Chapter 5 - Heat Exercise 191
Question 1
What do you mean by heat?
Solution 1
Heat is defined as a form of energy which flows from one point to another on account of temperature difference.
Question 2
Is it correct to say that heat is the cause of temperature?
Solution 2
Yes, heat is the cause of temperature because temperature of a body rises when the heat flows into the body.
Question 3
What causes a change in the temperature of a body?
Solution 3
Heat changes the temperature of a body due to flow of heat in or out of the given body.
Question 4
Which is more, a calorie or a joule?
Solution 4
Calorie. Because 1 calorie = 4.2 joules.
Question 5
1 joule = 4.2 calorie
Is this relation correct?
Is this relation correct?
Solution 5
No, the exact relation is as given
1 calorie = 4.2 joules.
1 calorie = 4.2 joules.
Question 6
Two bodies are at same temperature. Do they necessarily contain same amount of heat?
Solution 6
Yes, because the heat flow is only due to temperature difference between the temperature of two bodies.
Question 7
Is heat a form of energy?
Solution 7
Yes, heat is a form of energy
Question 8
Name the SI unit of heat.
Solution 8
Joule is the SI unit of heat.
Question 9
Define one joule of heat.
Solution 9
One calorie is defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water through 1oC.
Question 10
What is the relation between joule and calorie?
Solution 10
1 calorie = 4.2 joules.
Question 11
Define temperature and write its SI unit.
Solution 11
Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body compared to other bodies around it.
SI unit of temperature is Kelvin (K).
SI unit of temperature is Kelvin (K).
Question 12
Why does a piece of ice when touched with hands appear cold?
Solution 12
We feel cold on touching ice because heat flows from our warm hands to cold ice. Due to this flow of heat from hand to ice, the temperature of our hand falls. This is why we feel cold.
Question 13
Distinguish between heat and temperature.
Solution 13
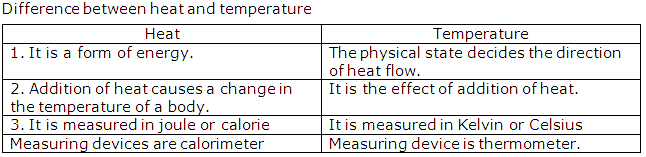
Question 14
Two bodies at different temperatures are placed in contact with each other. State the direction in which heat flows.
Solution 14
Heat flows from a body at a higher temperature to a body of lower temperature.
Chapter 5 - Heat Exercise 229
Question 1
What do you mean by temperature?
Solution 1
Temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of a body compared to other bodies around it.
SI unit of temperature is Kelvin (K)
SI unit of temperature is Kelvin (K)
Question 2
What is the principle of calorimetry?
Solution 2
According to principle of calorimetry of mixtures,
Heat gained = Heat lost
Heat gained = Heat lost
Question 3
Write the SI unit of coefficient of cubical expansion.
Solution 3
SI unit of coefficient of cubical expansion is oc-1.
Question 4
State two uses of a bimetallic strip.
Solution 4
Two uses of bimetallic strip are
(a). As thermostat in electric iron
(b). As balance wheel in watches
(a). As thermostat in electric iron
(b). As balance wheel in watches
Question 5
Why do telephone wires sag during summer?
Solution 5
Telephone wires sag in summer because due to heat of the sun, the wire expands and increases in length, thus they sag in summer.
Question 6
Solution 6
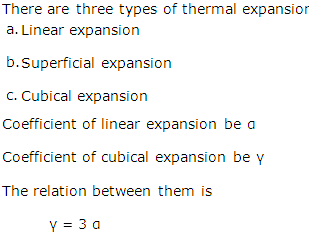
Question 7
Do all substances expand on heating? Give examples.
Solution 7
Not all substances expand on heating. Some examples of substances which do not expand on heating are plastics, polythene and rubber.
Question 8
What is evaporation? Why does it cause cooling?
Solution 8
Evaporation is the phenomenon of a change of a liquid into vapour without raising the temperature. Evaporation needs energy for phase change from liquid to gases. As water evaporates off your skin, it absorbs energy(heat) from the body to make the phase change to gas thus cooling the body.
Question 9
State three factors affecting evaporation.
Solution 9
Factors affecting evaporation are
(a). Humidity- more the humidity less is the evaporation
(b). surface area- more the surface area more is the evaporation
(c). wind- more the wind more is the evaporation
(d). temperature- more the temperature more is the evaporation
(a). Humidity- more the humidity less is the evaporation
(b). surface area- more the surface area more is the evaporation
(c). wind- more the wind more is the evaporation
(d). temperature- more the temperature more is the evaporation
Question 10
What are land and sea breezes? Explain with the help of a labeled diagram.
