Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 249
Question 1
Solution 1
Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3
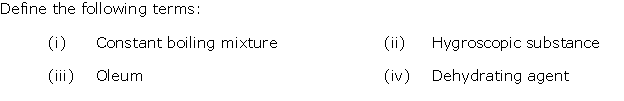
Solution 3

Question 4

Solution 4

Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 250
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2


Question 3

Solution 3

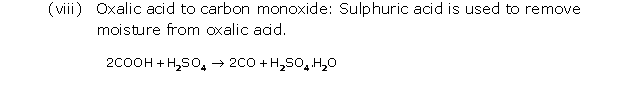
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5
Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7
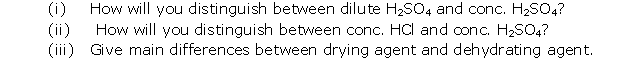
Solution 7
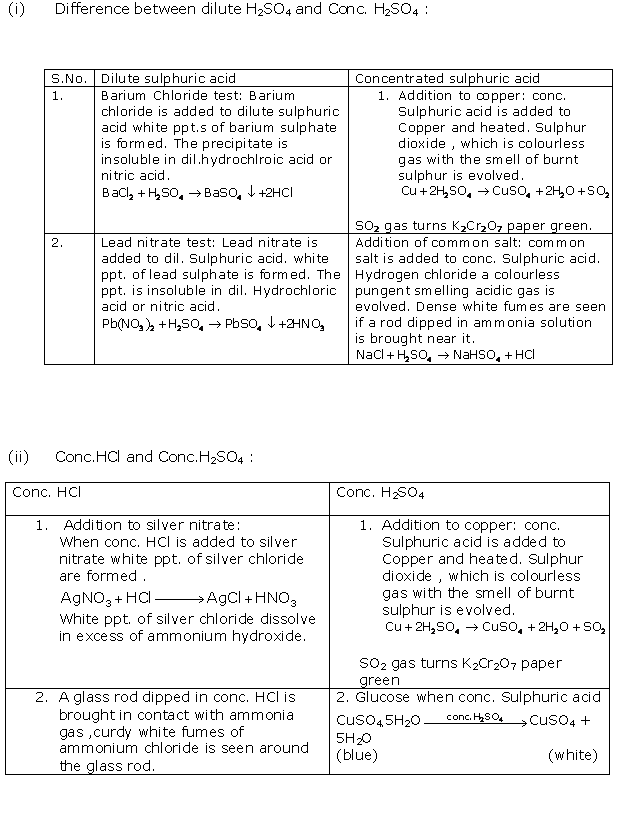


Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 251
Question 1
Choose
the current answer from the options given below :
(i) In the preparation of H2SO4 by
contact process V2O3 is used as a catalyst in the
reaction. It is
(a) S + O2→ SO2
(b) SO2 + H2SO4→
H2S2O7
(c) SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
(d) 2SO2 + O2→ 2SO3
(ii) When conc. H2SO4 comes in contact
with sugar, it becomes black due to
(a) Hydrolysis
(b) Decolourisation
(c) Dehydration
(d) Hydration
(iii) Which of the following gas dissolves in H2SO4
to give alum?
(a) SO2
(b) H2S
(c) S2O
(d) SO3
(iv) In the contact process, the impurities of arsenic are
removed by
(a) Fe2O3
(b) Fe(OH)3
(c) AlCOH3
(d) Cr(OH)3
(v) The catalyst used for the oxidation of SO2
to SO3 in contact process is
(a) Finally divided iron
(b) Molybdenum
(c) Vanadium
(d) Nitric oxide
Solution 1
(i) 2SO2 + O2→ 2SO3
(ii) Dehydration
(iii) SO3
(iv) Fe(OH)3
(v) Vanadium pentoxide
Question 2
Fill
in the blank with appropriate word/words :
(i) The catalyst used in contact process for the
manufacture of H2SO4 is platinum
or Vanadium pentoxide
(ii) For the reaction SO2 + O2⇌ SO3 + Heat, the favorable
conditions are high pressure
and low temperature
(iii) Oil of Vitriol is ___________
Solution 2
(i) The catalyst used in contact process for the
manufacture of H2SO4 is ___________ or _________.
(ii) For the reaction SO2 + O2⇌ SO3 + Heat, the favourable
conditions are _________ and __________.
(iii) Oil of vitriol is sulphuric acid.
Question 3

Solution 3
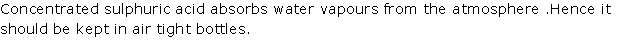
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5
Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7
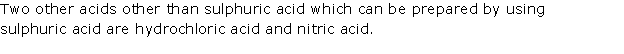
Question 8
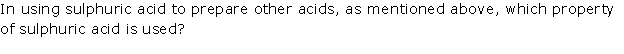
Solution 8

Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 252
Question 1
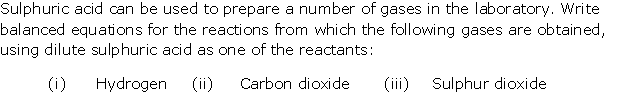
Solution 1
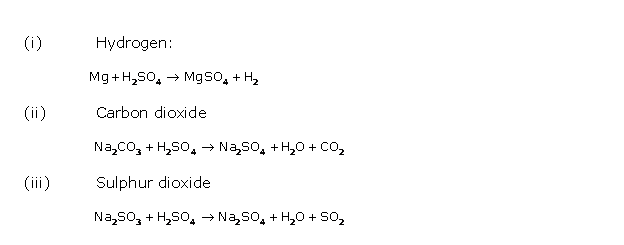
Question 2

Solution 2
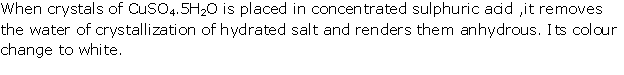
Question 3

Solution 3
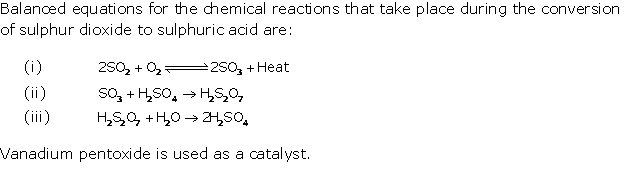
Question 4
Solution 4

Question 5
Solution 5
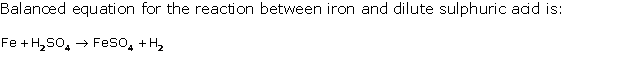
Question 6
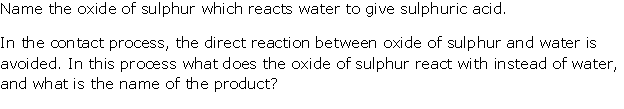
Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8

Solution 8
Question 9

Solution 9

Question 10

Solution 10
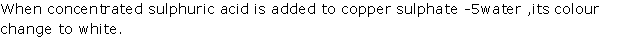
Question 11
Solution 11

Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 253
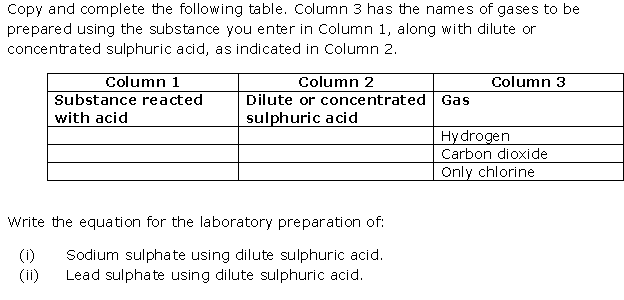
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2
Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4
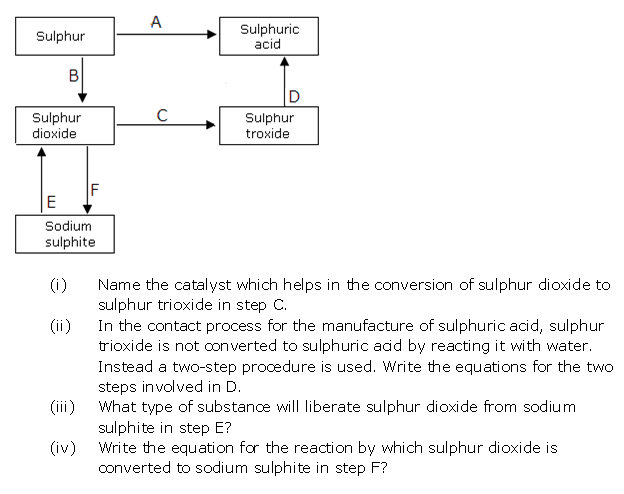
Solution 4
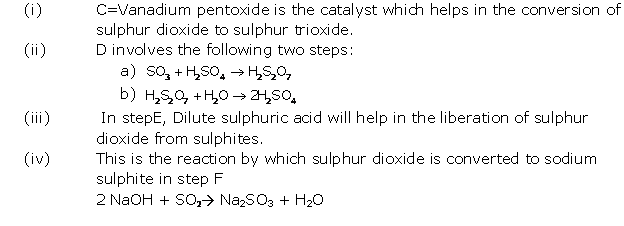
Question 5
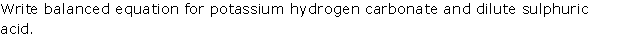
Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6

Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 254
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2
Question 3

Solution 3
(a) B
(b) D
(c) C
(d) A
(e) A
(b) D
(c) C
(d) A
(e) A
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5
Question 6

