Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 42
Question 1
What is meant by the term chemical bond and chemical bonding?
Solution 1
Chemical bond: A chemical bond may be defined as the linkage that stands for the force which actually holds the atoms together within the molecule.
Chemical bonding: The phenomenon during which a chemical bond is formed is called chemical bonding.
Chemical bonding: The phenomenon during which a chemical bond is formed is called chemical bonding.
Question 2
Why do atoms combine?
Solution 2
Atoms combine to attain the electronic configuration of nearest inert gases as the atoms of inert gases are very stable having 8 electrons or duplet (or 2 electrons in case of helium atom) in their outermost shell.
Question 3
Define: (a) an electrovalent compound (b) a covalent compound.
Solution 3
Electrovalent compounds: The chemical compounds containing electrovalent bonds are called electrovalent or ionic compounds.
For example: Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Covalent compounds: The chemical compound, formed as a result of mutual sharing of electrons or electron pairs thereby establishing a covalent bond is called a covalent or molecular compound.
For example: Hydrogen molecule (H2)
For example: Sodium chloride (NaCl).
Covalent compounds: The chemical compound, formed as a result of mutual sharing of electrons or electron pairs thereby establishing a covalent bond is called a covalent or molecular compound.
For example: Hydrogen molecule (H2)
Question 4
What are the conditions for the formation of an electrovalent bond?
Solution 4
The conditions for the formation of an electrovalent bond are:
1) Low ionization energy of electropositive atom
2) High electron affinity of the electronegative atom.
3) Large electronegativity difference.
4) High lattice energy.
Concept Insight: 1) Lower is the ionization energy of atom, higher is its tendency to lose electron to form a cation and form ionic bond.
2) Higher the value of electron affinity of an atom, greater will be its tendency to form anion and form ionic bond.
3) If the electronegativity difference of two elements is higher, more easy will be the transfer of electrons and hence more chances of ionic bond formation.
4) Lattice energy is the energy released when positive and negatively charged atoms called ions come closer to form a crystal because the attractive forces among the oppositely charged ions tend to decrease the energy of the system. Higher is the lattice energy, greater will be the ease of formation of the compound.
1) Low ionization energy of electropositive atom
2) High electron affinity of the electronegative atom.
3) Large electronegativity difference.
4) High lattice energy.
Concept Insight: 1) Lower is the ionization energy of atom, higher is its tendency to lose electron to form a cation and form ionic bond.
2) Higher the value of electron affinity of an atom, greater will be its tendency to form anion and form ionic bond.
3) If the electronegativity difference of two elements is higher, more easy will be the transfer of electrons and hence more chances of ionic bond formation.
4) Lattice energy is the energy released when positive and negatively charged atoms called ions come closer to form a crystal because the attractive forces among the oppositely charged ions tend to decrease the energy of the system. Higher is the lattice energy, greater will be the ease of formation of the compound.
Question 5
State differences between the properties of ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
Solution 5
| Ioniccompounds | Covalent compounds |
| These contain electrovalent or ionic bond. | These contain covalent bond. |
| They are generally crystalline solids. | They are generally volatile liquids or gases. |
| They have high melting and boiling points. | They have low melting and boiling points. |
| They are bad conductors of electricity in solid state but are good conductors in the molten or aqueous states. | They do not conduct electricity. |
| They are generally soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. | They are generally soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water. |
| They consist of ions. So, their reactions in solutions are fast. | They consist of molecules. So, their reactions in solutions are slow. |
Question 6
Taking hydrogen chloride and methane as examples, distinguish between a polar covalent bond and a non polar covalent bond.
Solution 6
Hydrogen chloride has a polar covalent bond because in hydrogen chloride the higher electronegativity of chlorine atom attracts the shared electron pair towards itself. As a result, the chlorine atom gets a partial negative charge while the hydrogen atom gets a partial positive charge. Hence such a covalent bond with charge separation is called polar covalent bond.
While methane has a non polar covalent bond because in case of methane molecule the shared electron pairs are at equal distance from the carbon and hydrogen atoms, because neither the carbon atom nor the hydrogen atom has enough electronegativity difference between each other to attract the shared pairs of electrons towards itself. Hence no charge separation occurs in the covalent bond due to which it is called non polar covalent bond.
Concept Insight: When a covalent bond is formed between the atoms of the same elements of equal electronegativity then the electron pairs are shared equally between the atoms and the bond so formed is called non polar covalent bond. On the other hand, if the covalent bond is formed between atoms of different elements, with difference in electro negativity, the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms. The more electronegative atom pulls the bonded pair of electrons towards itself and acquires negative charge while the other less electro negative atom acquires positive charge and the bond becomes polar covalent bond.
While methane has a non polar covalent bond because in case of methane molecule the shared electron pairs are at equal distance from the carbon and hydrogen atoms, because neither the carbon atom nor the hydrogen atom has enough electronegativity difference between each other to attract the shared pairs of electrons towards itself. Hence no charge separation occurs in the covalent bond due to which it is called non polar covalent bond.
Concept Insight: When a covalent bond is formed between the atoms of the same elements of equal electronegativity then the electron pairs are shared equally between the atoms and the bond so formed is called non polar covalent bond. On the other hand, if the covalent bond is formed between atoms of different elements, with difference in electro negativity, the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms. The more electronegative atom pulls the bonded pair of electrons towards itself and acquires negative charge while the other less electro negative atom acquires positive charge and the bond becomes polar covalent bond.