Solution 10
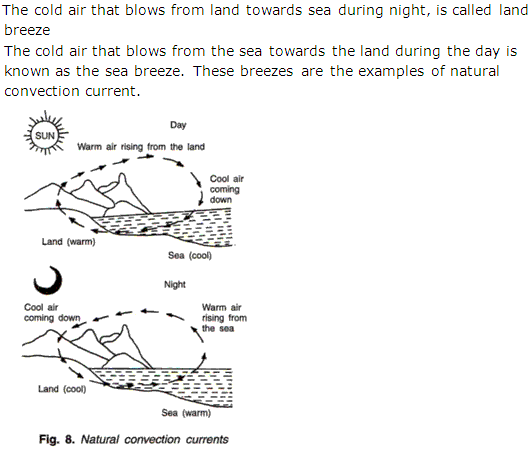
The cold air that blows from land towards sea during night, is called land breeze
The cold air that blows from the sea towards the land during the day is known as the sea breeze. These breezes are the examples of natural convection current.
The cold air that blows from the sea towards the land during the day is known as the sea breeze. These breezes are the examples of natural convection current.
Question 11
Is conduction possible in gases?
Solution 11
No, the conduction is not possible in gases. Gases are bad conductors.
Question 12
What is the normal temperature of human body?
Solution 12
Normal temperature of human body is 370C.
Question 13
Is conduction possible in vacuum?
Solution 13
No, conduction is not possible in vacuum.
Question 14
What is the velocity of thermal radiations?
Solution 14
The velocity of thermal radiations is equal to the speed of light i.e. 3 x 108 m/s.
Question 15
Convert 200C into Fahrenheit scale.
Solution 15
To convert 200c into0F
Toc /100 = (Tof -32)/180
20/100 = (Tof - 32)/180
20 X 180/100 = Tof -32
Tof = 36+32 = 680F
Toc /100 = (Tof -32)/180
20/100 = (Tof - 32)/180
20 X 180/100 = Tof -32
Tof = 36+32 = 680F
Question 16
What is the upper fixed point on the Celsius scale?
Solution 16
Upper fixed point on the Celsius scale is 1000C.
Question 17
Convert 80 K temperatures on the Celsius scale.
Solution 17
Tk = 80 K
Tc = Tk -273
Tc = 80 - 273
Tc = -1530C
Tc = Tk -273
Tc = 80 - 273
Tc = -1530C
Question 18
Write down the SI unit of latent heat.
Solution 18
SI unit of latent heat is Joule per kg (J/kg).
Question 19
What do you mean by relative humidity?
Solution 19
Relative humidity is defined as the amount of water vapour in the air compared to the amount needed for saturation.
Question 20
Define coefficient of linear expansion. Write its SI unit.
Solution 20
Coefficient of Linear expansion is equal to the change in length of a rod of length 1m when its temperature rises by 10C. Its SI unit is oc-1.
Question 21
Name the scientist who designed the first thermometer.
Solution 21
Celsius was the scientist who discovered the first thermometer in 1710.
Chapter 5 - Heat Exercise 230
Question 1
Why do we wear woolen clothes in winter?
Solution 1
We wear woolen clothes in winter because woolen clothes have tiny pores and air is trapped in these pores and being a bad conductor, the trapped air obstructs the flow of body heat to the surroundings.
Question 2
Why is a newly made quit warmer than an old one?
Solution 2
A newly made quilt is warmer than an old one because the cotton in the old quilt gets compressed and very little air will remain trapped in it, hence heat insulation is quite poor.
Question 3
In cold countries, the water pipes are covered with poor conductors. Why?
Solution 3
In cold countries, water pipes are covered with poor conductors because poor conductor prevents water from freezing and thus prevent these pipes from bursting.
Question 4
Name three devices which are used to detect heat radiations.
Solution 4
Three devices used to detect heat radiations are
(a). Blackened bulb thermometer
(b). Differential air thermo scope
(c). Thermopile
(a). Blackened bulb thermometer
(b). Differential air thermo scope
(c). Thermopile
Question 5
What is meant by thermal expansion?
Solution 5
The increase in size of a body on heating is called thermal expansion.
Question 6
What do you mean by linear expansion?
Solution 6
Linear expansion is the increase in length of a solid on heating.
Question 7
Define coefficient of linear expansion.
Solution 7
Coefficient of Linear expansion is equal to the change in length of a rod of length 1m when its temperature rises by 10C.
Question 8
What is a bimetallic strip?
Solution 8
A bimetallic strip consists of two metal strips- one with high coefficient of expansion and the other with low coefficient of expansion.
Question 9
What is the unit of coefficient of linear expansion?
Solution 9
SI unit of coefficient of linear expansion is oc-1.
Question 10
Name the substance which contracts when heated from 00C to 40C.
Solution 10
Water is the substance which contracts, when heated from 00C to 40C.
Question 11
Define coefficient of volume expansion.
Solution 11
Coefficient of volume expansion is equal to the change in volume of a rod of volume 1m3 when its temperature rises by 1oC.
Question 12
What is the unit of coefficient of volume expansion?
