
(b) Reddish brown ppt
(c) Colourless
(d) Dirty green ppt
(iv) Metal + alkali → salt + _________
(a) N2
(b) H2
(c) H2O
(d) OH
(v) Which salt solution is soluble in excess of NH4OH
(a) Iron (II) salts
(b) Iron (III) salts
(c) Lead salts
(d) Copper (II) salts
Solution 6
(i) Green
(ii) 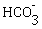
(iii) Colourless
(iv) H2
(v) Copper(II) salts
Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 87
Question 1
You are given a mixture of precipitated copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide. Name a solvent which will dissolve:
(a) Only copper hydroxide
(b) Only zinc hydroxide
(c) Both copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide
(a) Only copper hydroxide
(b) Only zinc hydroxide
(c) Both copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide
Solution 1
(a) Addition of KCN
(b) Addition of excess of NaOH.
(c) Addition of excess of NH4OH.
(b) Addition of excess of NaOH.
(c) Addition of excess of NH4OH.
Question 2
Using sodium hydroxide solution, how will you distinguish:
(a) Zinc nitrate solution from calcium nitrate solution
(b) Iron (II) chloride from iron (III) chloride
(c) Lead hydroxide from magnesium hydroxide.
(a) Zinc nitrate solution from calcium nitrate solution
(b) Iron (II) chloride from iron (III) chloride
(c) Lead hydroxide from magnesium hydroxide.
Solution 2

Question 3
(a) Sodium hydroxide solution is added to solution A. A white precipitate is formed which is soluble in excess sodium hydroxide. Name the metal ion present in A.
(b) When ammonium hydroxide is added to solution B, a pale blue precipitate is formed. This pale blue precipitate dissolves in excess ammonium hydroxide to give an inky blue solution. Name the cation present in solution B. What is the probable colour of solution B?
(b) When ammonium hydroxide is added to solution B, a pale blue precipitate is formed. This pale blue precipitate dissolves in excess ammonium hydroxide to give an inky blue solution. Name the cation present in solution B. What is the probable colour of solution B?
Solution 3
(a) The metal ion present in solution A is Pb2+.
(b) The cation present in solution B is Cu2+. The probable colour of solution B is blue.
(b) The cation present in solution B is Cu2+. The probable colour of solution B is blue.
Question 4
What do you see when sodium hydroxide solution is added to zinc sulphate solution, till it is in excess?
Solution 4

Question 5
You are given three white powders-calcium carbonate, lead carbonate and zinc carbonate. Describe the tests you would carry out in solution, to identify the metal ion in each of the above compounds. Indicate clearly how you would prepare the solutions for the tests.
Solution 5
The solutions for the tests will be prepared by dissolving the given powders separately in water.
(i) Solution of Calcium carbonate:
Calcium carbonate is CaCO3 and contains Ca2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Ca2+ since its addition to calcium carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Ca(OH)2 which are sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
(ii) Solution of Lead carbonate:
Lead carbonate is PbCO3 and contains Pb2+ ions. Ammonium hydroxide solution NH4OH can be used to identify Pb2+ since its addition to lead carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Pb(OH)2 which are insoluble in excess of NH4OH.
(iii) Solution of Zinc carbonate:
Zinc carbonate is ZnCO3 and contains Zn2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Zn2+ since its addition to zinc carbonate solution will give white gelatinous precipitates of Zn(OH)2 which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
(i) Solution of Calcium carbonate:
Calcium carbonate is CaCO3 and contains Ca2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Ca2+ since its addition to calcium carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Ca(OH)2 which are sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
(ii) Solution of Lead carbonate:
Lead carbonate is PbCO3 and contains Pb2+ ions. Ammonium hydroxide solution NH4OH can be used to identify Pb2+ since its addition to lead carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Pb(OH)2 which are insoluble in excess of NH4OH.
(iii) Solution of Zinc carbonate:
Zinc carbonate is ZnCO3 and contains Zn2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Zn2+ since its addition to zinc carbonate solution will give white gelatinous precipitates of Zn(OH)2 which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
Question 6
Write equation for the reaction that will take place when copper sulphate solution is added to sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution 6
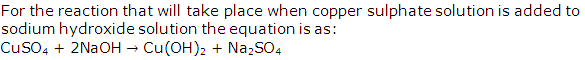
Question 7
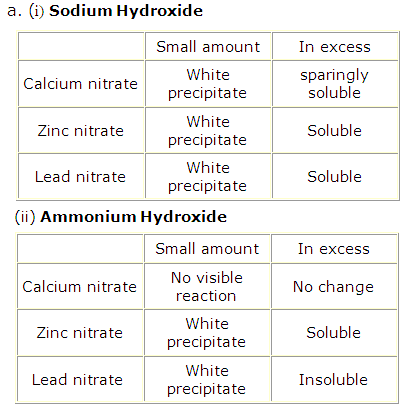
Three test tubes contain calcium nitrate solution, zinc nitrate solution and lead nitrate solution. Each solution is divided into two portions (i) and (ii). Describe the effect of
(i) Adding sodium hydroxide solution to each portion in turn till it is in excess.
(ii) Adding ammonium hydroxide to each portion in turn till it is in excess.
(i) Adding sodium hydroxide solution to each portion in turn till it is in excess.
(ii) Adding ammonium hydroxide to each portion in turn till it is in excess.
Solution 7
Question 8
(a) Sodium hydroxide solution can be used to distinguish between i. iron (II) sulphate solution and (ii) iron (III) sulphate solution; because these solutions give different coloured precipitates with sodium hydroxide solution. Give the colour of the precipitate formed with each of the solution.
(b) What will you observe when barium chloride solution is added to iron(II) sulphate solution.
(c) How will the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite enables you to distinguish between these two compounds?
(b) What will you observe when barium chloride solution is added to iron(II) sulphate solution.
(c) How will the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite enables you to distinguish between these two compounds?
Solution 8

Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 88
Question 1
Describe in each case, one chemical test that would enable you to distinguish between the following pairs of chemicals. Describe what happens with each chemical or state 'no visible reaction'.
(i) Sodium chloride solution and sodium nitrate solution.
(ii) Sodium sulphate solution and sodium chloride solution.
(iii) Calcium nitrate solution and zinc nitrate solution.
(i) Sodium chloride solution and sodium nitrate solution.
(ii) Sodium sulphate solution and sodium chloride solution.
(iii) Calcium nitrate solution and zinc nitrate solution.
Solution 1

Question 2
Write balanced equations for the following reactions:
(i) Iron(II) chloride solution with sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii) Chlorine and cold dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
(iii) Zinc and sodium hydroxide solution
(iv) Sulphur dioxide and sodium hydroxide solution
(Give the equation for the formation of the normal salt)
(i) Iron(II) chloride solution with sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii) Chlorine and cold dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
(iii) Zinc and sodium hydroxide solution
(iv) Sulphur dioxide and sodium hydroxide solution
(Give the equation for the formation of the normal salt)
Solution 2
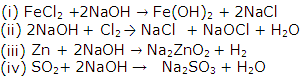
Question 3
State what do you observe when:
(i) Neutral litmus solution is added to alkaline solution
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide is added to iron (III) sulphate solution.
(iii) Lead nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed.
(iv) Ethane is bubbled through a solution of bromine in tetrachloromethane (carbon tetra chloride).
(v) Sulphur burns.
(i) Neutral litmus solution is added to alkaline solution
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide is added to iron (III) sulphate solution.
(iii) Lead nitrate and sodium chloride are mixed.
(iv) Ethane is bubbled through a solution of bromine in tetrachloromethane (carbon tetra chloride).
(v) Sulphur burns.
Solution 3

Question 4
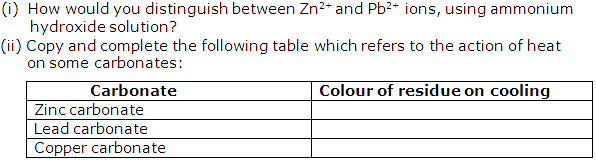
Solution 4
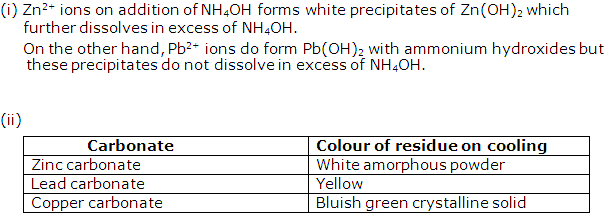
Question 5
Write the observations, and balanced equations for the following reactions:
(i) Sodium hydroxide is added dropwise to a solution of zinc sulphate, till it is in excess.
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide is added first in a small quantity, and then in excess, to a solution of copper sulphate.
(iii) Excess of ammonium hydroxide is added to a substance, obtained by adding hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate solution.
(iv) Moist starch iodide paper is placed at the mouth of a test tube containing chlorine gas.
(v) A paper dipped in potassium permanganate solution is placed at the mouth of a test tube, containing sulphur dioxide gas.
(i) Sodium hydroxide is added dropwise to a solution of zinc sulphate, till it is in excess.
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide is added first in a small quantity, and then in excess, to a solution of copper sulphate.
(iii) Excess of ammonium hydroxide is added to a substance, obtained by adding hydrochloric acid to silver nitrate solution.
(iv) Moist starch iodide paper is placed at the mouth of a test tube containing chlorine gas.
(v) A paper dipped in potassium permanganate solution is placed at the mouth of a test tube, containing sulphur dioxide gas.
Solution 5

Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 89
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
The questions (i) to (v) refer to the following salt solutions listed A to F:
A. Copper nitrate
B. Iron (II) sulphate
C. Iron (III) chloride
D. Lead nitrate
E. Magnesium sulphate
F. Zinc chloride
(i) Which two solutions will give a white precipitate when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid followed by barium chloride solution/
(ii) Which two solutions will give a white precipitate when treated with dilute nitric acid followed by silver nitrate solution?
(iii) Which solution will give a white precipitate when either dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid is added to it?
(iv) Which solution becomes a deep/inky blue colour when excess of ammonium hydroxide is added to it?
(v) Which solution gives a white precipitate with excess ammonium hydroxide?
A. Copper nitrate
B. Iron (II) sulphate
C. Iron (III) chloride
D. Lead nitrate
E. Magnesium sulphate
F. Zinc chloride
(i) Which two solutions will give a white precipitate when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid followed by barium chloride solution/
(ii) Which two solutions will give a white precipitate when treated with dilute nitric acid followed by silver nitrate solution?
(iii) Which solution will give a white precipitate when either dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid is added to it?
(iv) Which solution becomes a deep/inky blue colour when excess of ammonium hydroxide is added to it?
(v) Which solution gives a white precipitate with excess ammonium hydroxide?
Solution 2
(i) B and E (Iron (II) sulphate and Magnesium sulphate)
(ii) C and F (Iron (III) chloride and Zinc chloride)
(iii) D (Lead nitrate)
(iv) A (Copper nitrate)
(v) F (Zinc chloride)
(ii) C and F (Iron (III) chloride and Zinc chloride)
(iii) D (Lead nitrate)
(iv) A (Copper nitrate)
(v) F (Zinc chloride)
Question 3
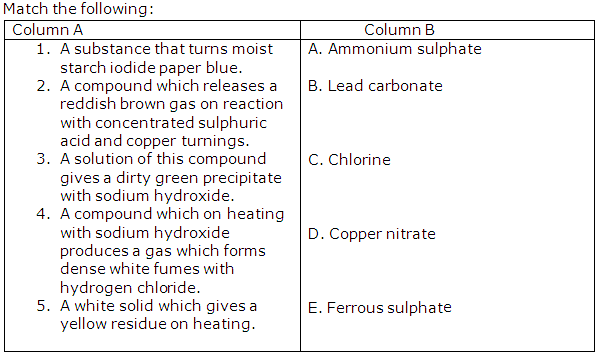
Solution 3

Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 90
Question 1
Choose the correct answer:
The metal oxide which can react with acid as well as alkali is:
(a) Silver oxide.
(b) Copper (II) oxide.
(c) Aluminium oxide
(d) Calcium oxide
The metal oxide which can react with acid as well as alkali is:
(a) Silver oxide.
(b) Copper (II) oxide.
(c) Aluminium oxide
(d) Calcium oxide
Solution 1
C ( Aluminium oxide)
Question 2
Identify the substances P, Q and R in each case based on the information given below:
(i) The deliquescent salt P, turns yellow on dissolving in water, and gives a reddish brown precipitate with sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii) The white crystalline solid Q is soluble in water. It liberates a pungent smelling gas when heated with sodium hydroxide solution.
(iii) The pale green solid R turns reddish brown on heating. Its aqueous solution gives a white precipitate with barium chloride solution. The precipitate is insoluble in mineral acids.
(i) The deliquescent salt P, turns yellow on dissolving in water, and gives a reddish brown precipitate with sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii) The white crystalline solid Q is soluble in water. It liberates a pungent smelling gas when heated with sodium hydroxide solution.
(iii) The pale green solid R turns reddish brown on heating. Its aqueous solution gives a white precipitate with barium chloride solution. The precipitate is insoluble in mineral acids.
Solution 2
(i) P is Ferric chloride
(ii) Q is an ammonium salt
(iii) R is ferrous sulphate
(ii) Q is an ammonium salt
(iii) R is ferrous sulphate
Question 3
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Zinc sulphate solution and Zinc chloride solution.
(ii) Iron (II) chloride solution and iron (III) chloride solution.
(i) Zinc sulphate solution and Zinc chloride solution.
(ii) Iron (II) chloride solution and iron (III) chloride solution.
Solution 3
(i) When BaCl2 solution is added to the given solution ZnSO4 gives a white precipitate while no precipitate is obtained with ZnCl2 solution.
(ii) When NaOH solution is added to the given solution, iron (II) chloride gives dirty green precipitate while reddish brown precipitate is obtained with iron(III) chloride.
(ii) When NaOH solution is added to the given solution, iron (II) chloride gives dirty green precipitate while reddish brown precipitate is obtained with iron(III) chloride.
Question 4
From
the list given below, select the word (s) required complete the blanks (i) to (v) in the following passage :
Note
: words chosen from the list are to be used
only once. Write only the answers. Do not copy the passage, [ reddish brown,
ammonium, nitrogen dioxide, hydroxyl, dirty green, ammonia, acidic, alkaline]
Nitrogen
and hydrogen combine in the presence of a catalyst to give (i) ________ gas. When the above mentioned gas is passed
through water it forms a solution which will be (ii) ______ in nature and the
solution contains (iii) ______ ions and (iv) _______ions. The above solution
when added to iron (II) sulphate solution gives a (v) _________coloured
precipitate of iron (II) hydroxide
Solution 4
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Alkaline
(iii) Ammonium
(iv) Hydroxyl
(v) Dirty green
Question 5
Write
the equation for the following reaction :
Zinc
oxide is treated with sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution 5
Question 6
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Hydroxide of this metal is soluble is sodium hydroxide
solution
(a) Magnesium
(b) Lead
(c) Silver
(d) Copper
(ii) When dilute sulphuric acid reacts with iron sulphide,
the gas evolved is _______
(a) Hydrogen sulphide
(b) Sulphur dioxide
(c) Sulphur trioxide
(d) Vapour of sulphuric acid
Solution 6
(i) Lead
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide
Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry Exercise 91
Question 1
State
two relevant observations for each of the following:
(i) Ammonium hydroxide solution is added to copper (II)
nitrate solution in small quantities and then in excess
(ii) Ammonium hydroxide solution is added to zinc nitrate
solution in minimum quantities and
then in excess
Solution 1
(i) (a) When NH4OH is added to copper (II)
nitrate solution in small quantities, a pale blue precipitate is observed.
(b) When
added in excess, NH4OH dissolves to give an inky blue solution
forming a complex salt.
(ii) (a) When NH4OH is added to zinc
nitrate solution in minimum quantity, it forms a gelatinous white precipitate.
(b) When
added in excess, it dissolves to form a complex salt.
Question 2
Distinguish
between the following pairs of compound using the test given within brackets.
(i) Iron (II) Sulpate an and iron(III) using ammonium hydroxide)
(ii) A lead salt and a zinc salt (using excess ammonium
hydroxide
Solution 2
(i) Iron (II):
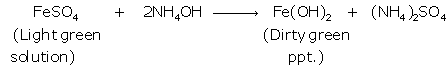
Iron
(III):
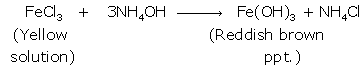
(ii) Pb(NO3)2+2 NH4OH
→
Pb(OH)2+2NH4NO3
On
adding excess of NH4OH, chalky white ppt. of
insoluble Pb(OH)2
is formed.
ZnSO4
+ 2NH4OH → Zn(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4
With
excess of NH4OH, white gelatinous ppt. of soluble Zn(OH)2 is formed.
Question 3
State
your observations when ammonium hydroxide solution is added drop by drop and
then in excess to each of the following solutions :
(i) Copper sulphate solution
(ii) Zinc sulphate solution
Solution 3
i) When NH4OH is added to copper sulphate
solution drop-wise, a pale blue ppt. is obtained.
CuSO4 + 2NH4OH → Cu(OH)2
+ (NH4)2SO4 + 4H2O
With
excess of NH4OH, the ppt. dissolves to give a deep blue solution
of tetra amine copper (II) sulphate.
Cu(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4
+ NH4OH → [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
+ H2O
ii) When NH4OH is added to zinc sulphate
solution drop-wise, a white, gelatinous ppt. is obtained.
ZnSO4 + 2NH4OH → Zn(OH)2
+ (NH4)2SO4
With an excess of NH4OH, the ppt. dissolves to
give a colourless solution of tetra amine zinc (II) sulphate.
Zn(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4
+ 2NH4OH → [Zn(NH3)4]SO4 + 4H2O
Question 4
Fill
in the blank from the choices given in bracket.
Potassium
sulphite on reacting with hydrochloric acid
releases ________
Solution 4
Potassium sulphite
on reacting with hydrochloric acid releases sulphur
dioxide.
Question 5
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
A
chloride which forms a precipitate that is soluble in excess of ammonium
hydroxide is :
(a) Calcium chloride
(b) Ferrous chloride
(c) Ferric chloride
(d) Copper chloride
Solution 5
Copper chloride

0 comments:
Post a Comment