Question 7
In terms of electron transfer, define
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
Solution 7
In terms of electron transfer, oxidation is defined as the phenomenon in which an atom loses electron to form a positively charged cation while reduction is defined as the phenomenon in which an atom gains electron to form a negatively charged ion called anion.
During formation of ionic bond one atom undergoes oxidation while another atom undergoes reduction.
During formation of ionic bond one atom undergoes oxidation while another atom undergoes reduction.
Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 43
Question 1
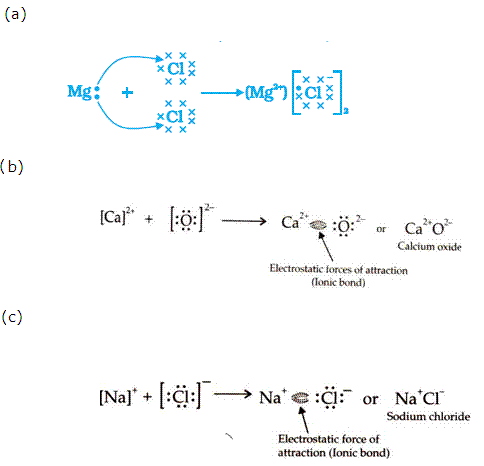
Draw electron dot structures for each of the following:
(a) MgCl2
(b) CaO
(c) NaCl
(a) MgCl2
(b) CaO
(c) NaCl
Solution 1
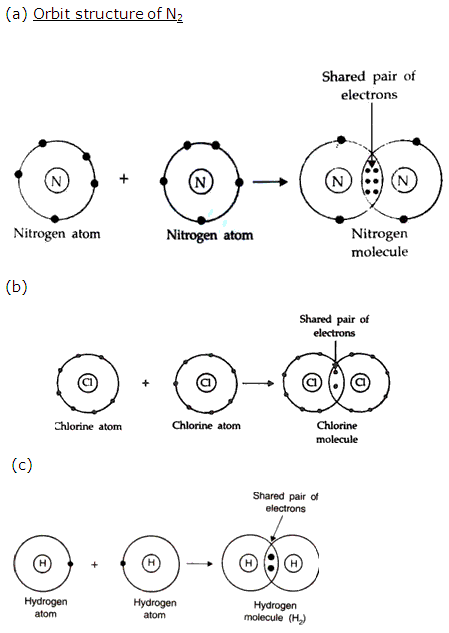
Question 2
Draw the orbit structure for each of the following:
(a) N2
(b) Cl2
(c) H2
(a) N2
(b) Cl2
(c) H2
Solution 2
Question 3
Explain the following briefly:
(a) Sodium chloride dissolves in water but carbon tetra chloride is insoluble in water.
(b) Helium does not form He2 molecule
(c) Pure water does not conduct electricity, but on adding sodium chloride to it, it starts conducting electricity.
(d) Cl2 is a non polar molecule, while HCl is a polar molecule.
(e) Metals are electropositive.
(a) Sodium chloride dissolves in water but carbon tetra chloride is insoluble in water.
(b) Helium does not form He2 molecule
(c) Pure water does not conduct electricity, but on adding sodium chloride to it, it starts conducting electricity.
(d) Cl2 is a non polar molecule, while HCl is a polar molecule.
(e) Metals are electropositive.
Solution 3
(a) Sodium chloride dissolves in water because it is an ionic compound and water is also a polar covalent compound. Water decreases the electrostatic forces of attraction among the sodium and chloride ions due to which these ions become free in water, hence sodium chloride dissolves.
On the other hand, carbon tetra chloride has non polar covalent bond and water has polar covalent bond. Hence, water is unable to break the non polar covalent bond of carbon tetra chloride. So it is insoluble in water
(b) Helium does not form He2 molecule as it has its outermost shell complete i.e. two electrons in its valence shell. Due to this complete valence shell helium atom is very stable hence does not participate in chemical bonding to form He2 molecule.
(c) Pure water does not conduct electricity because it has a polar covalent molecule hence does not have ions in it which can conduct electricity.
On adding sodium chloride to pure water, sodium chloride breaks apart into sodium and chloride ions because water being polar decreases the strong forces of attraction among sodium and chloride ions. Now, pure water has ions present in it which can conduct electricity.
(d) Cl2 is a non polar molecule because the bond is between same atoms that is chlorine with zero electronegativity difference among them. So the shared electron pair is attracted equally by the two chlorine atoms hence there is no separation of charges in the bond formed so the chlorine molecule is non polar.
In case of HCl the bond is formed between two different atoms that is hydrogen and chlorine with enough electro negativity difference so that the shared electron pair is attracted towards more electronegative chlorine atom which acquires partial negative charge while the hydrogen atom acquires partial positive charge hence HCl is a polar molecule.
(e) Metals have low ionization energy due to which they can lose their outermost electrons easily to form positive metallic ions hence metals are electropositive.
For example Sodium metal always form Na+ ions, Potassium forms K+ ions etc.
On the other hand, carbon tetra chloride has non polar covalent bond and water has polar covalent bond. Hence, water is unable to break the non polar covalent bond of carbon tetra chloride. So it is insoluble in water
(b) Helium does not form He2 molecule as it has its outermost shell complete i.e. two electrons in its valence shell. Due to this complete valence shell helium atom is very stable hence does not participate in chemical bonding to form He2 molecule.