Solution 12
SI unit of coefficient of volume expansion is oC-1.
Question 13
State two uses of bimetallic strip.
Solution 13
Two uses of bimetallic strip are
(a). As thermostat in electric iron
(b). As balance wheel in watches
(a). As thermostat in electric iron
(b). As balance wheel in watches
Question 14
How can a glass stopper jammed in the neck of a bottle be removed?
Solution 14
We should heat the neck of the bottle because due to heating the neck will expand and loosen the stopper stuck in the neck. In this way, we can easily remove the stopper from the bottle.
Question 15
Why does a thick glass tumbler crack when very hot water is poured in it?
Solution 15
When hot water is poured into a thick glass tumbler, it generally cracks because on pouring hot water in the tumbler the inner surface heats up and expands more as compared to its outer surface. This unequal expansion between the two surfaces causes a strain and the tumbler cracks.
Question 16
Why does a substance expand on heating?
Solution 16
A substance is made up of molecules arranged in a lattice. On heating, the molecules vibrate faster in the lattice and bump into each other harder. So the distance between the molecules increases thus expanding lattice. Thus, the substances expand on heating.
Question 17
What are the different types of thermal expansions?
Solution 17
There are three types of thermal expansion
(a). Linear expansion
(b). Superficial expansion
(c). Cubical expansion
(a). Linear expansion
(b). Superficial expansion
(c). Cubical expansion
Question 18
A small gap is left between two iron rails of the railway track. Why?
Solution 18
Gaps are left in the railway tracks because the tracks gets heated during the day and as a result they increase in length. If the gaps are not provided, the railway line would buckle outward and may cause derailment.
Question 19
Why are bridges made of steel girders put on rollers?
Solution 19
The beams of the bridges expand maximum during the summer days and contract maximum during the winter nights. If the beams are fixed at both ends on the pillars, they may develop crack due to expansion and contraction. To avoid this, beams are made to rest on rollers on the pillars to provide space for expansion.
Question 20
Solution 20

Question 21
A copper wire 10 cm long is heated from 200C to 300C. Find the increase in length of the wire, if coefficient of linear expansion of copper is 1.7 X 10-5oC-1
Solution 21
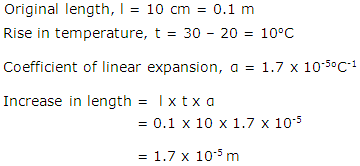
Question 22
One liter of mercury at 100C is heated to 300C. Find the increase in the volume of mercury. The coefficient of cubical expansion of mercury is 1.8 X 10-4 0C-1.
Solution 22
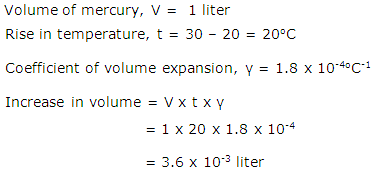
Question 23
Why is a ventilator provided in a room?
Solution 23
A ventilator is provided in a room because it helps in removing the hot air from the room and allows the fresh and cold air to come in.
Question 24
Is it possible to heat a liquid or gas from above? Explain your answer.
Solution 24
No, it is not possible to heat a liquid or gas from above because the transfer of heat through convection takes place vertically upwards in liquids and gases. So if they are heated from above, the liquid or gas at the top will only be heated because most liquids and gases are themselves bad conductor of heat so they cannot conduct heat from top layer to the bottom layer.
Question 25
Explain the following:
(i) Water is heated generally from below.
(ii) Land becomes warmer than water during the day.
(i) Water is heated generally from below.
(ii) Land becomes warmer than water during the day.
Solution 25
(a). Water is heated generally from below because water itself is a bad conductor of heat and the transfer of heat through convection take place vertically upwards.
(b). Land becomes warmer than water during the day because water has more specific heat capacity so it absorbs the heat and heats up slowly but on the other hand land has less specific heat and it heats up faster than water.
(b). Land becomes warmer than water during the day because water has more specific heat capacity so it absorbs the heat and heats up slowly but on the other hand land has less specific heat and it heats up faster than water.
Question 26
State three main characteristics of a thermometric substance.
Solution 26
Main characteristics of thermometric substance are
(a). The substance should have high coefficient of expansion so that it is sensitive to the smallest change in temperature
(b). The substance should have uniform expansion all over its entire volume
(c). The substance should have minimum specific heat so that it absorbs minimum heat from the body under measurement.
(a). The substance should have high coefficient of expansion so that it is sensitive to the smallest change in temperature
(b). The substance should have uniform expansion all over its entire volume
(c). The substance should have minimum specific heat so that it absorbs minimum heat from the body under measurement.
Question 27
Name a substance which is an insulator of heat.
Solution 27
Wood is an insulator of heat.
Question 28
(i) Why in cold countries windows have two glass panes with a thin layer
Of air between them?
(ii) What is the relation between joule and calorie?
(iii) Is it possible to boil water in a thin paper container? Explain with a reason.
