Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 219
Question 1
How ammonia occurs in nature?
Solution 1
Ammonia is found both in free state and in combined state. In free state, it is formed in traces amount by decaying urine and other organic matter.
In combined state, ammonia is found as ammonium salts mainly as ammonium chloride and ammonium sulphate.
In combined state, ammonia is found as ammonium salts mainly as ammonium chloride and ammonium sulphate.
Question 2
(a) Give the formula of (i) Liquid ammonia (ii) Liquor ammonia
(b) What is liquor ammonia fortis?
(b) What is liquor ammonia fortis?
Solution 2
(a) (i) Liquid ammonia - Compressed ammonia gas at 6 atmospheric pressure. Chemical formula - NH3
(ii) Liquor ammonia - It is saturated solution of ammonia in water. It is very dilute solution of ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
(b) A saturated solution of ammonia in water is called liquor ammonia Fortis.
(ii) Liquor ammonia - It is saturated solution of ammonia in water. It is very dilute solution of ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
(b) A saturated solution of ammonia in water is called liquor ammonia Fortis.
Question 3
(i) How is ammonia gas prepared in laboratory starting from NH4Cl? State the conditions and balanced equation for the preparation.
(ii) How is gas collected in the gas jar?
(iii) Name the substance used for drying ammonia gas? Why cannot substances such as conc.H2SO4, anhydrous calcium chloride and phosphorus pentoxide be used for drying ammonia gas?
(ii) How is gas collected in the gas jar?
(iii) Name the substance used for drying ammonia gas? Why cannot substances such as conc.H2SO4, anhydrous calcium chloride and phosphorus pentoxide be used for drying ammonia gas?
Solution 3

Question 4
Name the following
(i) Gas obtained by treating chlorine in excess of ammonia.
(ii) Solid obtained by passing ammonia over heated copper oxide
(iii) Products obtained by burning ammonia in oxygen.
(iv) Substance used to dry ammonia
(v) Liquid when added to metallic nitride that yield ammonia.
(vi) Indicator that turns deep pink when treated with NH4OH.
(vii) Products obtained by treating with excess chlorine.
(viii) Basic gas that is used as a refrigerant.
(ix) Solution used to remove fat grease.
(x) Salt known as ammoniac.
(xi) Salt used to clean metal surface before soldering, tinning, etc.
(xii) Ammonium salt used in explosive.
(xiii) An acidic gas which reacts with a basic gas liberating neutral gas.
(xiv) A nitride of divalent metal which reacts with hot water producing ammonia.
(i) Gas obtained by treating chlorine in excess of ammonia.
(ii) Solid obtained by passing ammonia over heated copper oxide
(iii) Products obtained by burning ammonia in oxygen.
(iv) Substance used to dry ammonia
(v) Liquid when added to metallic nitride that yield ammonia.
(vi) Indicator that turns deep pink when treated with NH4OH.
(vii) Products obtained by treating with excess chlorine.
(viii) Basic gas that is used as a refrigerant.
(ix) Solution used to remove fat grease.
(x) Salt known as ammoniac.
(xi) Salt used to clean metal surface before soldering, tinning, etc.
(xii) Ammonium salt used in explosive.
(xiii) An acidic gas which reacts with a basic gas liberating neutral gas.
(xiv) A nitride of divalent metal which reacts with hot water producing ammonia.
Solution 4

Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 220
Question 1
(a) Name the process used to manufacture ammonia from its elements.
(b) Under what conditions do the reactants combine to form ammonia? Give a balanced equation for the reaction.
(c) In what ratio by volume, are the above reactants used.
(d) State one possible source of each reactant used in the process.
(e) What is the function of:
(i) finely divided iron
(ii) Molybdenum in the above process
(f) Mention two possible ways by which ammonia produced is removed from unchanged gases.
(b) Under what conditions do the reactants combine to form ammonia? Give a balanced equation for the reaction.
(c) In what ratio by volume, are the above reactants used.
(d) State one possible source of each reactant used in the process.
(e) What is the function of:
(i) finely divided iron
(ii) Molybdenum in the above process
(f) Mention two possible ways by which ammonia produced is removed from unchanged gases.
Solution 1

