Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 198
Question 1

Solution 1


Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 199
Question 1
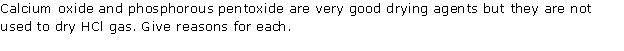
Solution 1
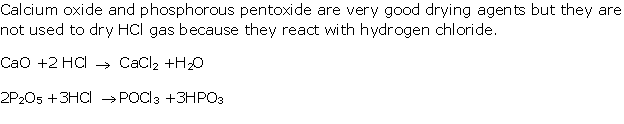
Question 2

Solution 2
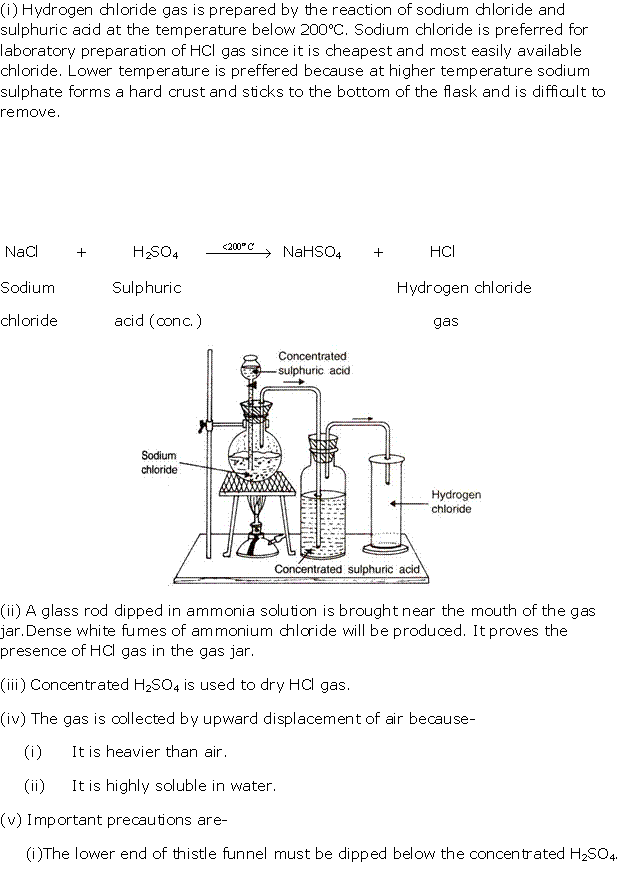

Question 3

Solution 3
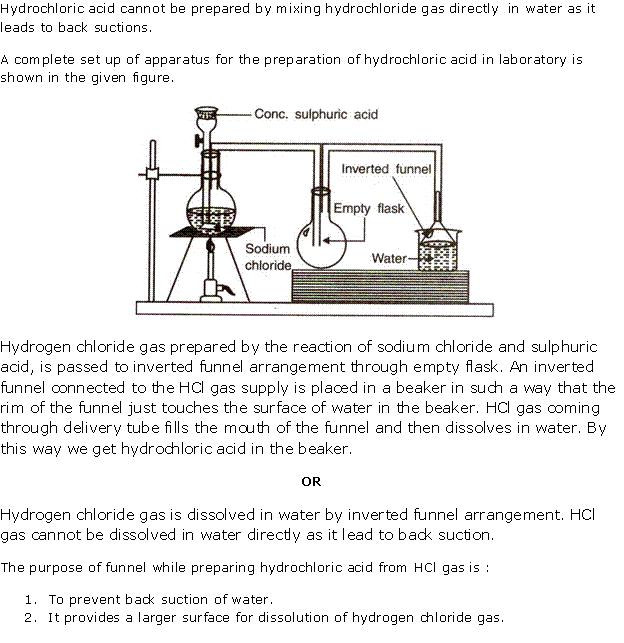
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7
Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 200
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3
Solution 3

Question 4
Solution 4

Question 5
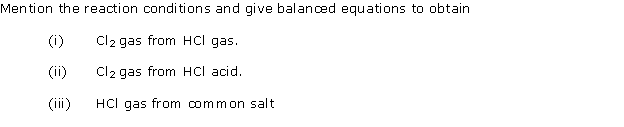
Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7
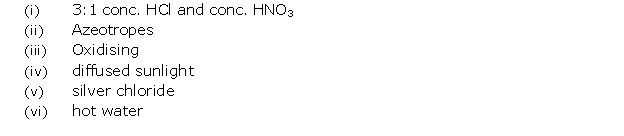
Question 8
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) HCl gas can be prepared by direct combination of hydrogen
and chlorine gas in presence of
(a) Direct sunlight
(b) Dark atmosphere
(c) Diffused sunlight
(d) MnO2 catalyst
(ii) Dilute hydrochloric acid solution cannot be
concentrated by boiling beyond
(a) 11%
(b) 33%
(c) 44%
(d) 22%
(iii) Bleaching powder reacts with few drops of concentrated HCl to give
(a) Chlorine
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Oxygen
(d) None of these
(iv) Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) HCl gas is collected by upward displacement of
air
(b) HCl acid gives white precipitate with AgNO3.
(c) HCl gas is collected by downward displacement of air
(d) HCl acid turns phenolphthalein solution colurless
Solution 8
(i) Diffused sunlight
(ii) 22%
(iii) Chlorine
(iv) HCl gas is
collected by the downward displacement of air.
Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 201
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3
Question 4
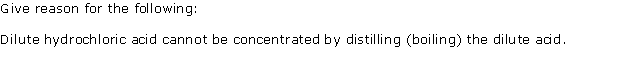
Solution 4

