Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 235
Question 1
Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3
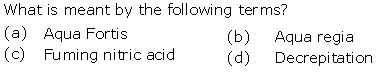
Solution 3

Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 236
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3
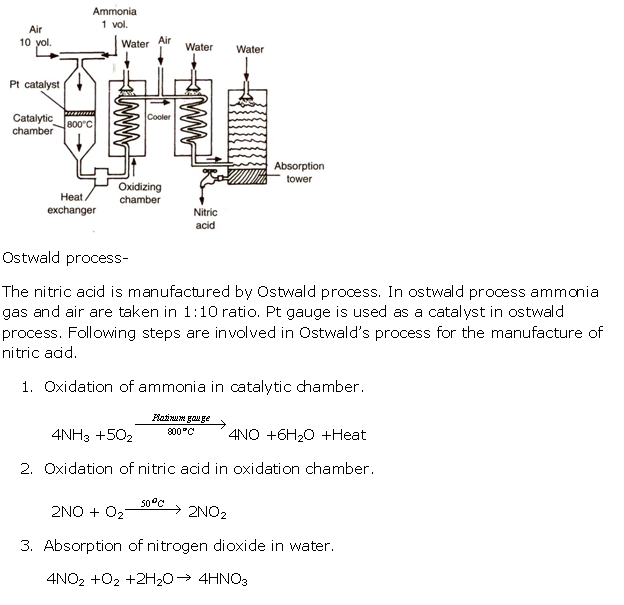
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5

Question 6
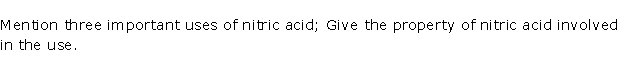
Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8