Question 2
How will you demonstrate the solubility of ammonia in water? Explain.
Solution 2

Question 3
Write the equation for the action of heat on:
(i) Ammonium chloride
(ii) Ammonium nitrate
State whether each reaction is an example of thermal dissociation or thermal decomposition.
(i) Ammonium chloride
(ii) Ammonium nitrate
State whether each reaction is an example of thermal dissociation or thermal decomposition.
Solution 3

Question 4
List the properties of ammonia that make it
(i) A good refrigerant
(ii) A cleaning agent
(iii) As a source of hydrogen
(i) A good refrigerant
(ii) A cleaning agent
(iii) As a source of hydrogen
Solution 4
(i) Liquid ammonia is used as refrigerant as:
(a) It is highly volatile
(b) It has high specific latent heat of vaporization. 1 mole (17g) of liquid ammonia vaporises by absorbing 5.7 kcals of heat from the surroundings, which is there by cooled.
(c) It easily liquefies under pressure at room temperature.
(ii) Ammonia emulsifies fats and grease. Thus it is used to clean oils, fats and body grease etc. from clothes.
(iii) Liquid hydrogen is dangerous to transport as it is highly combustible. Thus, hydrogen is converted to liquid ammonia and transported in cylinders. Later it is catalytically converted to hydrogen.
Key: Uses of ammonia
(a) It is highly volatile
(b) It has high specific latent heat of vaporization. 1 mole (17g) of liquid ammonia vaporises by absorbing 5.7 kcals of heat from the surroundings, which is there by cooled.
(c) It easily liquefies under pressure at room temperature.
(ii) Ammonia emulsifies fats and grease. Thus it is used to clean oils, fats and body grease etc. from clothes.
(iii) Liquid hydrogen is dangerous to transport as it is highly combustible. Thus, hydrogen is converted to liquid ammonia and transported in cylinders. Later it is catalytically converted to hydrogen.
Key: Uses of ammonia
Question 5
(a) Give three uses of ammonium chloride.
(b) Why is ammonium hydroxide used in qualitative analysis? Give two equations to justify your answer.
(b) Why is ammonium hydroxide used in qualitative analysis? Give two equations to justify your answer.
Solution 5

Question 6
Distinguish between liquid ammonia and liquid ammonia fortis.
Solution 6

Question 7
Give three reactions to show reducing property of ammonia.
Solution 7

Question 8
Draw the structure of ammonia and give the reason for alkaline nature of aqueous ammonia.
Solution 8

Question 9
How is an aqueous solution of ammonia prepared? Stage two advantages of method used.
Solution 9

Question 10
(a) Name two fertilizers manufactured from ammonia.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction to prepare one fertilizer from ammonia.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction to prepare one fertilizer from ammonia.
Solution 10

Question 11
Explain the following:
(i) The source of heat is removed after sometime in Haber's process.
(ii) Ammonium nitrate is not used in the laboratory preparation of NH3.
(iii) Ca(OH)2 is preferred over NaOH in the preparation of ammonia.
(iv) Liquid NH3 has no action on litmus, while liquor ammonia has an effect.
(v) Dry N2 and H2 must be used in the Haber's process.
(vi) A promoter is added along with the catalyst in the Haber's process.
(vii) Aqueous ammonia conducts electricity.
(viii) Ammonia cannot be collected over water.
(ix) Ammonia is present in sewage water.
(x) Ammonia solution is used in the laboratory to identify metal ions.
(i) The source of heat is removed after sometime in Haber's process.
(ii) Ammonium nitrate is not used in the laboratory preparation of NH3.
(iii) Ca(OH)2 is preferred over NaOH in the preparation of ammonia.
(iv) Liquid NH3 has no action on litmus, while liquor ammonia has an effect.
(v) Dry N2 and H2 must be used in the Haber's process.
(vi) A promoter is added along with the catalyst in the Haber's process.
(vii) Aqueous ammonia conducts electricity.
(viii) Ammonia cannot be collected over water.
(ix) Ammonia is present in sewage water.
(x) Ammonia solution is used in the laboratory to identify metal ions.
Solution 11

Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 221
Question 1
Give balanced reactions for the following conversions:
(i) Ammonia to nitrogen using an acidic gas.
(ii) Ammonia to nitrogen using copper oxide.
(iii) Ammonia to nitrogen using oxygen.
(iv) Ammonia to nitrogen using trichloride.
(v) Ammonia to ammonium sulphate.
(vi) Ammonia solution to an amphoteric hydroxide.
(vii) Ammonia to ammonium carbonate
(viii) Copper oxide to copper.
(i) Ammonia to nitrogen using an acidic gas.
(ii) Ammonia to nitrogen using copper oxide.
(iii) Ammonia to nitrogen using oxygen.
(iv) Ammonia to nitrogen using trichloride.
(v) Ammonia to ammonium sulphate.
(vi) Ammonia solution to an amphoteric hydroxide.
(vii) Ammonia to ammonium carbonate
(viii) Copper oxide to copper.
Solution 1

Question 2
What do you observe when
(i) Excess ammonia is mixed with chlorine.
(ii) Ammonia in excess is mixed with chlorine.
(iii) Filter paper dipped in colourless phenolphthalein is introduced into ammonia.
(iv) Ammonia is passed over heated lead oxide.
(v) Ammonium solution is added to ferric chloride solution.
(vi) Ammonia solution is added drop by drop and then in excess to aqueous copper sulphate solution.
(vii) Ammonia comes in contact with the eyes of a person.
(i) Excess ammonia is mixed with chlorine.
(ii) Ammonia in excess is mixed with chlorine.
(iii) Filter paper dipped in colourless phenolphthalein is introduced into ammonia.
(iv) Ammonia is passed over heated lead oxide.
(v) Ammonium solution is added to ferric chloride solution.
(vi) Ammonia solution is added drop by drop and then in excess to aqueous copper sulphate solution.
(vii) Ammonia comes in contact with the eyes of a person.
Solution 2

Question 3
Give balanced equation to prove that ammonia
(a) Is alkaline in nature
(b) Has the element hydrogen in it.
(c) Has the element nitrogen in it.
(a) Is alkaline in nature
(b) Has the element hydrogen in it.
(c) Has the element nitrogen in it.
Solution 3

Question 4
Differentiate between:
(i) Action on indicators or dry ammonia gas and aqueous ammonia
(ii) Reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine and NH3 with excess chlorine
(iii) Aqueous ferrous and ferric sulphate solution
(i) Action on indicators or dry ammonia gas and aqueous ammonia
(ii) Reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine and NH3 with excess chlorine
(iii) Aqueous ferrous and ferric sulphate solution
Solution 4

Question 5
(a) Give one use each of four different compounds of ammonia.
(b) Describe two tests to identify ammonia and ammonium ions in an aqueous solution.
(b) Describe two tests to identify ammonia and ammonium ions in an aqueous solution.
Solution 5
(a) (i) Use of Ammonium Chloride
Used in Leclanche cell and dry cell
(ii) Use of Ammonium Sulphate
Used as a fertilizer
(iii)use of Ammonium nitrate
Used in fireworks
(i) Use of Ammonium Carbonate
Used in baking powder
(b) Test of ammonia and ammonium ions:
(i) Ammonia gas has a characteristic pungent smell
(ii) A glass rod dipped in concentrated hydrochloric acid and is introduced into the gas produces thick white fumes of ammonium chloride.
Used in Leclanche cell and dry cell
(ii) Use of Ammonium Sulphate
Used as a fertilizer
(iii)use of Ammonium nitrate
Used in fireworks
(i) Use of Ammonium Carbonate
Used in baking powder
(b) Test of ammonia and ammonium ions:
(i) Ammonia gas has a characteristic pungent smell
(ii) A glass rod dipped in concentrated hydrochloric acid and is introduced into the gas produces thick white fumes of ammonium chloride.
Question 6
Ammonia reacts with a monobasic acid (A) to form a salt (B). B decompose at about 250oC to give two products (C) and (D), leaving no residue. The oxide (D) is a liquid at room temperature and neutral to moist litmus, while gas (C) is a neutral oxide. Identify A, B, C, D. Write the balanced equation involved the above process.
Solution 6