Of air between them?
(ii) What is the relation between joule and calorie?
(iii) Is it possible to boil water in a thin paper container? Explain with a reason.
Solution 28
(a). In cold countries, windows are provided with two glass panes because in between these two glass panes, a thin layer of air is present: air being a bad conductor obstructs the conduction of heat from the room to outside.
(b). 1 calorie = 4.2 joules
(c). Yes, it is possible to boil water in a thin paper cup because when heated the heat in the paper cup is transferred to the water through convection and paper cup doesn't get sufficient heat to get burnt
(b). 1 calorie = 4.2 joules
(c). Yes, it is possible to boil water in a thin paper cup because when heated the heat in the paper cup is transferred to the water through convection and paper cup doesn't get sufficient heat to get burnt
Question 29
What is the principle of the thermometer?
Solution 29
Thermometer works on the principle that substances expand on heating and contract on cooling. So we use a thermometric substance which expands and contracts uniformly.
Question 30
State the advantages and disadvantages of mercury and alcohol as thermometric liquids.
Solution 30
Advantages of mercury and alcohol as thermometric liquid are
(a). They both are good conductors of heat.
(b). They have high coefficient of expansion thus are sensitive to the smallest change in temperature
(c). Their freezing points are very low and boiling point is high in case of mercury
Disadvantages
(d). Alcohol is transparent and this makes hard to read the thermometer.
(e). It does not have uniform expansion.
(f). Mercury is less sensitive than alcohol as its coefficient of expansion is less than alcohol.
(g). Alcohol is a volatile liquid.
(a). They both are good conductors of heat.
(b). They have high coefficient of expansion thus are sensitive to the smallest change in temperature
(c). Their freezing points are very low and boiling point is high in case of mercury
Disadvantages
(d). Alcohol is transparent and this makes hard to read the thermometer.
(e). It does not have uniform expansion.
(f). Mercury is less sensitive than alcohol as its coefficient of expansion is less than alcohol.
(g). Alcohol is a volatile liquid.
Question 31
What is meant by the lower and upper fixed points of a thermometer?
Solution 31
Lower point of a thermometer is the temperature at which ice starts melting at normal atmospheric pressure i.e. 0oC
Upper point of a thermometer is the temperature at which water just starts boiling at normal atmospheric pressure i.e. 100oC.
Upper point of a thermometer is the temperature at which water just starts boiling at normal atmospheric pressure i.e. 100oC.
Question 32
Draw a neat and labeled diagram of a clinical thermometer.
Solution 32
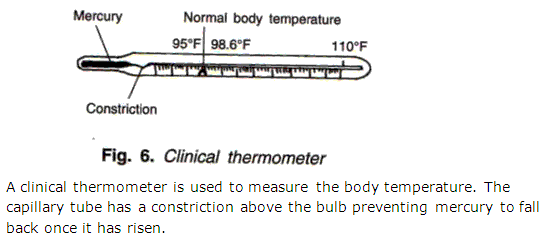
Question 33
State one use of each of the following types of thermometers: (i) Laboratory thermometer, (ii) Clinical thermometer, (iii) Six's maximum and minimum thermometer.
Solution 33
(i). Laboratory thermometer is used to measure and observe the temperature of various chemical reactions
(ii). Clinical thermometer is used to measure human body temperature
(iii). Six's maximum and minimum thermometer is used in meteorology and horticulture.
(ii). Clinical thermometer is used to measure human body temperature
(iii). Six's maximum and minimum thermometer is used in meteorology and horticulture.
Question 34
Distinguish between a clinical and a laboratory thermometer.
Solution 34
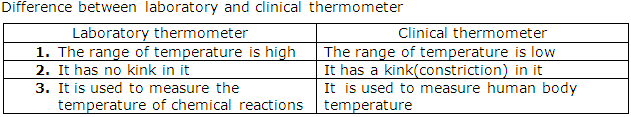
Question 35
Which is the temperature that is common in the Celsius and the Fahrenheit scale?
Solution 35
The temperature that is common in both clinical and Fahrenheit scale is -40oC
Derivation is as follows
Let the temperature be x
C/100= (F - 32)/180
x/100 = (x-32)/180
x X 180/100 = x-32
9/5x = x-32
-4/5x =32
X = - 40
Derivation is as follows
Let the temperature be x
C/100= (F - 32)/180
x/100 = (x-32)/180
x X 180/100 = x-32
9/5x = x-32
-4/5x =32
X = - 40
Question 36
Convert the following temperatures into Fahrenheit scale:
600C, 1000C, -400C, 850C.
600C, 1000C, -400C, 850C.
