Chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism Exercise 323
Question 1
What are two kinds of charges?
Solution 1
Positive and negative are the two kind of charges.
Question 2
What is direct current?
Solution 2
The flow of electrons in a particular direction is called direct current.
Question 3
Write two differences between the primary and secondary cells.
Solution 3
The two differences between primary and secondary cell are :
(a) Primary cells cannot be charged again while secondary cells can be charged again and again.
(b) In primary cells, chemical reaction is irreversible while in secondary cells , chemical reaction is reversible.
(a) Primary cells cannot be charged again while secondary cells can be charged again and again.
(b) In primary cells, chemical reaction is irreversible while in secondary cells , chemical reaction is reversible.
Question 4
What is the SI unit of current?
Solution 4
S.I. unit of current is ampere.
Question 5
What is the difference between a cell and a battery?
Solution 5
A battery is the made up of multiple cells.
Question 6
Is current a scalar or a vector quantity?
Solution 6
Current is a scalar quantity.
Question 7
Name the physical quantity which defines the rate of flow of charge.
Solution 7
Current is defined as the rate of flow of charge.
Question 8
Which is bigger: a milliampere or a microampere?
Solution 8
A milliampere is bigger than microampere.
Question 9
What is the other name for a variable resistor?
Solution 9
Rheostat is other name of variable resistor.
Question 10
Name two sources of current.
Solution 10
A cell and battery are the two sources of current.
Question 11
Is voltmeter same as voltameter?
Solution 11
No, voltmeter is not the same as voltameter.
Question 12
What is the net charge on an atom?
Solution 12
Net charge on an atom is zero.
Question 13
Name the instrument used to measure the magnitude of current flowing in the circuit.
Solution 13
Ammeter is used to measure the magnitude of current in the circuit.
Question 14
What is responsible for the flow of current through a metallic conductor?
Solution 14
Electrons flow inside the metallic conductor and a battery and cell helps in the movement of electrons in it.
Question 15
Which has a greater resistance: an ammeter or a voltmeter?
Solution 15
Voltmeter has high resistance than the ammeter.
Question 16
What is an artificial magnet?
Solution 16
An artificial magnet is the magnetized piece of iron or steel.
Question 17
How is a voltmeter connected in a circuit?
Solution 17
Voltmeter is always connected in parallel to the circuit.
Question 18
How is an ammeter connected in a circuit?
Solution 18
Ammeter is always connected in series in the circuit.
Question 19
Write the SI unit of resistance.
Solution 19
S.I unit of resistance is ohm.
Question 20
Define one ohm resistance.
Solution 20
The resistance of conductor is 1 ohm when a current of 1 ampere flows through it when the potential difference across it is 1 volt.
Question 21
0.8 C charge passes through a cross-section of a cross-section of a conductor in 5 s. Calculate the current.
Solution 21
I = Q/t = 0.8/5 = 0.16 Ampere.
Question 22
Name the instrument used to control current in an electric circuit.
Solution 22
Rheostat is an instrument to control the current in the circuit.
Question 23
How many electrons are present in Na+ ? The atomic number of Na is 11.
Solution 23
10 is the number of electrons present in Na+.
Question 24
What is a horse shoe magnet?
Solution 24
Horse-shoe magnet is the shape of the magnet. This shape helps in bringing the poles near to each other and make the strong magnet.
Question 25
What do you mean by an induced magnetism?
Solution 25
The magnetism acquired by a magnetic material when it is kept near a magnet is called induced magnetism.
Question 26
What are magnetic poles? Where are they situated?
Solution 26
The points of the magnet where attraction appears the maximum are called poles of magnet and they are situated at ends of the magnet.
Question 27
Distinguish between the primary and secondary cells.
Solution 27
The differences between primary and secondary cell are :
(a) Primary cells cannot be charged again while secondary cells can be charged again and again.
(b) In primary cells, chemical reaction is irreversible while in secondary cells , chemical reaction is reversible.
(a) Primary cells cannot be charged again while secondary cells can be charged again and again.
(b) In primary cells, chemical reaction is irreversible while in secondary cells , chemical reaction is reversible.
Question 28
What is a cell? Name the important constituents of a cell.
Solution 28
A cell is a source of energy which converts the chemical energy into electrical energy. The cell consists of two electrodes in the form of conducting rod immersed in the solution called electrolyte.
Question 29
Find the number of electrons that would flow per second through the cross-section of a wire when 1 A current flows in it.