(c) Pure water does not conduct electricity because it has a polar covalent molecule hence does not have ions in it which can conduct electricity.
On adding sodium chloride to pure water, sodium chloride breaks apart into sodium and chloride ions because water being polar decreases the strong forces of attraction among sodium and chloride ions. Now, pure water has ions present in it which can conduct electricity.
(d) Cl2 is a non polar molecule because the bond is between same atoms that is chlorine with zero electronegativity difference among them. So the shared electron pair is attracted equally by the two chlorine atoms hence there is no separation of charges in the bond formed so the chlorine molecule is non polar.
In case of HCl the bond is formed between two different atoms that is hydrogen and chlorine with enough electro negativity difference so that the shared electron pair is attracted towards more electronegative chlorine atom which acquires partial negative charge while the hydrogen atom acquires partial positive charge hence HCl is a polar molecule.
(e) Metals have low ionization energy due to which they can lose their outermost electrons easily to form positive metallic ions hence metals are electropositive.
For example Sodium metal always form Na+ ions, Potassium forms K+ ions etc.
Question 4
(a) What type of bond is formed between two atoms, when the electronegative difference between them is:
(i) High (ii) low (iii) zero?
(b) Separate the following compounds into three categories - ionic, polar and covalent compounds; N2, NH4Cl, NH3, NO, NH4NO3, NCl3.
(i) High (ii) low (iii) zero?
(b) Separate the following compounds into three categories - ionic, polar and covalent compounds; N2, NH4Cl, NH3, NO, NH4NO3, NCl3.
Solution 4
(a) (i) when the electro negativity difference between the two atoms is high then the bond formed will be purely ionic.
(ii) When the electro negativity difference between the two atoms is low then the bond formed will be polar covalent bond.
(iii) When the electro negativity difference between the two atoms is zero then the bond formed will be purely covalent.
(b) Ionic compounds = NO, NH4Cl, NH4NO3
Covalent compounds = N2, NH3, NO
Polar compounds = NCl3
Concept Insight: Electro negativity difference between the bonded atoms determines the ease of transfer of electrons between the atoms. On the basis of extent of transfer of electrons between the two atoms the bond will be ionic, covalent or polar.
(ii) When the electro negativity difference between the two atoms is low then the bond formed will be polar covalent bond.
(iii) When the electro negativity difference between the two atoms is zero then the bond formed will be purely covalent.
(b) Ionic compounds = NO, NH4Cl, NH4NO3
Covalent compounds = N2, NH3, NO
Polar compounds = NCl3
Concept Insight: Electro negativity difference between the bonded atoms determines the ease of transfer of electrons between the atoms. On the basis of extent of transfer of electrons between the two atoms the bond will be ionic, covalent or polar.
Question 5
Elements X and Y have the following configurations:
X (2, 8, 7), Y (2, 8, 8, 2)
Answer the following questions:
(a) What will be the nature of bond between X and Y?
(b) Draw the diagram to show the bond formation between X and Y?
(c) Sate three main properties of this compound.
X (2, 8, 7), Y (2, 8, 8, 2)
Answer the following questions:
(a) What will be the nature of bond between X and Y?
(b) Draw the diagram to show the bond formation between X and Y?
(c) Sate three main properties of this compound.
Solution 5
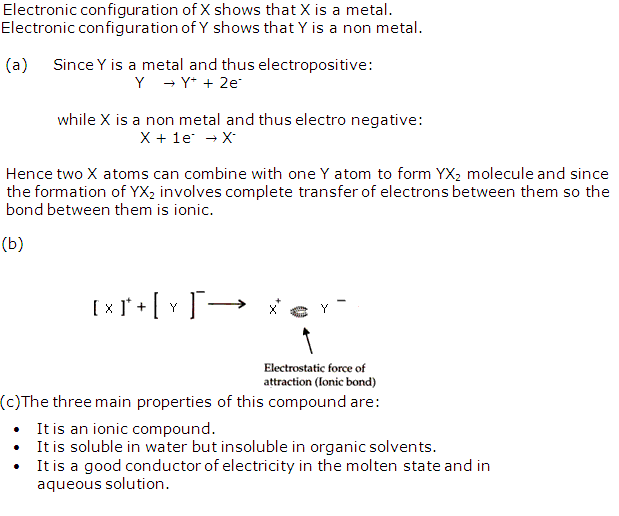
Question 6
Give examples for the following:
(a) Ionic chlorides of two different divalent metals.
(b) Two solid covalent compounds.
(c) Two liquid non polar compounds.
(d) Two gaseous polar compounds.
(e) Two gaseous non polar compounds.
(a) Ionic chlorides of two different divalent metals.
(b) Two solid covalent compounds.
(c) Two liquid non polar compounds.
(d) Two gaseous polar compounds.
(e) Two gaseous non polar compounds.
Solution 6
(a) MgCl2, CaCl2.
(b) Urea, Glucose.
(c) CH4, benzene.
(d) SO2, H2S
(e) H2, N2
(b) Urea, Glucose.
(c) CH4, benzene.
(d) SO2, H2S
(e) H2, N2
Question 7
What are the conditions necessary for the formation of covalent molecule? Give their properties.