Solution 36
(a). 60oC
60/100 = (F-32) / 180
F = 6 X 18 +32
= 110oF
(b). 100oC
100/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = 180 X 1 + 32
= 212oF
(c). -40oC
-40/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = -4 X 18 + 32
= 40oF
(d).85oC
85/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = 85 X 18/10 +32
= 185oF
60/100 = (F-32) / 180
F = 6 X 18 +32
= 110oF
(b). 100oC
100/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = 180 X 1 + 32
= 212oF
(c). -40oC
-40/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = -4 X 18 + 32
= 40oF
(d).85oC
85/100 = (F - 32) /180
F = 85 X 18/10 +32
= 185oF
Question 37
Convert the following temperatures into Celsius scale:
Solution 37
(a). 104oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
C = 72 X 100/180
= 40 oC
(b). 95oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 63 X 10/18
= 35oC
(c). 113oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 81 X 10/18
= 45oC
(d). 32oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 0 X 10/18
= 0oC
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
C = 72 X 100/180
= 40 oC
(b). 95oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 63 X 10/18
= 35oC
(c). 113oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 81 X 10/18
= 45oC
(d). 32oF
C = (F - 32) X 100/180
= 0 X 10/18
= 0oC
Question 38
Draw a neat and labeled diagram of a Six's maximum and minimum thermometer. Explain briefly, the working of this thermometer. Give a use of this thermometer.
Solution 38
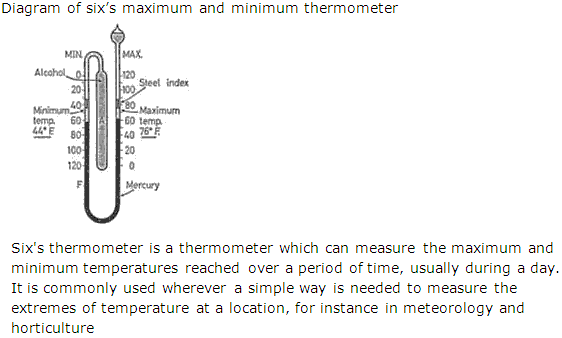
Question 39
Explain the three modes of transfer of heat.
Solution 39
Three modes of heat transfer are
(a). Conduction involves the transfer of heat from the hot end to the cold end from particle to particle of the medium.
(b). Convection is the transfer of heat from one body to another by actual movement of the particles of the medium
(c). Radiation is the transfer of heat from one body to another without the need of an intervening material medium
(a). Conduction involves the transfer of heat from the hot end to the cold end from particle to particle of the medium.
(b). Convection is the transfer of heat from one body to another by actual movement of the particles of the medium
(c). Radiation is the transfer of heat from one body to another without the need of an intervening material medium
Question 40
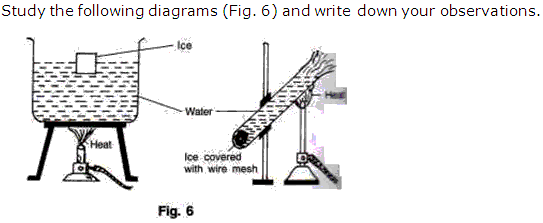
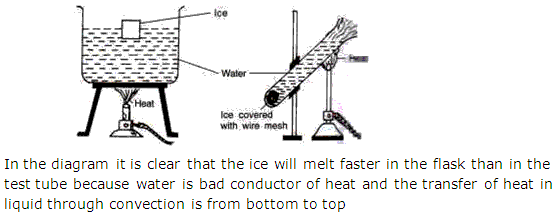
With the help of a diagram, show that water is a bad conductor of heat.
Solution 40
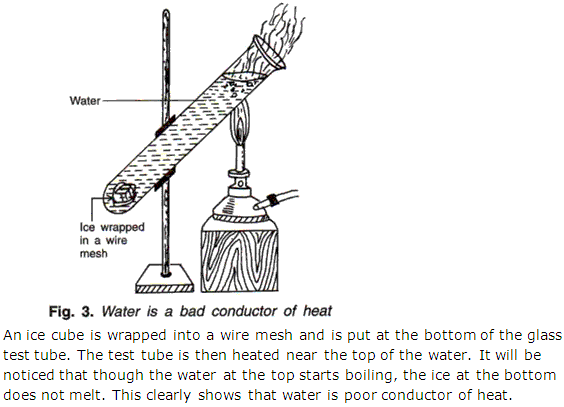
Question 41
Write a short note on Land Breeze and Sea Breeze.
Solution 41
Question 42
A wooden knob and a metal latch on a door are both at room temperatures. Explain, why the latch is colder to touch.
Solution 42
A wooden knob and a metal latch are both being at same temperature but it feels colder to touch the latch because metal is a good conductor and as soon as we touch it heat from our hand flows to the latch and we feel cold while on the other hand wood is a bad conductor of heat, heat of our hand does not flow into it therefore it does not feel cold.
Question 43
Draw a neat and labeled diagram of a vacuum flask (thermos flask). Explain, how it minimizes loss of heat by preventing conduction, convection and radiation.