Solution 6
Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 255
Question 1

Solution 1
Question 2
Write
the equation for each of the following reactions :
(i) Sulphur is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid
(ii) Concentrated sulphuric acid is poured over sugar
Solution 2
(i) S + H2SO4→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) 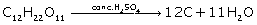
Question 3
State
your observation for the following cases :
(i) Moist blue litmus is introduced into a gas jar of
sulphur dioxide
(ii) Dry red rose petals are placed in the jar of sulphur
dioxide
(iii) Paper soaked in potassium permanganate solution is
introduced into a gas jar of sulphur diaoxide.
Solution 3
(i) Litmus turns blue to red, and then gets
bleached.
(ii) Dry SO2 has no effect on dry red
rose petals.
(iii) Paper turns from pink to white.
Question 4
What
would you observe in the following case :
Sugar
crystals are added to hard glass test tube containing concentrated sulphuric
acid.
Solution 4
Charring of sugar takes place.
Sulphuric acid dehydrates sugar leaving behind carbon which is black.
Question 5
(i) With the help of equations, give an outline for the
manufacture of sulphuric acid by the contact process
(ii) What property of sulphuric acid is shown by
the reaction of concentrated sulphuric acid when heated with
(i) Potassium nitrate
(ii) carbon
Solution 5
(i) Formation of sulphur dioxide:
S + O2 → SO2
Conversion of SO2 to
SO3
Conversion of sulphur trioxide to oleum:
SO3 + H2SO4→ H2S2O7
Dilution of oleum:
H2S2O7
+ H2O → 2H2SO4
(ii)
i. Non-volatile nature
ii. As an oxidising agent
Question 6
In
the given equation identify the role played by concentrated sulphuric acid S
+ 2H2SO4→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
(a) Non-volatile acid
(b) Oxidising agent
(c) Dehydrating agent
(d) None of the above
Solution 6
(b) Oxidising agent
Question 7
State
one appropriate observation for each of the following.
(i) Concentrated sulphuric acid is added dropwise to a
crystal of hydrated copper sulphate.
(ii) Dehydration of Concentrated Sulphuric acid
with sugar crystals
Solution 7
(i) When conc. H2SO4 is added to a
crystal of hydrated copper sulphate, it removes water of crystallisation
from salt.
(ii) C12H22O11 + conc. H2SO4→ 6C + 6H2O
Question 8
Give
one equation each to show the following properties of sulphuric acid :
(i) Dehydrating property
(ii) Acidic nature
(iii) As a non-volatile acid
Solution 8
(i) Dehydrating property of sulphuric acid:
H2SO4 has a great affinity for
water, and therefore, it acts as a dehydrating agent.
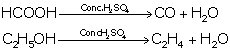
(ii) Acidic nature of sulphuric acid:
It acts as a strong dibasic acid.
It reacts with metals, metal oxides, metal
hydroxides and carbonates to form metallic sulphates
and hydrogen at ordinary temperature.
Mg + H2SO4→ MgSO4 + H2↑
CuO + H2SO4
→
CuSO4 + H2O
2NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
ZnCO3 + H2SO4→
ZnSO4 + H2O + CO2↑
(iii) As a non-volatile acid:
It has a high boiling point, so it is used to prepare
volatile acids such as HCl, HNO3 and acetic acid from their salts.
NaCl + H2SO4→ NaHSO4 + HCl
NaNO3 + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3
CH3COONa + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + CH3COOH
Question 9
(i) Give balanced chemical equations for the action of
sulphuric acid on each of the following
1. Potassium hydrogen carbonate
2. Sulphur
(ii) In the contact process for the manufacture
of sulphuric acid give the equations for the conversion of sulphur trioxide
to sulphuric acid.
Solution 9
(i)
1. Action of sulphuric acid on potassium hydrogen
carbonate
2KHCO3 + H2SO4→ K2SO4 + 2H2O
+ 2CO2↑
2. Action of sulphuric acid on sulphur
S + 2H2SO4→ 3SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) In the contact process for the manufacture
of sulphuric acid, the equations for the conversion of sulphur trioxide to
sulphuric acid are
SO3 + H2SO4→ H2S2O7
(oleum or pyrosulphuric acid)
H2S2O7 + H2O
→
2H2SO4
Chapter 10 - Study of Sulphur Compound: Sulphuric Acid Exercise 256
Question 1
A,B,C
and D summarise the properties of sulphuric acid depending on whether it is
dilute or concentrated.
A
= Typical acid property
B
= Non-Volatile acid
C
= Oxidising agent
D
= Dehydrating agent
Choose
the property (A,B,C or D) depending on which is relevant to each of the
following :
(i) Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
(ii) Preparation of copper sulphate from copper oxide
(iii) Action of cone, sulphuric acid on sulphur
Solution 1
(i) B
(ii) A
(iii) C
Question 2
Write
balanced chemical equations to show :
(i) The oxidizing action of conc.sulphuric acid on carbon
(ii) The behavior of H2SO4 as an acid when it reacts with
magnesium
(iii) The dehydrating property of conc.sulphuric acid
Solution 2
(i) 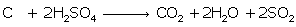
(ii) 
(iii) 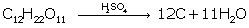

0 comments:
Post a Comment