Solution 7
The necessary conditions for the formation of covalent molecule are:
Number of valence electrons: Both the participating atoms should have four or more valence electrons in their valence shell.
Equal electro negativities: The combining atoms should have equal electro negativities so that no transfer of electrons takes place.
Equal electron affinities: The combining atoms should also have equal electron affinities i.e. equal attraction for electrons.
Ionization energy: It should be high for both the atoms so that there is no chance of removal of electrons.
High nuclear charge and small inter nuclear distance: Both these conditions favor the formation of covalent bond because during the formation of a covalent bond the electron density gets concentrated between the nuclei of the combining atoms and this electronic charge is responsible for holding the two nuclei together.
The properties of covalent compounds are:
Nature: They are generally volatile liquids or gases. Some may be gases like urea, sugar etc.
Low melting and boiling points: Since the intermolecular forces of attraction are weak, very small amount of heat energy is required to overcome these forces hence their melting and boiling points are low.
Electrical conductivity: Since covalent compounds are made up of molecules and not ions, so they do not conduct electricity.
Solubility: These are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Ionization in solution: These do not ionize when dissolved in water except some polar covalent compounds like HCl.
Molecular reactions: These participate in reactions as a molecule so the reactions are called molecular reactions. These are slow reactions.
Number of valence electrons: Both the participating atoms should have four or more valence electrons in their valence shell.
Equal electro negativities: The combining atoms should have equal electro negativities so that no transfer of electrons takes place.
Equal electron affinities: The combining atoms should also have equal electron affinities i.e. equal attraction for electrons.
Ionization energy: It should be high for both the atoms so that there is no chance of removal of electrons.
High nuclear charge and small inter nuclear distance: Both these conditions favor the formation of covalent bond because during the formation of a covalent bond the electron density gets concentrated between the nuclei of the combining atoms and this electronic charge is responsible for holding the two nuclei together.
The properties of covalent compounds are:
Nature: They are generally volatile liquids or gases. Some may be gases like urea, sugar etc.
Low melting and boiling points: Since the intermolecular forces of attraction are weak, very small amount of heat energy is required to overcome these forces hence their melting and boiling points are low.
Electrical conductivity: Since covalent compounds are made up of molecules and not ions, so they do not conduct electricity.
Solubility: These are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Ionization in solution: These do not ionize when dissolved in water except some polar covalent compounds like HCl.
Molecular reactions: These participate in reactions as a molecule so the reactions are called molecular reactions. These are slow reactions.
Question 8
Define a coordinate bond and give the conditions for its formation.
Solution 8
Coordinate bond: The bond formed between two atoms by a pair of electrons, provided entirely by one of the combining atoms, is called a coordinate bond or dative bond.
Conditions for the formation of coordinate bond:
One of the two atoms must have at least one lone pair of electrons.
Another atom should be short of at least a lone pair of electrons.
Conditions for the formation of coordinate bond:
One of the two atoms must have at least one lone pair of electrons.
Another atom should be short of at least a lone pair of electrons.
Question 9
What do you understand by lone pair and shared pair?
Solution 9
Lone pair: A pair of electrons which is not shared with any other atom is known as the lone pair of electrons.
For example in NH3, Nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons which is not shared with any hydrogen atom.
Shared pair: A pair of electrons which is shared with other atoms to form a bond is known as shared pair of electrons.
For example in HCl the pair of electrons responsible for bond formation between H and Cl is called shared pair.
For example in NH3, Nitrogen has a lone pair of electrons which is not shared with any hydrogen atom.
Shared pair: A pair of electrons which is shared with other atoms to form a bond is known as shared pair of electrons.
For example in HCl the pair of electrons responsible for bond formation between H and Cl is called shared pair.
Question 10
Explain the structures of (a) Hydronium ion, and (b) Ammonium ion.
Solution 10
(a) Structure of hydronium ion: Hydronium ions (H3O+) are formed when a hydrogen ion released from acid combines with water molecules.
Oxygen atom in water molecule attains an octet by forming two single covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms but it still contains two lone pairs of electrons.
H3O+ is formed when the oxygen atom in water molecule donates a lone pair of electrons to a hydrogen ion thus establishing a coordinate bond between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen ion.
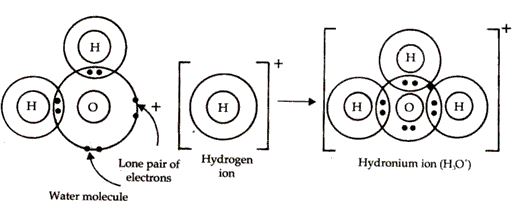
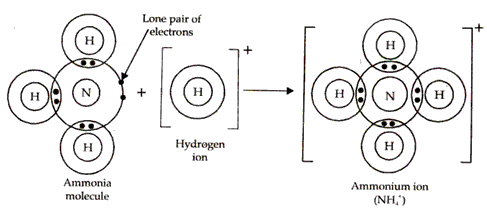
(b) Structure of Ammonium ion: Ammonium ion (NH4+) is formed when a hydrogen ion or proton combines with ammonia molecule. Nitrogen atom in ammonia has a lone pair of electrons on it which it shares with the hydrogen ion which tends to acquire the configuration of helium atom. Thus, a co-ordinate bond results between nitrogen atom and hydrogen ion in ammonium ion.