Solution 43
The flask consists of double walled glass container with vacuum between the walls A and B to prevent heat loss due to conduction and convection as vacuum is the excellent insulator .to prevent heat loss by radiation, the inner side of the wall A and outer side of wall B is silvered. It has a narrow mouth which is closed by a non-conducting rubber stopper.
Question 44

Solution 44
The spiral starts moving because due to the flame of the candle the spiral heats up and expands. While expanding, the spiral tries to create space for the extension in length and an outward pull is created which causes the spiral to move.
Question 45
Give scientific reasons for the following:
(i) In winter the human body covered with a blanket keeps warm.
(ii) It is better to use thin blankets to keep the body warm rather than
using a single blanket of thickness equal to their combined thickness.
(iii) In winter the birds fluff up their feathers.
(iv) Old quits are less warm than the new ones.
(v) On a hot sunny day, it is advisable to wear light coloured clothes.
(i) In winter the human body covered with a blanket keeps warm.
(ii) It is better to use thin blankets to keep the body warm rather than
using a single blanket of thickness equal to their combined thickness.
(iii) In winter the birds fluff up their feathers.
(iv) Old quits are less warm than the new ones.
(v) On a hot sunny day, it is advisable to wear light coloured clothes.
Solution 45
(i). In winters, the human body covered with a blanket keeps warm because the blanket has air trapped in it which provide heat insulation to the body from the surroundings and keep us warm
(ii). It is better to use two thin blankets to keep the body warm rather than using a single blanket of equal thickness because in between the two thin blankets there is more air trapped than in the single blanket of equal thickness so using two thin blankets better heat insulation is provided to the body from the surroundings and keep us warm
(iii). In winter the birds fluff their feathers in order to trap air in their feathers so that the air provides heat insulation to their body from the surroundings and keep them warm and save them from winter.
(iv). Old quilts are less warmer than new ones because the cotton in the old quilt gets compressed and very little air will remain trapped in it, hence heat insulation is quite poor
(v). People wear light colured clothes in winter because these clothes reflect most of the sun's radiations and absorb only a little of them. Therefore, they keep themselves cool.
(ii). It is better to use two thin blankets to keep the body warm rather than using a single blanket of equal thickness because in between the two thin blankets there is more air trapped than in the single blanket of equal thickness so using two thin blankets better heat insulation is provided to the body from the surroundings and keep us warm
(iii). In winter the birds fluff their feathers in order to trap air in their feathers so that the air provides heat insulation to their body from the surroundings and keep them warm and save them from winter.
(iv). Old quilts are less warmer than new ones because the cotton in the old quilt gets compressed and very little air will remain trapped in it, hence heat insulation is quite poor
(v). People wear light colured clothes in winter because these clothes reflect most of the sun's radiations and absorb only a little of them. Therefore, they keep themselves cool.
Chapter 5 - Heat Exercise 231
Question 1
What is meant by energy flow?
Solution 1
Transformation of Sun's energy in sun-eco system through a food chain is called energy flow.
Question 2
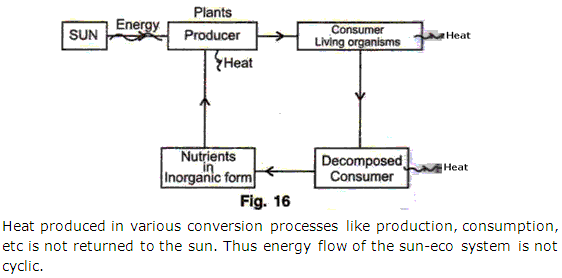
Draw a flow chart to establish that the transfer of sun's energy in a sun-eco system combination in not cyclic.
Solution 2
Question 3
State reason why any energy transfer cannot be 100%.
Solution 3
Any energy transfer is not 100% because energy is lost to the surroundings in the form of heat, friction losses during the transfer of energy. Therefore complete energy is not transferred.
Question 4
State briefly the functioning of a biogas power-source.
Solution 4
Bio gas is produced by the action of bacteria on decaying organic matter. The primary source of bio gas in villages is dung of cow, or buffalo. The bio gas is mostly methane which can be used as a chief source of light and heat energy.