Question 7
Describe all what you will observe and write chemical equations, when limited amount of ammonia gas is passed through the following aqueous solutions:
(i) ZnCl2
(ii) FeSO4
(iii) FeCl3
(iv) Pb(NO3)2
(v) CuSO4
(vi) CrCl3
(i) ZnCl2
(ii) FeSO4
(iii) FeCl3
(iv) Pb(NO3)2
(v) CuSO4
(vi) CrCl3
Solution 7

Question 8
What
are chlorofluorocarbons, why they become popular as substitute of ammonia as
refrigerant?
Solution 8
A
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) is an organic compound which contains carbon,
chlorine and fluorine produced as a volatile derivative of methane and
ethane.
Pure
ammonia gas is highly toxic to humans and would pose a threat if the
refrigerator were to leak. Hence, CFCs became popular as a substitute of
ammonia as a refrigerant.
Question 9
Give
two examples of suitable alternatives of CFCs which can be used as
refrigerant and are non-ozone deflecting?
Solution 9
(i) Hydrochlorofluorocarbon (CF3CHCl2)
(ii) Hyrofluorocarbon (HFC)
Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 222
Question 1
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Ammonia is produced when ammonium chloride is heated
with
(a) Potassium nitrate
(b) Slacked lime
(c) Quick lime
(d) Sodium nitrate
(ii) Ammonia reacts with excess chlorine to form
(a) NH4Cl
(b) NH3,NCl3,HCl
(c) N2,NH4Cl
(d) NCl3,HCl
(iii) Nessler's reagent is an alkaline solution of
(a) HgI2
(b) K2HgI4
(c) HgNH2I
(d) NH2HgO HgI
(iv) Ammonia is commercially prepared by
(a) Haber's process
(b) Ostwald process
(c) Contact process
(d) Head chamber process
(v) The other products obtained along with
water where NH3 is passed over heated CuO are
(a) Cu(NH2)2 and H2
(b) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
and O2
(c) Cu and N2
(d) None of these
(vi) Liquid ammonia is used in refrigeration because of its
(a) High dipole moment
(b) Baricity
(c) Stability
(d) High heat of vaporization
(vii) In the Haber's process for the manufacture
of NH3, iron is used as catalyst and molybedenum as promoter. The
function of promoter is
(a) To Increase the rate of combination of
gases
(b) To raise the activation energy of the
reaction
(c) To increase the activity of the catalyst
(d) To increase the yield of ammonia.
Solution 1
(i) Slacked lime
(ii) NCl3, HCl
(iii) K2HgI4
(iv) Cu and N2
(v) Haber's process
(vi) High heat of vaporisation
(vii) To increase the activity of the catalyst
Question 2
Name a chloride which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide.
Solution 2
Silver chloride
Question 3
Ammonia cannot be collected over water. Give reasons.
Solution 3
Ammonia is highly soluble gas in water and so cannot be collected over water.
Question 4
Pick the odd number out from the list, giving reasons for your answer:
Ammonia, sulphur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, carbon dioxide
Ammonia, sulphur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, carbon dioxide
Solution 4
Ammonia is the odd one out.
Ammonia forms weakly basic solution when dissolved in water.
The others give acidic solution when dissolved in water.
Ammonia forms weakly basic solution when dissolved in water.
The others give acidic solution when dissolved in water.
Question 5
Write balanced equation for the preparation of ammonia for ammonium chloride.
Solution 5

Question 6
Give two large scale use of ammonia.
Solution 6
(i) Ammonia is used in the manufacture of fertilisers such as ammonium sulphate, ammonium nitrate, etc.
(ii) It is used in the industrial preparation of nitric acid by Ostwald's process.
(ii) It is used in the industrial preparation of nitric acid by Ostwald's process.
Question 7
State what will you observe when ammonium hydroxide solution is added to copper sulphate in excess.
Solution 7