Oxygen atom in water molecule attains an octet by forming two single covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms but it still contains two lone pairs of electrons.
H3O+ is formed when the oxygen atom in water molecule donates a lone pair of electrons to a hydrogen ion thus establishing a coordinate bond between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen ion.

(b) Structure of Ammonium ion: Ammonium ion (NH4+) is formed when a hydrogen ion or proton combines with ammonia molecule. Nitrogen atom in ammonia has a lone pair of electrons on it which it shares with the hydrogen ion which tends to acquire the configuration of helium atom. Thus, a co-ordinate bond results between nitrogen atom and hydrogen ion in ammonium ion.

Question 11
Explain the following:
(a) Covalent compounds are generally gases or liquids or soft solids.
(b) Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point.
(c) Non-polar covalent compounds are insoluble in water.
(d) Polar covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity.
(a) Covalent compounds are generally gases or liquids or soft solids.
(b) Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point.
(c) Non-polar covalent compounds are insoluble in water.
(d) Polar covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity.
Solution 11
(a) The forces of attraction between the molecules of covalent compounds are weak because the molecules are neutral. So, they are generally gases or liquids or soft solids.
(b)Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point because the intermolecular forces of attraction among the molecules of covalent compounds are weak. Hence very small amount of heat energy is required to overcome the attraction between the molecules.
(c) On the basis of principle like dissolves like we can interpret the insolubility of non polar covalent compounds. Since water is a polar covalent compound that is it has positively and negatively charged ends but the non-polar covalent compounds do not have any kind of charge separation. So water molecules are unable to interact with the molecules of non polar compound and break apart the intermolecular forces of attraction among non-polar molecules making them soluble in water.
(d) Polar covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity because when these are dissolved in water, they ionize and act as electrolyte to produce ions which are responsible for conduction of electricity.
For example polar covalent compound HCl in water behaves as:
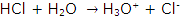
These hydronium and chloride ions produced on dissolution of HCl in water are responsible for conduction of electricity.
(b)Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point because the intermolecular forces of attraction among the molecules of covalent compounds are weak. Hence very small amount of heat energy is required to overcome the attraction between the molecules.
(c) On the basis of principle like dissolves like we can interpret the insolubility of non polar covalent compounds. Since water is a polar covalent compound that is it has positively and negatively charged ends but the non-polar covalent compounds do not have any kind of charge separation. So water molecules are unable to interact with the molecules of non polar compound and break apart the intermolecular forces of attraction among non-polar molecules making them soluble in water.
(d) Polar covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity because when these are dissolved in water, they ionize and act as electrolyte to produce ions which are responsible for conduction of electricity.
For example polar covalent compound HCl in water behaves as:
These hydronium and chloride ions produced on dissolution of HCl in water are responsible for conduction of electricity.
Question 12
Fill in the blanks
(a) The electrovalent bond or ionic bond is called as _____ bond
(b) When ionic compound are dissolved in water
their constituent ions get separated, this phenomenon is called _______ or
________
(c) __________ compounds generally are soluble in water and
insoluble in organic solvents
(d) Coordinate bond is also called
__________bond.
(e) A coordinate bond is represented by an
arrow pointing from ________ to__________ atom
(f) ___________ single covalent
bonds are formed between the carbon and chlorine atoms.
Solution 12
(a) The electrovalent bond or ionic bond is called heteropolar bond.
(b) When ionic compounds are dissolved in water,
their constituent ions get separated; this phenomenon is called ionisation
or dissociation.
(c) Ionic compounds
generally are soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents.
(d) Coordinate bond is also called dative bond.
(e) A coordinate bond is represented by an
arrow pointing from donor to acceptor atom.
(f) Four
single covalent bonds are formed between the carbon and chlorine atoms.
Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 44
Question 1
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Condition favorable for formation of a electrovalent bond is
(i) High ionization energy
(ii) Low electron affinity
(iii)Less electronegativity difference
(iv)High lattice energy
(ii) Which one is not the characteristic of the electrovalent or ionic compound
(a) They are generally solid at ordinary compounds
(b) Low boiling and low melting points
(c) Good conductors of electricity in the molten state and aqueous solution
(d) Generally soluble in water
(iii) Condition favorable for formation of a covalent bond is
(a) Equal electro negativities of combining atoms
(b) Difference in electron affinities between combining atoms
(c) Atoms should have low ionistation energy
(d) Low nuclear charge and large internuclear distance
(iv) Which one is coordinate molecule?
(a) H2O
(b) CH4
(c) N2
(d) 
(v) Which one is not example of polar covalent compound?
(a) H2O
(b) Methane
(c) Hydrogen fluoride
(d) Ammonia
Solution 1
(i) (d) High lattice energy
(ii) (b) Low boiling and low melting points
(iii) (a) Equal electro negativities of combining atoms
(iv) (d) NH4⁻
(v) (b) Methane
Question 2
Solution 2

Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 45
Question 1
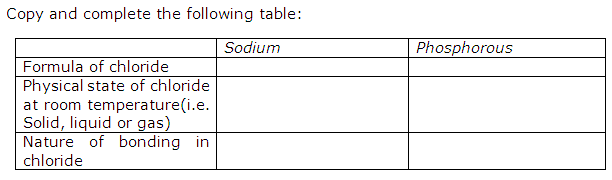
Element X is a metal with a valency 2. Element Y is a non metal with a valency 3.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(b) If Y is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(b) If Y is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
Solution 1
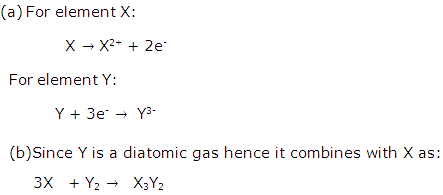
Question 2
(a) Compound X consists of molecules.