Solution 8

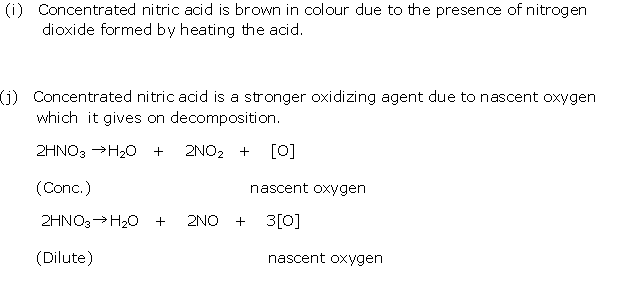
Question 9

Solution 9

Question 10

Solution 10
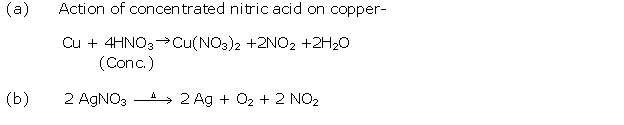
Question 11

Solution 11

Question 12

Solution 12
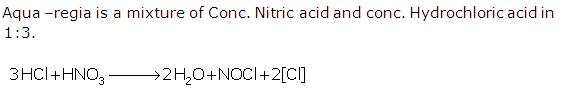
Question 13

Solution 13

Question 14

Solution 14

Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 237
Question 1
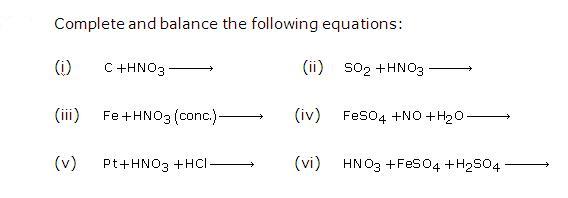
Solution 1
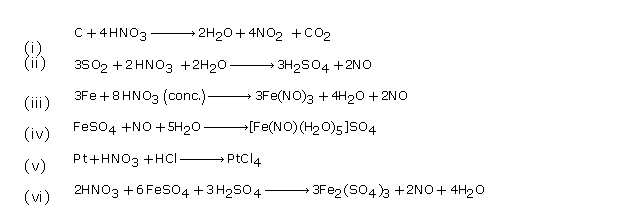
Question 2
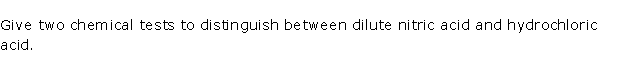
Solution 2
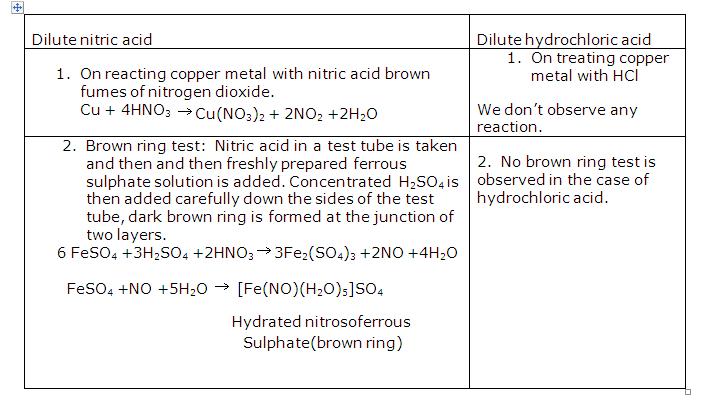
Question 3
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Nitric acid on standing develops brownish colour which
may be attributed to the presence of :
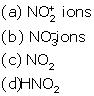
(ii) Concentrated nitric acid oxidises phosphorus to :
(a) H3PO4
(b) P2O3
(c) H3PO2
(d) H4P2O7
(iii) When treated with nitric acid which of the following
liberate hydrogen?
(a) Zinc
(b) Magnesium
(c) Copper
(d) Mercury
(iv) The catalyst used in the manufacture of HNO3
by Ostwald process is
(a) Platinum black
(b) Finely dividend nickel
(c) Vanadium pentoxide
(d) Platinum gauze
Solution 3
(i) NO2
(ii) H3PO4
(iii) Magnesium
(iv) Platinum gauze
Question 4
Fill
in the blank with appropriate word/words
(i) Aqua regia is a mixture of
_______ and________
(ii) Furning nitric acid is obtained by dissolving an excess of
_______ in conc. Nitric acid
(iii) 98% nitric acid is obtained by distilling 68% nitric
acid with ________ under ______
(iv) Ammonal is a mixture of ________ and __________
(v) 3 Cu + 8 HNO3 (dilute) → _______ + 4H2O + _________
Solution 4
(i) Aqua regia is a mixture of nitric acid
and hydrochloric acid.
(ii) Fuming nitric acid is obtained by dissolving excess of nitrogen oxide in conc. nitric acid.
(iii) 98% nitric acid is obtained by distilling 68% nitric
acid with conc. H2SO4
under pressure.
(iv) Ammonal is a mixture of ammonium
nitrate and aluminium powder.
(v) 3Cu + 8HNO3 (dilute) → 3Cu(NO3)2
+ 4H2O + 2NO
Question 5
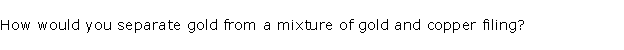
Solution 5

Question 6
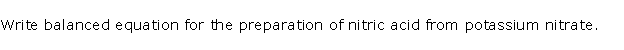
Solution 6
Question 7
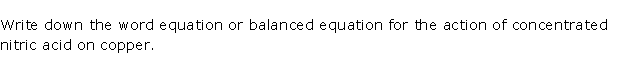
Solution 7
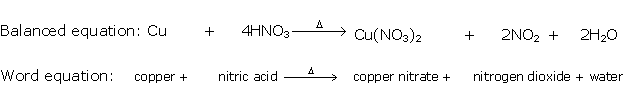
Question 8

Solution 8

Question 9
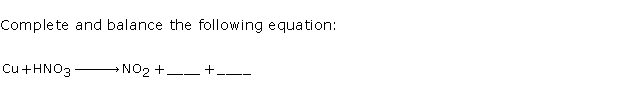
Solution 9
Question 10

Solution 10

Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 238
Question 1
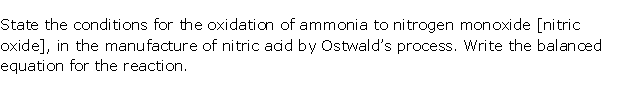
Solution 1
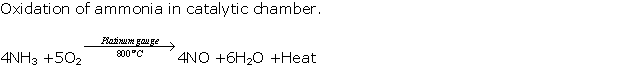
Question 2