Question 5
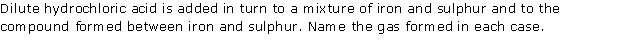
Solution 5
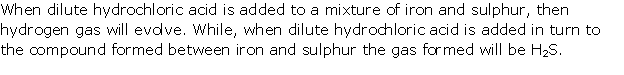
Question 6
Solution 6
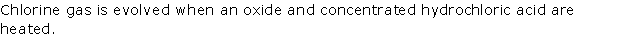
Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8
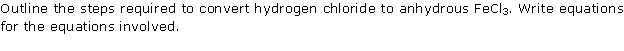
Solution 8
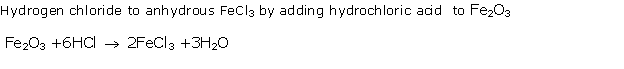
Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 202
Question 1
Solution 1
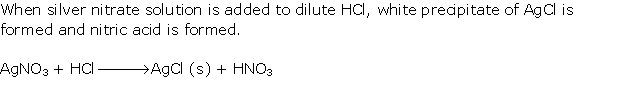
Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4

Solution 4
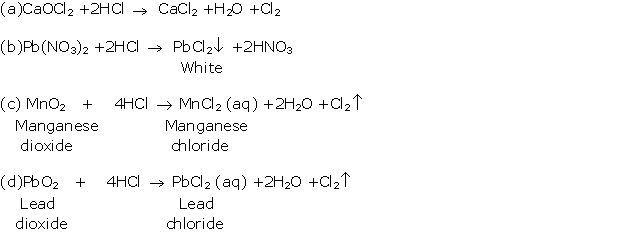
Question 5
Solution 5
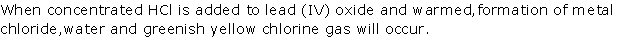
Question 6
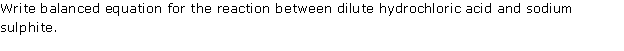
Solution 6
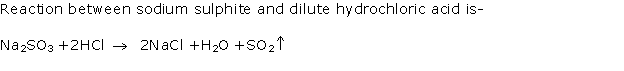
Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8
Solution 8
Question 9
Solution 9

Question 10
Solution 10

Question 11
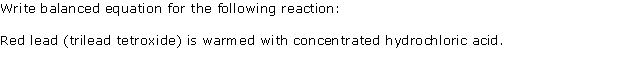
Solution 11
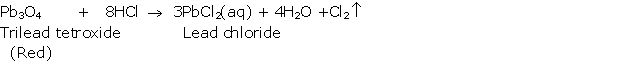
Question 12

Solution 12

Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 203
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
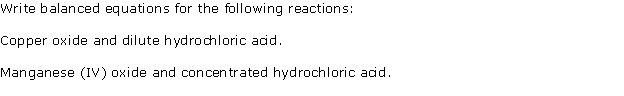
Solution 2
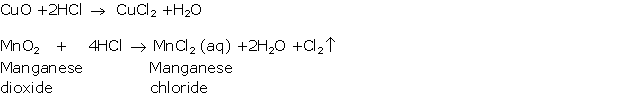
Question 3
Solution 3
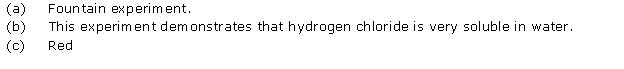
Question 4

Solution 4
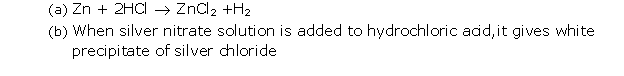
Question 5

Solution 5

Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7
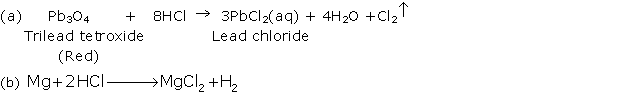
Question 8