Choose the letter corresponding to the correct answer from the choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below:
(i) The type of bonding in X will be:
(a) Ionic (b) electrovalent (c) covalent (d) Molecular
(ii) X is likely to have a:
(a) Low melting point and high boiling point
(b) High melting point and low boiling point
(c) Low melting point and low boiling point
(d) High melting point and high boiling point
(iii) In the liquid state, X will:
(a) become ionic (b) be an electrolyte (c) Conduct electricity (d) not conduct electricity
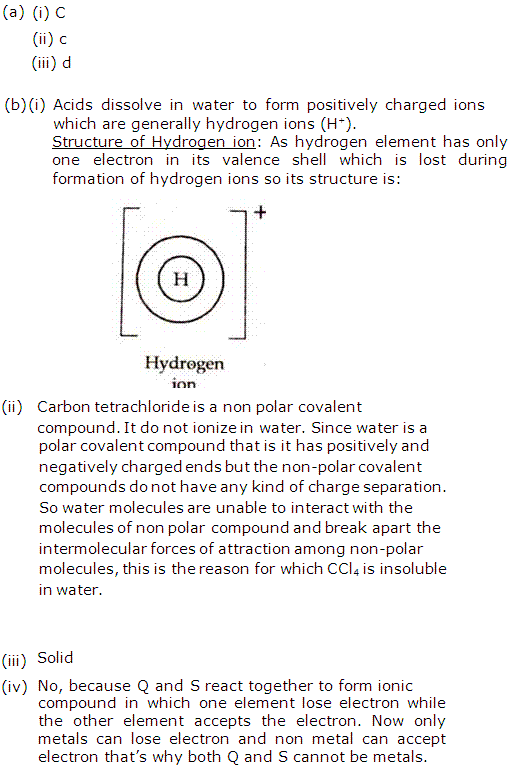
(b) (i) Acids dissolve in water to produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these positive ions.
(ii) Explain, why carbon tetra chloride does not dissolve in water?
(iii) Elements Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. Under normal conditions, which physical state will the compound QS exist in?
(iv) Can Q and S both be metals? Justify your answer.
Choose the letter corresponding to the correct answer from the choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below:
(i) The type of bonding in X will be:
(a) Ionic (b) electrovalent (c) covalent (d) Molecular
(ii) X is likely to have a:
(a) Low melting point and high boiling point
(b) High melting point and low boiling point
(c) Low melting point and low boiling point
(d) High melting point and high boiling point
(iii) In the liquid state, X will:
(a) become ionic (b) be an electrolyte (c) Conduct electricity (d) not conduct electricity
(b) (i) Acids dissolve in water to produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these positive ions.
(ii) Explain, why carbon tetra chloride does not dissolve in water?
(iii) Elements Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. Under normal conditions, which physical state will the compound QS exist in?
(iv) Can Q and S both be metals? Justify your answer.
Solution 2
Question 3
(i) What is a lone pair of electrons?
(ii) Draw an electron dot diagram of a hydronium ion and label the lone pair of electrons.
(iii) Name a neutral covalent molecule which contains one lone pair of electrons.
(ii) Draw an electron dot diagram of a hydronium ion and label the lone pair of electrons.
(iii) Name a neutral covalent molecule which contains one lone pair of electrons.
Solution 3
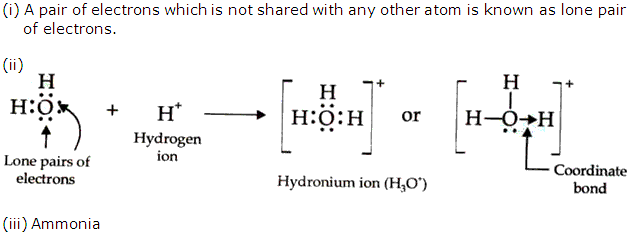
Question 4
Choose the correct answer from the choices (a), (b), (c) and (d):
(i) The property which is characteristic of an electrovalent compound is that:
(a) It is easily vaporized
(b) It has high melting point
(c) It is a weak electrolyte
(d) It often exists as a liquid
(ii) When a metal atom becomes an ion:
(a) It loses electrons and is oxidized
(b) It gains electrons and is reduced
(c) It gains electrons and is oxidized
(d) It loses electrons and is reduced
(i) The property which is characteristic of an electrovalent compound is that:
(a) It is easily vaporized
(b) It has high melting point
(c) It is a weak electrolyte
(d) It often exists as a liquid
(ii) When a metal atom becomes an ion:
(a) It loses electrons and is oxidized
(b) It gains electrons and is reduced
(c) It gains electrons and is oxidized
(d) It loses electrons and is reduced
Solution 4
(i) (b)
(ii) (a)
(ii) (a)
Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 46
Question 1
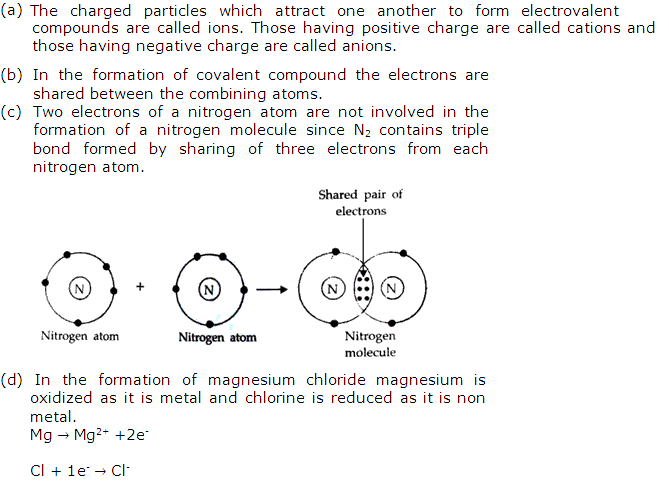
(a) Name the charged particles which attract one another to form electrovalent compound?