Solution 2
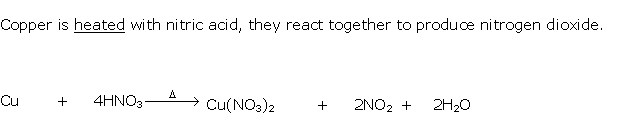
Question 3
Solution 3
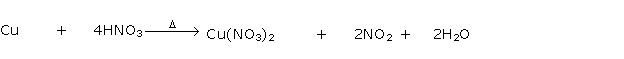
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5
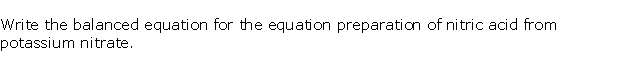
Solution 5
Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7
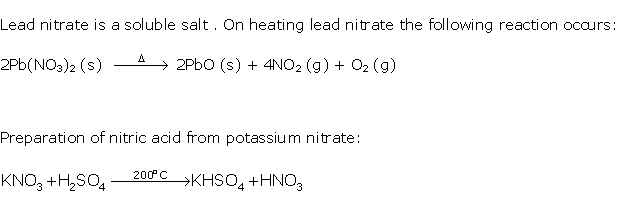
Question 8
Solution 8
Question 9
Describe what you see when concentrated nitric acid is added to copper.
Solution 9
When concentrated nitric acid is added to copper brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide are observed.
Question 10
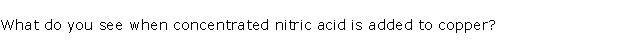
Solution 10
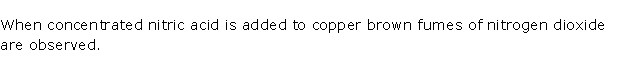
Question 11
Name (formula is not acceptable) the gas produced in each of the following reactions:
(i) By the action of concentrated nitric acid on copper.
(ii) On warming ammonium sulphate with sodium hydroxide solution.
(i) By the action of concentrated nitric acid on copper.
(ii) On warming ammonium sulphate with sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution 11
(i) Nitrogen dioxide
(ii) Ammonia gas
(ii) Ammonia gas
Question 12

Solution 12
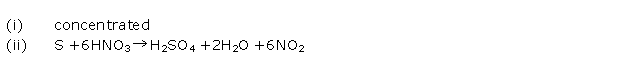
Question 13

Solution 13
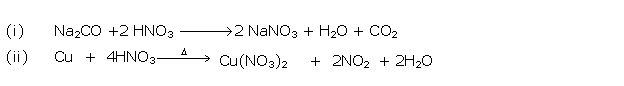
Question 14
Solution 14
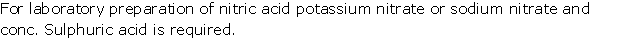
Question 15

Solution 15

Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 239
Question 1

Solution 1
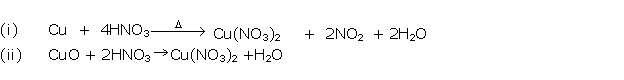
Question 2

Solution 2
Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4

Solution 4
Question 5
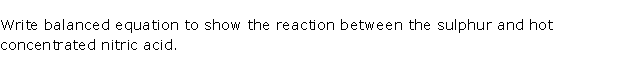
Solution 5
Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8
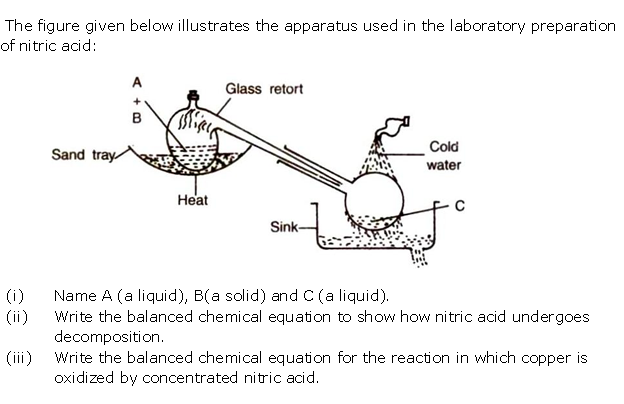
Solution 8
Question 9