Solution 29
I = Q/t = n e/t
So, n = I.t / e = 1. 1 / 1.6 x 10-19 = 6.25 x 1018
So, 6.25 x 1018 will be the number of electrons.
So, n = I.t / e = 1. 1 / 1.6 x 10-19 = 6.25 x 1018
So, 6.25 x 1018 will be the number of electrons.
Question 30
A current of 4.5 A flows through a conductor for 2.5 s. What amount of charge passes through the conductor?
Solution 30
Q = I.t = 4.5 x 2.5 = 11.25 C.
Question 31
What is the function of a key in an electric current?
Solution 31
A key is used to put the current on and off in the circuit.
Question 32
Define electrical resistance of a metal. Write its SI unit.
Solution 32
The effect to rate of flow of current by the wire is called its electrical reistance. Its S.I unit is ohm.
Question 33
State the factors on which the resistance of a wire depends.
Solution 33
The resistance of the wire depends on the following factors :
(i) Length of the wire
(ii) Cross-section of the wire
(iii) Temperature of the wire.
(iv) Material of the wire.
(i) Length of the wire
(ii) Cross-section of the wire
(iii) Temperature of the wire.
(iv) Material of the wire.
Question 34
Distinguish between an atom and an ion.
Solution 34
An atom does not have any net charge while ion is either a positive charge or a negative charged.
Question 35
What is the effect of temperature on the resistance of a wire?
Solution 35
With increase in temperature of the wire, the resistance of wire increases.
Question 36
Solution 36
The resistance of wire will become 4 ohm.
Question 37
What is a variable resistance? Explain its function using a labeled diagram.
Solution 37
Variable resistors consist of a resistance track with connections at both ends and a wiper which moves along the track as you turn the spindle. The track may be made from carbon, cermet (ceramic and metal mixture) or a coil of wire (for low resistances). The track is usually rotary but straight track versions, usually called sliders, are also available.
A variable resistance is a device used to change the resistance and hence the current flowing through a circuit; without changing the voltage.
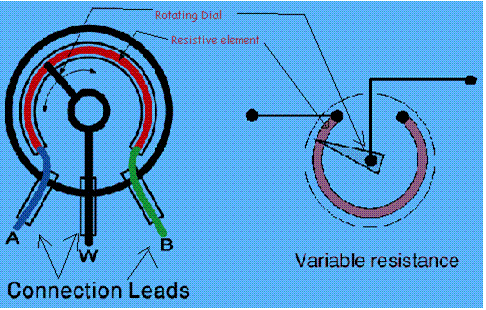
A variable resistance is a device used to change the resistance and hence the current flowing through a circuit; without changing the voltage.

Question 38
How is a galvanometer different from an ammeter?
Solution 38
Galvanometer is used to detect the direction of current as well as to detect very weak current. Ammeter is used to measure the magnitude of an electric current in the circuit.
Question 39
How is a voltameter different from a voltmeter?
Solution 39
Voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference between two points in the circuit. Voltameter is an instrument for measuring the voltaic electricity passing through it, by its effect in decomposing water or some other chemical compound acting as an electrolyte.
Question 40
What is a natural magnet? State three important properties of a magnet.
Solution 40
The magnets (pieces of lodestone) found in nature is called natural magnet. The properties of magnet are : (a) Attractive propery (ii) Directive property (iii) like poles repel while unlike poles attract.
Question 41
Show by diagrams two usual shapes of the artificial magnets.
Solution 41

Question 42
What do you understand by magnetic induction? What role does it play in the attraction of a piece of iron by a magnet?
Solution 42
The mechanism in which magnetism acquired by the magnetic material when kept near a magnet is called magnetic induction. When the magnetic material get magnetized, the pole developed on its side will be opposite to the magnet's pole taken near to it. So, opposite poles attract each other. So, induction causes attraction.
Question 43
Explain the method of plotting the magnet field lines by using a small compass needle.
Solution 43
We will start drawing the magnetic field of lines from the north pole of magnet. When a small compass is placed at a point near the north pole of the magnet , the needle turns round on its pivot and settle in the fixed direction. At other points away from the pole the needle settles tangent to the drawn field line. By plotting the directions indicated by the needle, we can draw magnetic field of lines.
Question 44
A small magnet is suspended by a silk thread from a rigid support such that the magnet can freely swing. How will it rest? Explain by drawing a diagram.
Solution 44

Question 45
What causes electrification of two bodies when they are rubbed together?