Solution 8

Question 9
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below:
Aqua
regia is a mixture of :
(a) Dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated
nitric acid
(b) Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute
nitric acid
(c) Cocentrated hydrochloric acid [1 part] and concentrated nitric
acid [ 3 parts]
(d) Concentrated hydrochloric acid [3 parts]
and concentrated nitric acid [ 1 part]
Solution 9
Aqua
regia is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid [3
parts] and concentrated nitric acid [1 part].
Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 204
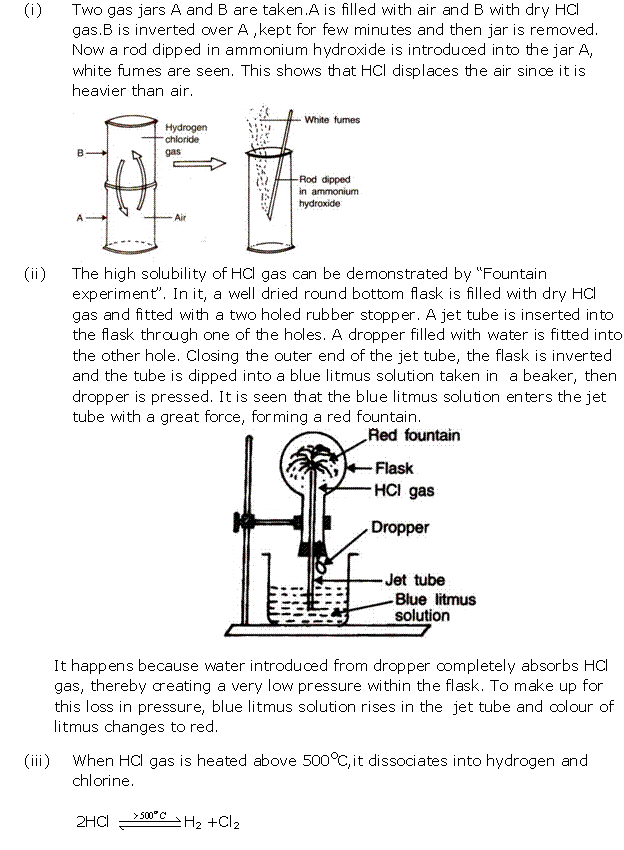
Question 1
The
diagram shows an apparatus for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen
chloride.
(i) Identify A and B
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction
(iii) How would you check whether or not the gas jar is
filled with hydrogen chloride?
(iv) What does the method of collection tell you about the
density of hydrogen chloride
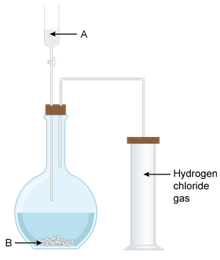
Solution 1
(i) A = conc. H2SO4 B = NaCl
(ii) 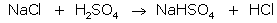
(iii) When a rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide is
brought near the mouth of the gas jar, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride
are produced.
(iv) Hydrogen chloride is denser than air.
Question 2
By
the addition of only one solution how would you distinguish between dilute
hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid?
Solution 2
Silver nitrate solution will give a white ppt.
when added to dil. hydrochloric acid, and no change will be observed when it
is added to dil. nitric acid.
Question 3
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below :
(i) Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is
dried by :
(a) Anhydrous calcium chloride
(b) Phosphorous pentaoxide
(c) Quick time
(d) Concentrated sulphuric
acid
Solution 3
Being highly soluble in water, hydrogen
chloride gas is dried by conc. sulphuric acid.
Question 4
In the laboratory preparation of hydrochloric acid, HCl gas is dissolved in water.
(i) Draw a diagram to show the arrangement used for the absorption of HCl in water.
(ii) Why is such an arrangement necessary? Give two reasons.
(iii) Write the chemical equation for the laboratory preparation of HCl gas when the reactants are :
(a) Below 200oC
(b) Above 200oC
Solution 4
(i) Diagram to show the arrangement used for the absorption of HCl gas in water:
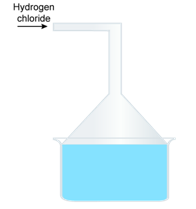
(ii) Such an arrangement is necessary to prevent back suction of water into the apparatus, and it provides a large surface area for dissolution of hydrogen chloride gas.
(iii) Balanced chemical equations for the laboratory preparation of HCl gas:
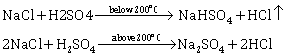
Question 5
State one appropriate observation for each of the following
(i) Copper sulphate is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid
(ii) A few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid are added to silver nitrate solution, followed by the addition of ammonium hydroxide solution
(iii) Which gas is evolved when potassium sulphite with dilute hydrochloric acid
(iv) Concentrated HCl is made to react with mangese diaoxide
(v) Action of dilute HCl or sodium sulphite
Solution 5
(i) Add silver nitrate solution to both solutions. Sodium chloride will form a curdy white ppt., whereas sodium nitrate will not undergo any reaction.
(ii) Hydrogen chloride gas gives thick white fumes of ammonium chloride when a glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near the vapours of the acid, whereas no white fumes are observed in case of hydrogen sulphide gas.
(iii) Ethene gas decolourises the purple colour of KMnO4, whereas ethane does not decolourise KMnO4 solution.