(b) In the formation of electrovalent compounds, electrons are transferred from one element to another. How are electrons involved in the formation of a covalent compound?
(c) The electronic configuration of N2 is 2, 5. How many electrons in the outer shell of a N atom are not involved in the formation of a nitrogen molecule?
(d) In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine) name the substance that is oxidized and the substance that is reduced.
(b) In the formation of electrovalent compounds, electrons are transferred from one element to another. How are electrons involved in the formation of a covalent compound?
(c) The electronic configuration of N2 is 2, 5. How many electrons in the outer shell of a N atom are not involved in the formation of a nitrogen molecule?
(d) In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine) name the substance that is oxidized and the substance that is reduced.
Solution 1
Question 2
Choose the correct answer:
Which of the following is not a common characteristic of an electrovalent compound?
(a) High melting point.
(b) Conducts electricity when molten.
(c) Consists of oppositely charged ions.
(d) Ionises when dissolved in water.
Which of the following is not a common characteristic of an electrovalent compound?
(a) High melting point.
(b) Conducts electricity when molten.
(c) Consists of oppositely charged ions.
(d) Ionises when dissolved in water.
Solution 2
ionises when dissolved in water
Question 3
What are the terms defined in (i) and (ii) below?
(i) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons, each bonding atom contributing one electron to the pair.
(ii) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom.
(i) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons, each bonding atom contributing one electron to the pair.
(ii) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom.
Solution 3
(i) Covalent bond.
(ii) Co-ordinate bond
(ii) Co-ordinate bond
Question 4
Fill in the blanks with correct words from the brackets:
(i) Generally ionic compounds exist in ______ (solid, liquid, gas) state.
(ii) Melting and boiling points of covalent compounds are generally ______ (low, high).
(i) Generally ionic compounds exist in ______ (solid, liquid, gas) state.
(ii) Melting and boiling points of covalent compounds are generally ______ (low, high).
Solution 4
(i) solid
(ii) low
(ii) low
Question 5
Match
the column A with Column B.
Column A
|
Column B
|
(i) Sodium chloride
(ii) Ammonium ion
(iii) Carbon tetrachloride
|
Covalent bond
Ionic bond
Covalent and coordinate
bond
|
Solution 5
Column A
|
Column B
|
(i) Sodium chloride
(ii) Ammonium ion
(iii) Carbon tetrachloride
|
Ionic bond
Covalent and coordinate bond
Covalent bond
|
Question 6
Give
reason as to why hydrogen chloride can be termed as a polar covalent compound
Solution 6
HCl is a
covalent compound formed by sharing one electron between chlorine and
hydrogen. Because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen, the shared
pair of electrons shifts towards the chlorine atom. So, a partial negative
charge (δ-) develops on chlorine and a partial positive charge (δ+) develops on hydrogen. Hence, the covalent bond is polar in nature.
Question 7
By
drawing an electron dot diagram, show the lone pair effect leading to the
formation of ammonium ion from ammonia gas and hydrogen ion.
Solution 7
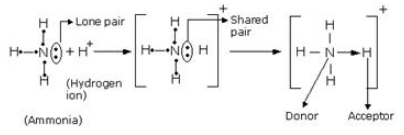
Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 47
Question 1
Compare
the compounds carbon tetrachloride and sodium chloride with regard to solubility
in water and electrical conductivity.
Solution 1
Carbon tetrachloride
|
Sodium chloride
|
It is insoluble in water but
dissolves in organic
solvents.
|
It is soluble in water but
insoluble in organic
solvents.
|
It is a non-conductor of
electricity due to the
absence of ions.
|
It does not conduct electricity in the
solid state but conducts electricity in the fused or aqueous state.
|
Question 2
Give
suitable chemical terms for the bond formed by a shared pair of electrons
with both electrons coming from the same atom.
Solution 2
Dative or coordinate bond
Question 3
Which
of the following is not a typical property of an ionic compound?
(a) High melting point
(b) Conducts electricity in the molten and the
aqueous solution state.
(c) Insoluble in water
(d) Exist as oppositely charged ions even in
the solid state
Solution 3
(c) insoluble in water
Question 4
Among
the following compounds identify the compound that has all three bonds
(ionic, covalent and coordinate bond).