Question 8
Solution 8

Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 223
Question 1
Explain, why ammonia is evolved when water is added to the product formed, when magnesium is burned in air.
Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3
Write a balanced equation for the laboratory preparation of ammonia from ammonium chloride.
Solution 3

Question 4
When ammonium hydroxide is added to a solution B, a pale blue precipitate is formed. The pale blue precipitate dissolves in excess of ammonium hydroxide to give an inky blue solution. What is the cation (positive ion) present in solution B? What is the probable colour of solution B?
Solution 4
The cation is Cu2+ ion. Solution B is copper sulphate. It is bright blue in colour.
Question 5
When an ammonium salt is warmed with sodium hydroxide solution, ammonia gas is evolved. State three ways by which you can identify this gas.
Solution 5
Three ways to identify ammonia gas:
1. It is a pungent smell gas.
2. It gives white precipitate when bubbles through a solution of lead nitrate.
3. It gives a brown colour or precipitate when treated with Nessler's reagent.
1. It is a pungent smell gas.
2. It gives white precipitate when bubbles through a solution of lead nitrate.
3. It gives a brown colour or precipitate when treated with Nessler's reagent.
Question 6
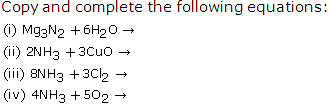
Solution 6

Question 7
Which property of ammonia is illustrated by the reaction (3-ii) in the above equation?
Solution 7
This reaction shows that ammonia is a reducing agent.
Question 8
Name the important process that starts with the reaction in (3-iv). Name the catalyst used.
Solution 8
This process is called as Ostwald's Process .The catalyst used is platinum.
Question 9
During the laboratory preparation, how is ammonia dried and collected?
Solution 9
During laboratory preparation of ammonia, it is passed through a drying tower containing quicklime (calcium oxide).
Ammonia is collected in an inverted dry gas jar by the downward displacement of air.
Ammonia is collected in an inverted dry gas jar by the downward displacement of air.
Question 10
Name the gas evolved when the mixture of calcium hydroxide and ammonium chloride is heated.
Solution 10
Ammonia gas
Question 11
What do you observe when ammonia is bubbled through red litmus solution?
Solution 11
Ammonia forms ammonium hydroxide and turns red litmus blue as it is alkaline in nature.
Question 12
Write an equation for the reaction, when ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide solution are mixed and heated.
Solution 12
Question 13
What is the purpose of Haber's process? Name the gaseous inputs in the Haber's process and state the ratio by volume in which the gases are mixed. What is done to increase the rate of the reaction in Haber's process? Give two different ways by which the product can be separated from the reactants.
Solution 13
Haber's process is used in industrial preparation of ammonia.
Gaseous inputs in Haber's process are dry nitrogen and dry hydrogen gas. They are mixed in the ratio of 1:3 by volume.
The following conditions favour maximum yield of ammonia:
(a) Low temperature
(b) High pressure
(c) Use of catalyst
The gases after reaction pass through condensing pipes of cooling chamber where ammonia gets liquefied and is collected in receiver.
Ammonia can also be collected by downward displacement of air.
Gaseous inputs in Haber's process are dry nitrogen and dry hydrogen gas. They are mixed in the ratio of 1:3 by volume.
The following conditions favour maximum yield of ammonia:
(a) Low temperature
(b) High pressure
(c) Use of catalyst
The gases after reaction pass through condensing pipes of cooling chamber where ammonia gets liquefied and is collected in receiver.
Ammonia can also be collected by downward displacement of air.
Question 14
Write equation for the following:
(i) Burning of ammonia in oxygen
(ii) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(iii) (a) Name the catalyst used in 1(ii)
(b) In the reaction referred to in 1(ii), the catalyst glows red hot. Why?
(c) What is the name of the industrial process which starts with the reaction reffered to in 1 (ii)?
(i) Burning of ammonia in oxygen
(ii) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(iii) (a) Name the catalyst used in 1(ii)
(b) In the reaction referred to in 1(ii), the catalyst glows red hot. Why?
(c) What is the name of the industrial process which starts with the reaction reffered to in 1 (ii)?
Solution 14

Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 224
Question 1
(i) How is ammonia soluble in water?
(ii) Give two reasons to show that the solution of ammonia in water contains hydroxyl ions.
(iii) Name a simple method you would employ to prepare ammonium salts in your laboratory.
(ii) Give two reasons to show that the solution of ammonia in water contains hydroxyl ions.
(iii) Name a simple method you would employ to prepare ammonium salts in your laboratory.
Solution 1

Question 2
State what would you observe when a piece of moist red litmus paper is placed in a gas jar of ammonia.
Solution 2
Dry ammonia are neutral to litmus. An aqueous solution of ammonia turns red litmus blue stating that it is basic in nature.
Question 3
Ammonium salt decompose on heating. What other property do ammonium salts have in common?
Solution 3
Ammonium salts are used as fertilizers in fields.
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5
Industrially, ammonia is obtained by direct combination of nitrogen and hydrogen.
(i) Write balanced equation for the direct combination of nitrogen and hydrogen.
(ii) Which of the metals - iron, platinum, copper - catalyse this direct combination?
(iii) Is the formation of ammonia promoted by high pressure or low pressure?
(i) Write balanced equation for the direct combination of nitrogen and hydrogen.
(ii) Which of the metals - iron, platinum, copper - catalyse this direct combination?
(iii) Is the formation of ammonia promoted by high pressure or low pressure?
Solution 5

Question 6
Is ammonia denser than air? Which property of ammonia is demonstrated by the Fountain experiment? Write the balanced equation for the reaction between ammonia and sulphuric acid.
Solution 6

Question 7
Choose the correct word or phrase from the bracket to complete the following sentences:
(i) Heating ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide produces ______ (ammonia, nitrogen).
(ii) Heating solution of ammonium chloride with sodium nitrite produces ______(ammonia, nitrogen).
(i) Heating ammonium chloride with sodium hydroxide produces ______ (ammonia, nitrogen).
(ii) Heating solution of ammonium chloride with sodium nitrite produces ______(ammonia, nitrogen).
Solution 7
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Nitrogen
(ii) Nitrogen
Question 8
Name the gas produced on warming ammonium sulphate with sodium hydroxide solution.
Solution 8
Ammonia
Question 9
Write the equation for:
(i) The preparation of ammonia from ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide.
(ii) The reaction of hydrogen chloride with ammonia.
(i) The preparation of ammonia from ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide.
(ii) The reaction of hydrogen chloride with ammonia.
Solution 9

Question 10
What are the products formed when ammonia is oxidised with copper oxide?
Solution 10
Question 11
What is the difference between the chemical nature of an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride and an aqueous solution of ammonia?
Solution 11
Aqueous solution is acidic in nature due to presence of hydrogen ion.
Aqueous solution of ammonia is weakly basic in nature due to presence of hydroxyl ion.
Aqueous solution of ammonia is weakly basic in nature due to presence of hydroxyl ion.
Question 12
Write the equations for the action of heat on ammonium chloride and ammonium nitrate?
Solution 12

Question 13
State whether each of the above reactions is an example of thermal decomposition or thermal dissociation.
Solution 13
Thermal dissociation.
Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 225
Question 1
Write the equation for the formation of ammonia by the action of water on magnesium nitride.
Solution 1
Question 2
How is ammonia collected?
Solution 2
Ammonia is collected by downward displacement of air.
Question 3
Why is ammonia not collected over water?
Solution 3
Ammonia is highly soluble in water and so it is not collected over water.
Question 4
Which compound is normally used as a drying agent for ammonia?
Solution 4
Quick lime (calcium oxide) is used as a drying agent for ammonia.
Question 5
Write equation for the reaction of chlorine with excess of ammonia.
Solution 5
Question 6
(i) Write the equation for the reaction in the Haber process, that forms ammonia.
(ii) State the purpose of liquefying ammonia produced in the process.
(ii) State the purpose of liquefying ammonia produced in the process.
Solution 6