(iv) Calcium nitrate forms no ppt. even with addition of excess of NH4OH, whereas zinc nitrate forms a white gelatinous ppt. which dissolves in excess of NH4OH.
(v) Carbon dioxide gas has no effect on acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7, but sulphur dioxide turns potassium permanganate from pink to colourless.
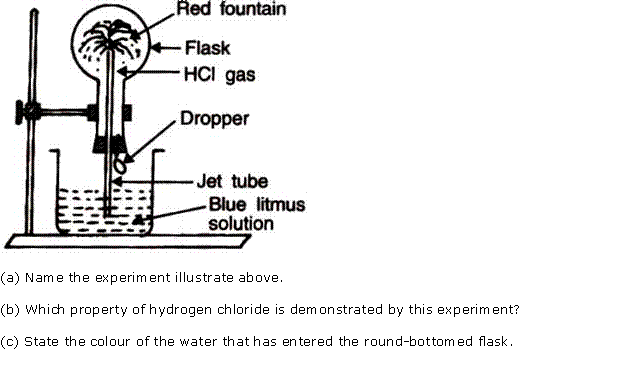
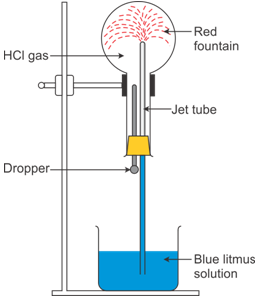
Question 6
Study
the figure given alongside and answer that questions that follow:
(i) Identify the gas Y.
(ii) What property of gas Y does this experiment
demonstrate?
(iii) Name another gas which has the same property and can be
demonstrated through this experiment
Solution 6
(i) The gas is HCl (hydrogen
chloride) gas.
(ii) Extreme solubility of hydrogen chloride gas is
demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
(iii) Ammonia gas is another gas which has the same property which
can be demonstrated through this experiment.
Chapter 8 - Study of Compounds-I: Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 205
Question 1
The
following questions are pertaining to the laboratory pertaining hydrogen
chloride gas.
(i) Write the equation for its preparation mentioning the
condition required
(ii) Name the drying agent used and justify your choice
(iii) State a safety precaution you would take during the
preparation of hydrochloric acid.
Solution 1
(i) Equation for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas:
Although it is a reversible reaction, it goes to
completion as hydrogen chloride continuously escapes as a gas.
The reaction can occur up to the stage of the
formation of sodium sulphate on heating above 200°C.
(ii) The drying agent used in the
laboratory preparation of hydrochloric acid is conc. sulphuric acid.
The other drying agents such as phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) and quick lime (CaO) cannot be used because they react with hydrogen
chloride.
2P2O5 + 3HCl → POCl3 + 3HPO3
CaO + 2HCl → POCl3 + 3HPO3
(iii) A safety precaution which should be taken during the preparation of hydrochloric
acid:
Always wear chemical splash
goggles, chemical-
resistant gloves and a chemical-resistant
apron in the
laboratory during the preparation
of hydrochloric
acid.
Question 2
The
aim of the fountain experiment is to prove that
(a) HCl turns blue litmus red
(b) HCl is denser than air
(c) HCl is highly soluble in water
(d) HCl fumes in moist air
Solution 2
(a) HCl turns blue litmus red
Question 3
State
your observations when :
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to lead nitrate
solution and the mixture is heated
(ii) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium thisulphate
(iii) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper carbonate
Solution 3
(i) When dil. HCl is added to
lead nitrate solution and heated, it forms a white precipitate of lead
chloride.
Pb(NO3)2 +
2HCl →
PbCl2 + 2HNO3
(ii) Dil. HCl reacts with thiosulphate to produce sulphur
dioxide, and yellow sulphur is precipitated.
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + SO2 +
S ↓
(iii) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper
carbonate, it decomposes to give copper chloride.
CuCO3 + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O + CO2↑
Question 4
State
the observation for action of dilute hydrochloiric
acid or iron (II) sulphate.
Solution 4
Dilute
hydrochloric acid decomposes iron(II) sulphide to produce iron(II) chloride and hydrogen sulphide having rotten egg smell.
FeS + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2S
Question 5
How
will you distinguished between dilute HCl and
dilute H2SO4 using lead nitrate solution?
Solution 5
Sulphuric acid precipitates the insoluble sulphate from lead nitrate solution.
Lead
nitrate reacts with hydrochloric acid to give a white ppt. of lead chloride.

0 comments:
Post a Comment