(a) Ammonia
(b) Ammonium chloride
(c) Sodium hydroxide
(d) Calcium chloride
Solution 4
(b) Ammonium chloride
Question 5
The molecule which contains a triple covalent bond is
A. ammonia
B. methane
C. water
D. nitrogen
Solution 5
b. D
Question 6
A Compound 'X' consists of only molecules. Hence 'X' will have
A. a Crystalline hard structure
B. A low melting point and low boiling point
C. An ionic bond
D. A strong force of attraction between its molecules
Solution 6
a. B
Question 7
Name the kind of particles present in :
(a) Sodium hydroxide solution
(b) Carbonic acid
(c) Sugar solution
Solution 7
(a) Ions, Na+ and OH-
(b) Ions, H+ and OH-
(c) Molecules, C12H22O11
Question 8
Bonding
in this molecule can be understood to involve coordinate bonding.
(a) Carbon tetrachloride
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Hydrogen chloride
(d) Ammonium chloride
Solution 8
(d) Ammonium chloride
Question 9
Explain
the bonding in methane molecule using electron dot structure.
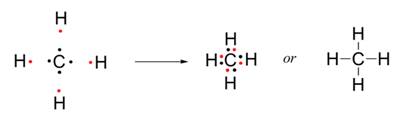
Solution 9
Atom
|
Electronic
configuration
|
Nearest noble gas
|
To attain stable electronic
configuration of a nearest noble gas
|
Carbon
|
126C [2,4]
|
Neon [2,8]
|
Carbon needs
four electrons
to complete
the octet.
|
Hydrogen
|
11H [1]
|
Helium [2]
|
Hydrogen needs one electron to complete
the duplet.
|
One
atom of carbon shares four electron pairs, one with each of the four atoms of
hydrogen.
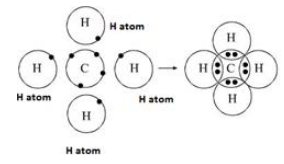
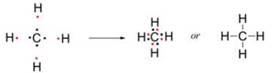 |
|
Before combination
(4 [H] atoms and 1 [C] atom)
|
After combination
(CH4 - Methane molecule)
|
Question 10
Element
X is a metal with a valency 2; Y is a non-metal
with a valency 3.
(a) Write an equation to show how Y forms as
ion
(b) If Y is a diatomic gas, write an equation
for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
Solution 10
(a) Y + 3e-→ Y3-
(b) 3X +Y2 → X3Y2
Question 11
An
element L consists of molecules.
(a) What type of bonding is present in the particles
that make up L?
(b) Why L is heated with iron metal, it forms a
compound FeL. What chemical term would you use to
describe the change undergone by L?
Solution 11
(a) Covalent bonding
(b) Reduction
Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding Exercise 48
Question 1
The
following table shows the electronic configuration of the elements W,X,Y,Z:
Element
|
W
|
X
|
Y
|
Z
|
Electronic
Configuration
|
2,8,1
|
2,8,7
|
2,5
|
1
|
Answer the following questions based on the table above:
(a) What type of bond is formed between
1. W and X
2. Y and Z
(b) What is the formula of the compound formed
between
1. X and Z
2. W and X
Solution 1
(a) 1. Electrovalent bond
2. Covalent bond
(b) 1. XZ
2. WX
Question 2
The
particles present in strong electrolytes are
(a) Only molecules
(b) Mainly ions
(c) Ions and molecules
(d) Only atoms
Solution 2
(b) Mainly ions
Question 3
An
element with the atomic number 19 will most likely combine chemically with
the element whose atomic number is
(a) 17
(b) 11
(c) 18
(d) 20
Solution 3
(a) 17
Question 4
By
drawing an electron dot diagram, show the formation of ammonium ion [Atomic
No: N = 7 and H = 7]
Solution 4
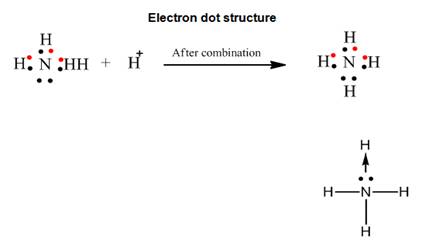
Question 5
Fill
in the blanks from the choice given in bracket :
(a) The compound that does not have a lone pair
of electrons is ___________. (Water, Ammonia, carbon tetrachloride)
Solution 5
(a) The compound that does not have a lone pair of
electrons is carbon tetrachloride.
Question 6
Which
of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
(a) High melting point
(b) Consists of molecules
(c) Always soluble in water
(d) Conducts electricity when it is in the
molten state
Solution 6
(c) Always soluble in water
Question 7
State
the type of bonding in the following molecules.
(a) Water
(b) Calcium oxide
Solution 7
(a) Polar covalent bond
(b) Ionic bond
Question 8
Draw
an electron dot diagram to show the formation of each of the following
compounds:
(a) Methane
(b) Magnesium chloride [H=1,C=6,Mg=12,Cl=17]
Solution 8
(a)
Formation
of carbon tetrachloride
(b)
Electron
dot structure of magnesium chloride:
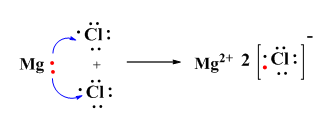

0 comments:
Post a Comment