Solution 45
The friction between two bodies when they are rubbed against each other is the reason of electrification.
Question 46
What is the function of a lighting conductor?
Solution 46
A lightening conductor is a device used to protect the large buildings against lightening during a thunderstorm.
Question 47
The lighting and the thunder are produced simultaneously, but the sound of the thunder is heard a few seconds after the lighting is seen. Why?
Solution 47
The speed of light is very fast as compared to the speed of sound in air. So, the thunder is seen fast and then we hear the sound of thunderstorm.
Question 48
What is the purpose of an electroscope?
Solution 48
Electroscope is used to determine the nature of the charge and to detect the presence of charge on the body.
Question 49
A positively charged rod is brought near the cap of a positively charged gold leaf electroscope. State your observation and give a reason.
Solution 49
When a positively charged rod is brought near the positively charged cap then , the positive charge on the cap will spread over because of repulsion and some of them will reach to the leaves . Now, the leaves will have the same positive charge , they will repel each other and hence, leaves will diverge.
Chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism Exercise 324
Question 1
What do you mean by the term lines of magnetic field?
Solution 1
The magnetic field of lines are the lines which get formed by joining the poles of the magnet and they are the continuous curves in which tangent drawn to it will give the direction of magnetic field.
Question 2
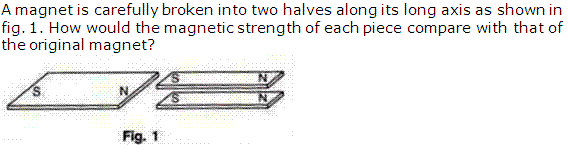
Solution 2
By breaking the magnet into two halves, magnetic strength will always get half.
Question 3
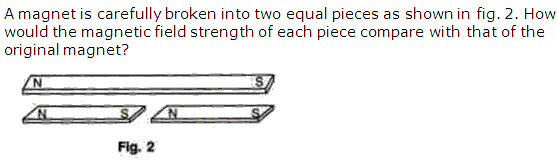
Solution 3
By breaking the magnet into two halves, magnetic strength will always get half. So, the raio of magnetic strength will be 1:2.
Question 4

Solution 4
(i) The charge gained by the B will be positive charge
(ii) The B will be charged by the charging by contact. The charge on A will spread on B.
(ii) The B will be charged by the charging by contact. The charge on A will spread on B.
Question 5
What is an electroscope? Describe the different stages of charging a gold leaf electroscope negatively with the help of a diagram.
Solution 5
(1) Electroscope is the device used to detect the presence of charge and the nature of charge on the body. The four stages of the charging a gold leaf electroscope by induction are :
(i) Bring a positively charged rod near the cap of an electroscope. The cap will acquire the negative charge on it by induction. The leaves will diverge
(ii) Earth the electroscope by touching the cap will finger.
(iii) Remove the finger and keep the positively charged rod as such.
(iv) Now, take away the rod. The leaves will diverge because of charges induced by induction..
(i) Bring a positively charged rod near the cap of an electroscope. The cap will acquire the negative charge on it by induction. The leaves will diverge
(ii) Earth the electroscope by touching the cap will finger.
(iii) Remove the finger and keep the positively charged rod as such.
(iv) Now, take away the rod. The leaves will diverge because of charges induced by induction..

Question 6

Solution 6
Electrostatic induction is the process of charging a body by bringing another charged body near to it. When the X will come near to body B, the opposite charge will be acquired by body B. So, negative charge will be acquired. Similarly, by electrostatic induction, A will acquire the opposite charge of B so A will acquire the positive charge.
Question 7
(a) Write a short note on lighting conductors.
(b) Explain the following:
(i) Resistance of a conductor
(ii) Potential difference
(iii) Open circuit
(iv) Closed circuit
(b) Explain the following:
(i) Resistance of a conductor
(ii) Potential difference
(iii) Open circuit
(iv) Closed circuit
Solution 7
(a) Lightening conductor is a device used to safeguard the large buildings against lightening of thunderstorm. Normally, they are fitted on the top of tall buildings as a safety device. It consist of few metal spikes fitted to the highest part of building and connected to thick copper strip which is buried inside the earth .
(b)
(i) Resistance of the conductor: It is the property of the conductor by virtue of which it obstructs the flow of current in the circuit.
(ii) Potential Difference: It is defined as the amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another .
(iii) Open Circuit: In the circuit, if the switch is off or the wire is cut then flow of current in circuit stops and we say that its an open circuit.