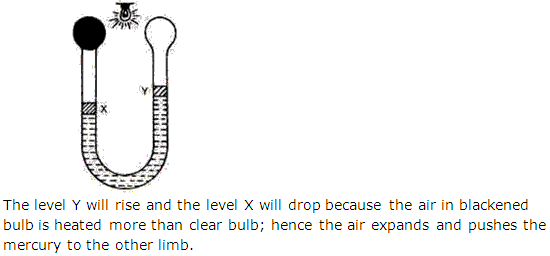
Question 5
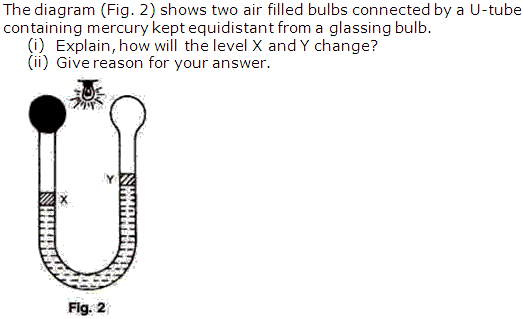
Solution 5
Question 6
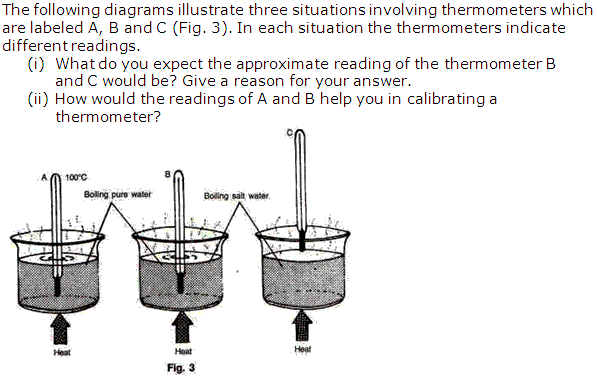
Solution 6
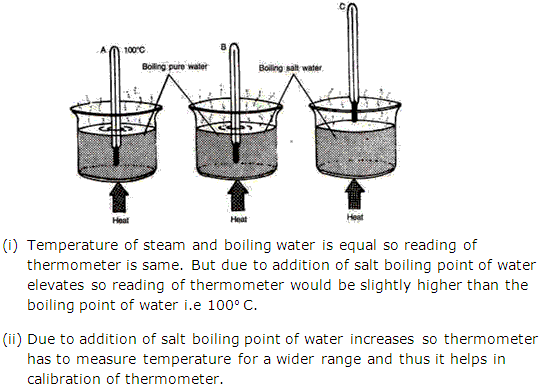
Question 7
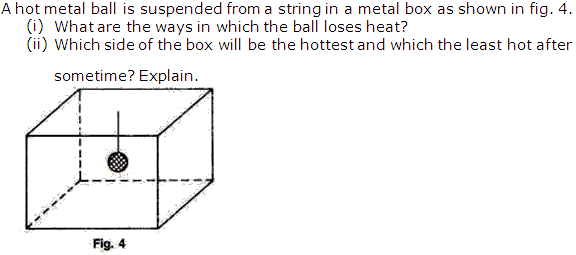
Solution 7
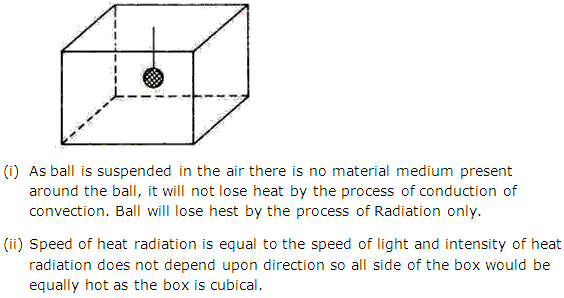
Question 8
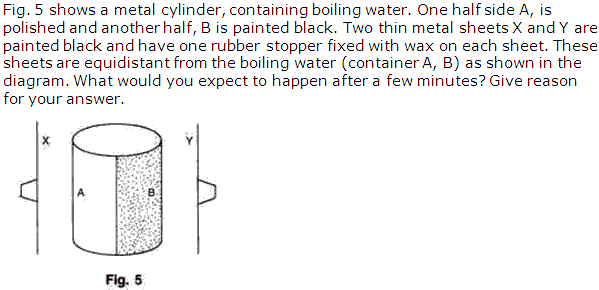
Solution 8
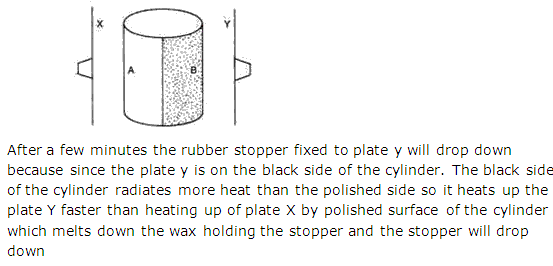
Chapter 5 - Heat Exercise 232
Question 1
Distinguish between Mercury and Alcohol as a thermometric liquid.
Solution 1
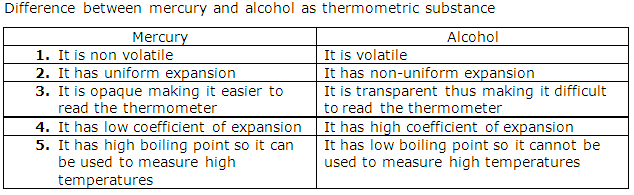
Question 2
Water is not used as a thermometric liquid. Why?
Solution 2
Water is not used as a thermometric liquid because It has low coefficient of expansion so it is less sensitive to temperature changes. Moreover, It is transparent thus making it difficult to read the thermometer and water evaporates with time thus producing error and also the freezing and boiling points are also low.