Solution 9
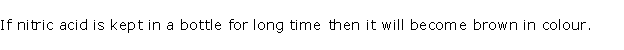
Chapter 9B - Nitric acid Exercise 240
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

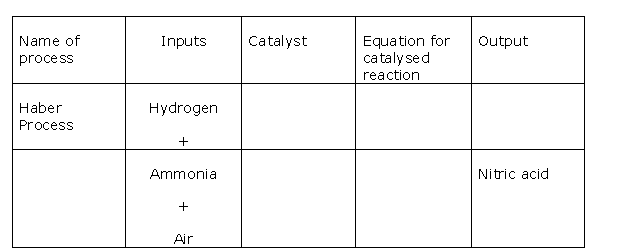
Solution 2
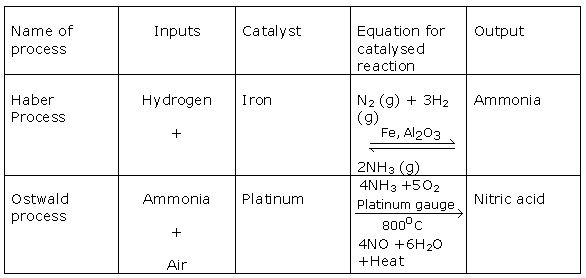
Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4
(i) What is the special feature of the apparatus that is
used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid?
(ii) Why should the temperature of the reaction
mixture of nitric acid not be allowed to rise above 200oC?
Solution 4
(i) The complete apparatus should be made of glass
only.
(ii) At high
temperature, nitric acid decomposes and the glass apparatus may get damaged. Sodium
formed at a higher temperature forms a hard crust which sticks to the walls
of the retort.
Question 5
What
would you observe in the following case :
Copper
is heated with concentrated nitric acid in a hard glass test rube.
Solution 5
Brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide are produced.
Copper reacts with concentrated nitric acid to produce copper nitrate, water
and nitrogen dioxide.
Question 6
(i) Identify the gas evolved when sulphur is treated with
concentrated NH3.
(ii) Balanced equation of oxidation of carbon
with concentrated HNO3
Solution 6
(i) When sulphur is treated with conc. nitric acid, it
produces nitrogen dioxide.
(ii) 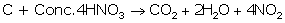
Question 7
Explain
the following :
(i) Dilute nitric acid is generally considered a typical
acid but not so in its reaction with metals
(ii) Concentrated nitric acid appears yellow when it is left
standing in a glass bottle.
(iii) An all glass apparatus is used in the laboratory
preparation of nitric acid.
Solution 7
(i) Dilute nitric acid is generally considered a typical
acid except for its reaction with metals because it does not liberate
hydrogen. It is a powerful oxidising agent, and nascent oxygen formed oxidises hydrogen in water.
(ii) Although pure concentrated nitric acid is colourless,
it appears yellow when left standing in a glass bottle due to the dissolution
of reddish brown nitrogen dioxide gas in the acid. Nitrogen dioxide is
produced because of the thermal decomposition of a portion of nitric acid.
4HNO3
→ 2H2O + 4NO2 + O2
(iii) An all-glass apparatus is used in the laboratory
preparation of nitric acid because nitric acid vapour corrodes rubber and
cork.
Question 8
Fill
in the blanks using the appropriate words given below :
(Sulphur
dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, Nitric oxide, Sulphuric acid)
(i) Cold, dilute nitric acid reacts with copper to give
______.
(ii) Hot, concentrated nitric add reacts with sulphur to
form ______.
Solution 8
(i) Cold, dilute nitric acid reacts with copper to give nitric oxide.
(ii) Hot, concentrated nitric acid reacts with
sulphur to form nitrogen dioxide.
Question 9
Write
a balanced equation for following :
(i) Action of cold and dilute nitric acid on copper
(ii) Action of conc. Nitric acid on sulphur
(iii) Reaction of ammonia with nitric acid
(iv) Laboratory preparation nitric acid.
Solution 9
(i) 3Cu + 8HNO3→ 3Cu(NO3)2
+ 4H2O+ 2NO↑
(ii) 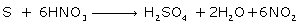
(iii) 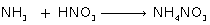
(iv) 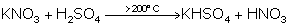

0 comments:
Post a Comment