(iv) Closed Circuit: The circuit in which current flows without any obstruction then it's a closed circuit.
(b)
(i) Resistance of the conductor: It is the property of the conductor by virtue of which it obstructs the flow of current in the circuit.
(ii) Potential Difference: It is defined as the amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another .
(iii) Open Circuit: In the circuit, if the switch is off or the wire is cut then flow of current in circuit stops and we say that its an open circuit.
(iv) Closed Circuit: The circuit in which current flows without any obstruction then it's a closed circuit.
Question 8
Compare the brightness of two 60 watt bulbs
(i) When they are connected in series.
(ii) When they are connected in parallel.
Explain giving scientific reasons.
(i) When they are connected in series.
(ii) When they are connected in parallel.
Explain giving scientific reasons.
Solution 8
(i) When two bulbs will connect in series then resistance of the circuit will increase so the brightness of the bulbs will decrease.
(ii) When the two bulbs will be connected in parallel then resistance of circuit will decrease so the bulbs brightness will increase.
(ii) When the two bulbs will be connected in parallel then resistance of circuit will decrease so the bulbs brightness will increase.
Question 9
Differentiate between:
(i) Conductors and insulators.
(ii) Flow of electron and flow of conventional current.
(iii) Primary and secondary cell.
(i) Conductors and insulators.
(ii) Flow of electron and flow of conventional current.
(iii) Primary and secondary cell.
Solution 9
(i) Differences between Conductor and insulators::
(a) Conductors allow passing of electric current through it. Insulator does not allow passing of current through it.
(b) Silver, Gold are good examples of conductor of electricity . Rubber, Cotton are good examples of insulators.
(ii) Flow of electrons is the flow of negative charges inside the conductor while flow of conventional current is the flow of positive charges inside a conductor.
(iii) Primary cells are the cells in which chemical reaction is irreversible so they can't be charged again and again. While , secondary cells are the cells in which chemical reaction is reversible and can be charged again and again.
(a) Conductors allow passing of electric current through it. Insulator does not allow passing of current through it.
(b) Silver, Gold are good examples of conductor of electricity . Rubber, Cotton are good examples of insulators.
(ii) Flow of electrons is the flow of negative charges inside the conductor while flow of conventional current is the flow of positive charges inside a conductor.
(iii) Primary cells are the cells in which chemical reaction is irreversible so they can't be charged again and again. While , secondary cells are the cells in which chemical reaction is reversible and can be charged again and again.
Question 10
(a) What are the properties of a magnet?
(b) State the laws of magnetism.
(c) Distinguish between
(i) Magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
(ii) Natural and artificial magnets.
(iii) Magnetic properties of iron and steel.
(b) State the laws of magnetism.
(c) Distinguish between
(i) Magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
(ii) Natural and artificial magnets.
(iii) Magnetic properties of iron and steel.
Solution 10
(a)Following are the properties of magnet
(i) Like poles of magnet repel each other while unlike poles attract.
(ii) Magnet have an attractive property means it attract the magnetic material towards it.
(iii) Magnet have the directive property means when it is held freely , it always point towards north-south direction.
(b) The Laws of Magnetism: Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
(c) (i) Magnetic materials get attracted towards the magnet but non-magnetic materials does not get attracted towards the magnet.
(ii) Natural magnets are the pieces of lodestone which are found in nature while artificial magnet is the magnetized piece of iron or steel.
(iii)Iron has high susceptibility and low retentivity means it acquires the magnetism faster and removes it soon as well. While , steel has low susceptibility and high retentivity.
(i) Like poles of magnet repel each other while unlike poles attract.
(ii) Magnet have an attractive property means it attract the magnetic material towards it.
(iii) Magnet have the directive property means when it is held freely , it always point towards north-south direction.
(b) The Laws of Magnetism: Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
(c) (i) Magnetic materials get attracted towards the magnet but non-magnetic materials does not get attracted towards the magnet.
(ii) Natural magnets are the pieces of lodestone which are found in nature while artificial magnet is the magnetized piece of iron or steel.
(iii)Iron has high susceptibility and low retentivity means it acquires the magnetism faster and removes it soon as well. While , steel has low susceptibility and high retentivity.