Question 7
(i) Which feature of the ammonia molecule leads to the formation of the ammonium ion when ammonia dissolves in water?
(ii) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolves in water.
(iii) Give one test that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced in (i) and (ii).
(ii) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolves in water.
(iii) Give one test that can be used to detect the presence of the ion produced in (i) and (ii).
Solution 7

Question 8
Write the equations for the following reactions, which result in the formation of ammonia:
(i) A mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime is heated.
(ii) Aluminium nitride and water.
(i) A mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime is heated.
(ii) Aluminium nitride and water.
Solution 8

Question 9
State what is observed when excess of ammonia is passed through an aqueous solution of lead nitrate?
Solution 9

Question 10
(a) Name the substance used for drying ammonia.
(b) Write an equation to illustrate the reducing nature of ammonia.
(c) With reference to Haber's process for the preparation of ammonia, write the equation and the conditions required.
(b) Write an equation to illustrate the reducing nature of ammonia.
(c) With reference to Haber's process for the preparation of ammonia, write the equation and the conditions required.
Solution 10

Question 11
You enter a laboratory after a class has completed the Fountain experiment. How will you be able to tell whether the gas used in experiment was hydrogen chloride or ammonia?
Solution 11
By the pungent smell of ammonia gas.
Question 12
Write balanced chemical equations for a reaction in which ammonia is oxidised by the following:
(i) A metal oxide
(ii) A gas which is not oxygen
(i) A metal oxide
(ii) A gas which is not oxygen
Solution 12

Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 226
Question 1
Choose the correct answer:
Ammonia can be obtained by adding water to:
(a) Ammonium chloride
(b) Ammonium nitrite
(c) Magnesium nitride
(d) Magnesium nitrate
Ammonia can be obtained by adding water to:
(a) Ammonium chloride
(b) Ammonium nitrite
(c) Magnesium nitride
(d) Magnesium nitrate
Solution 1
(c) Magnesium nitride
Question 2
Write
the equation for the following :
Ammonium
chloride is treated with sodium hydroxide.
Solution 2
Question 3
State
your observation for the following cases
(i) Ammonia gas is burnt in an atomosphere of oxygen in the
absence of a catalyst
(ii) Glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide is brought near
the mouth of the concentrated hydrochloric acid bottle
Solution 3
(i) Ammonia burns with a yellowish flame. It produces water
vapour and nitrogen.
(ii) When ammonium hydroxide is brought near the mouth of
concentrated hydrochloric acid, it produces dense white fumes of ammonium
chloride.
Question 4
The
questions below are related to the manufacture of ammonia.
(i) Name the process
(ii) In what ratio must the reactants be taken
(iii) Name the catalyst used
(iv) Give the equation for the manufacture of ammonia
(v) Ammonia can act as a reducing agent write a relevant
equation for such a reaction.
Solution 4
(i) Haber's process
(ii) 1 part of nitrogen and 3 parts of hydrogen
(iii) Finely divided iron (Fe)
(iv) 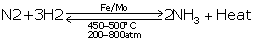
(v) 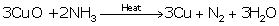
Question 5
The
diagram shows a simple arrangement of the fountain experiment:
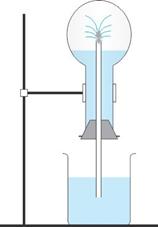
(i) Name the two gases you have studied which can be used
in this experiment
(ii) What is the common properly demonstrated by this
experiment
Solution 5
(i) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas
(ii) High solubility of gases in water
Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 227
Question 1
The
diagram shows an experimental set-up for the laboratory prepration of a
pungent smelling gas. The gas is alkaline in nature.
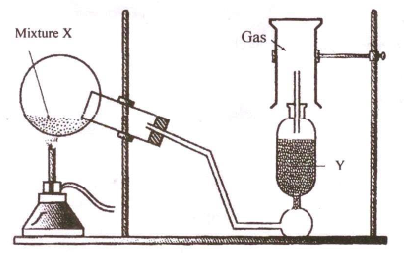
(i) Nature the gas collected in the jar.
(ii) Write the balance equation for the above preparation.
(iii) How is the gas being collected?
(iv) Name the drying agent used.
(v) How will you find that the jar is full of gas?
Solution 1
(i) Ammonia
(ii) 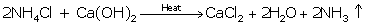
(iii) By downward displacement of air
(iv) Quicklime/CaO
(v) Bring moist red litmus paper to the mouth
of the inverted jar; it immediately turns blue.
Or
Bring
a glass rod dipped in hydrochloric acid to the
mouth
of the inverted jar. If it produces dense white
fumes,
then the jar is full of gas.
Question 2
Copy
and complete the following table relating to important industrial process.
Name of the process
|
Temperature
|
Catalyst
|
Equation for the catalyzed reaction
|
Haber's Process
|
Solution 2
Name of the process
|
Temperature
|
Catalyst
|
Equation for the catalyzed reaction
|
Haber's Process
|
450-500oC
|
Finely divided iron (Fe)
|
Question 3
Give
balanced equation of
(a) Reduction of hot copper (II) oxide to
copper using ammonia gas
(b) Action of heat an a mixture of copper an
nitric acid
Solution 3
(a) 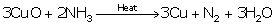
(b) C + 4HNO3→ CO2
+ 2H2O + 4NO2
Question 4
(i) Name the other ion formed when ammonia dissolves in
water
(ii) Given one test can be used to detect the
presence of the ion produced
Solution 4
(i) Hydroxyl (OH-) ion other than ammonium ion
(ii) Red litmus turns blue, methyl orange turns yellow and
phenolphthalein turns pink.
Question 5
Give
balanced chemical equations for each of the following :
(i) Lab preparation of ammonia using an ammonium salt
(ii) Reaction of ammonia with excess chlorine
(iii) Reaction of ammonia with sulphuric acid
Solution 5
(i) 2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2→ CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2NH3
(ii) NH3 + 3Cl2→ NCl3 + 3HCl
(nitrogen trichloride)
(iii) 2NH3+H2SO4→ (NH4)2SO4
(ammonium sulphate)
Chapter 9A - Ammonia Exercise 228
Question 1
Name
the gas evolved when the following mixtures are heated:
(i) Calcium hydroxide and ammonium chloride
(ii) Sodium nitrate and ammonium chloride
Solution 1
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Nitrogen
Question 2
Write
balanced chemical equations for each of the following
(i) When excess of ammonia is treated with chlorine
(ii) An equation to illustrate the reducing
nature of ammonia
Solution 2
(i) 8NH3 + 3Cl2→ N2 + 6NH4Cl
(ii) 3PbO + 2NH3 →3Pb + 3H2O + N2
Question 3
Identify
the substance underlined, in the following case:
(i) Cation that does not form a precipitate with ammonium
hydroxide but forms one with sodium hydroxide.
(ii) A solid formed by reaction of two gaes, one of which is
acidic and the other basic in nature.
Solution 3
(i) Cation that does not form
a precipitate with ammonium hydroxide but forms one with sodium hydroxide: Ca2+
(ii) A solid formed by a reaction of two
gases, one of which is acidic and the other basic in nature: Salt
Question 4
(i) Write a balanced chemical equation for reaction of
ammonia with heated copper oxide
(ii) Laboratory preparation of ammonia from aammonia
chloride
(iii) Catalyst oxidation of ammonia
Solution 4
(i) 3CuO + 3NH3→ 3Cu + 3H2O + N2↑
(ii) 2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 +
2H2O + 2NH3↑
(iii) 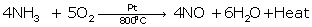
Question 5
State
one relevant observation of burning of ammonia in air.
Solution 5
Since
ammonia is not a supporter of combustion, it extinguishes a burning splint
and does not burn in air.
Question 6
Certain
blank spaces are left in the following table and these are labelled as
A,B,C,Da and E. Identify each of then
1
|
HCl gas
|
NaCl + H2SO4
|
A
|
Conc.H2SO4
|
B
|
2
|
NH3 gas
|
C
|
Mg(OH)2NH3
|
D
|
E
|
Solution 6
(i) A = NaHSO4 + HCl
B = upward
displacement of air
(ii) C = Mg3N2
+ H2O
D = quicklime
E = downward displacement of air

0 comments:
Post a Comment