Question 3
How can you increase the sensitivity of a thermometer?
Solution 3
The sensitivity of a thermometer can be increased by using a substance having high coefficient of expansion and uniform expansion so that its expands with the slightest change in temperature.
Question 4
Explain the following:
(i) Why a thick glass tumbler is likely to crack when hot water is poured
in it?
(ii) Why does not a Pyrex tumbler crack when hot water is poured in it?
(i) Why a thick glass tumbler is likely to crack when hot water is poured
in it?
(ii) Why does not a Pyrex tumbler crack when hot water is poured in it?
Solution 4
(i). When hot water is poured into a thick glass tumbler, it generally cracks because on pouring hot water in the tumbler the inner surface heats up and expands more as compared to its outer surface. This unequal expansion between the two surfaces causes a strain and the tumbler cracks.
(ii). Pyrex glass tumbler does not crack on adding hot water because Pyrex glass has low coefficient of expansion. It does not expand less when hot water is added to the tumbler.
(ii). Pyrex glass tumbler does not crack on adding hot water because Pyrex glass has low coefficient of expansion. It does not expand less when hot water is added to the tumbler.
Question 5
Water at 00C is heated to 100C. Sketch a temperature-volume graph to show the behavior on heating.
Solution 5
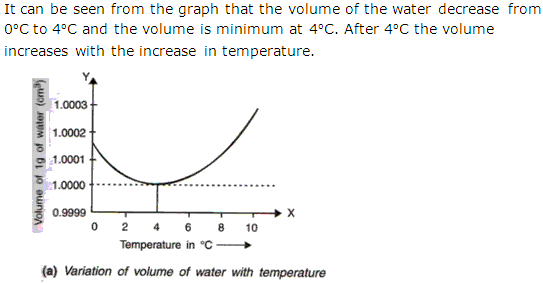
Question 6
Differentiate between clinical thermometer and laboratory thermometer.
Solution 6
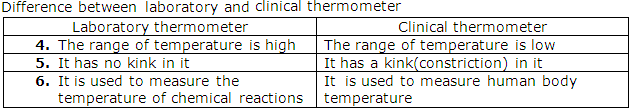
Question 7
Solution 7
Question 8
The temperature of two bodies A and B differ by 10C. By how much will it differ on a Fahrenheit scale?
Solution 8
Temperature in oC = 1oC
C/100 = (F-32)/180
F = 1x18/10 + 32
= 33.8oF
C/100 = (F-32)/180
F = 1x18/10 + 32
= 33.8oF
Question 9
On a faulty thermometer lower fixed point is marked at 100C and upper fixed point is marked as 1300C. What will be the reading on this thermometer when it is placed in a liquid which is actually at 400C?
Solution 9
Lower fixed point = 10oC
Upper fixed point =130oC
Range of thermometer= 130oC - 10oC
= 120oC
No of divisions = 100
So least count = 120/100 = 1.2oC
On actual thermometer 40oC would have 40 divisions
So, on this thermometer it would show
= 40 x LC = 48oC
Upper fixed point =130oC
Range of thermometer= 130oC - 10oC
= 120oC
No of divisions = 100
So least count = 120/100 = 1.2oC
On actual thermometer 40oC would have 40 divisions
So, on this thermometer it would show
= 40 x LC = 48oC
Question 10
What is greenhouse effect?
Solution 10
The green house is referred to a glass house. The heat enters the house but cannot escape out, because the glass reflects the heat back to the inside of the house. This makes glass house warmer than the outside environment. This phenomenon is called green house effect.
Question 11
How global warming occurs?
Solution 11
Global warming occurs due to the presence of carbon di oxide, CFCs, methane in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide acts as a transparent gas to incoming shortwave radiations which the earth re-radiates into space. It, therefore traps the outgoing radiations thus warming lower atmosphere of the earth thereby causing global warming.
Question 12
What are the harmful effects of global warming?
Solution 12
Harmful effects of global warming are
(a). The atmospheric temperature of earth would increase thereby making it difficult for a living being to survive
(b). It would melt down the polar caps thus increasing the size of the ocean and leading to floods, tsunami, etc.
(c). The increase in temperature would affect climate and rainfall thus affecting flora and fauna.
(d). Human beings would be vulnerable to diseases as microbes would get warmth to grow.
(a). The atmospheric temperature of earth would increase thereby making it difficult for a living being to survive
(b). It would melt down the polar caps thus increasing the size of the ocean and leading to floods, tsunami, etc.
(c). The increase in temperature would affect climate and rainfall thus affecting flora and fauna.
(d). Human beings would be vulnerable to diseases as microbes would get warmth to grow.
Question 13
What is the reason behind rising of temperature inside a greenhouse?
Solution 13
The temperature in a green house rises because heat enters the house through the glass but cannot escape out, because the glass reflects the heat back to the inside of the house. This makes glass house warmer than the outside environment.

0 comments:
Post a Comment