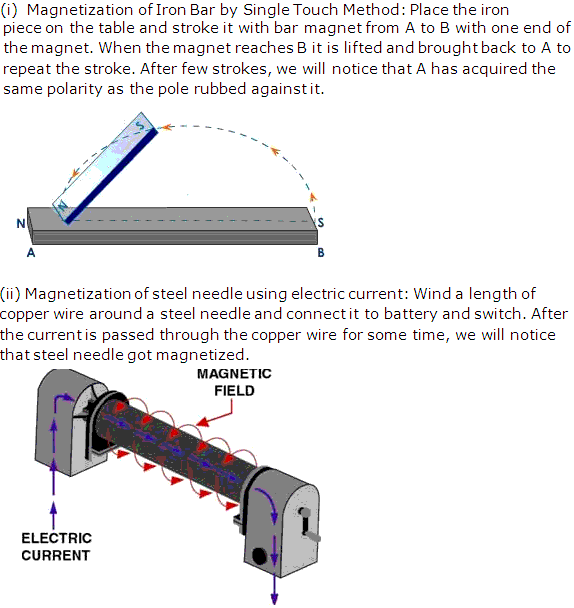
Question 11
With the help of a diagram explain the following:
(i) Magnetisation of an iron bar by single touch method.
(ii) Magnetisation of steel neddle using electric current such that the pointed end should have north polarity.
(i) Magnetisation of an iron bar by single touch method.
(ii) Magnetisation of steel neddle using electric current such that the pointed end should have north polarity.
Solution 11
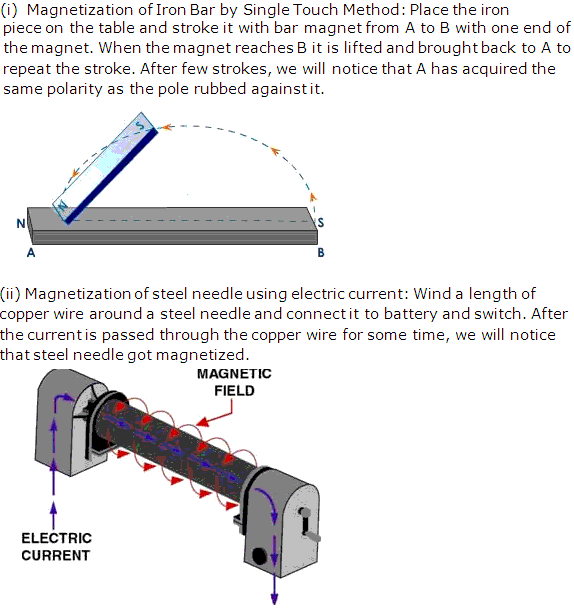
Chapter 8 - Electricity and Magnetism Exercise 325
Question 1
(a) Explain, what is meant by magnetic induction.
(b) How would you test whether a piece of steel was magnetised
(i) If you had a magnet.
(ii) If there was no magnet available.
(c) Define the following terms:
(i) Magnetic meridian
(ii) Geographic meridian
(iii) Angle of declination
(iv) Angle of dip
(b) How would you test whether a piece of steel was magnetised
(i) If you had a magnet.
(ii) If there was no magnet available.
(c) Define the following terms:
(i) Magnetic meridian
(ii) Geographic meridian
(iii) Angle of declination
(iv) Angle of dip
Solution 1
(a) Magnetic induction is the process in which magnetism is acquired by the magnetic material when a magnet is brought near it.
b)(i) If we had a magnet then we will bring the magnet near to steel , if there is force of repulsion or attraction is experienced then steel was magnetized otherwise not.
(ii) We will held the steel freely, if it points to north-south direction only then it is magnetized otherwise not.
c) (i) Magnetic Meridian: It is the vertical plane containing the magnetic axis of a freely suspended magnet at rest under the earth's field.
(ii) Geographic Meridian: It is the vertical plane containing the geographic north and south poles of the earth and passing through the given place in the surface of earth.
(iii)Angle of declination: The angle between geographic and magnetic meridian is called angle of declination.
(iv)Angle of Dip: The angle between the horizontal and earth's magnetic field is known as angle of dip.
b)(i) If we had a magnet then we will bring the magnet near to steel , if there is force of repulsion or attraction is experienced then steel was magnetized otherwise not.
(ii) We will held the steel freely, if it points to north-south direction only then it is magnetized otherwise not.
c) (i) Magnetic Meridian: It is the vertical plane containing the magnetic axis of a freely suspended magnet at rest under the earth's field.
(ii) Geographic Meridian: It is the vertical plane containing the geographic north and south poles of the earth and passing through the given place in the surface of earth.
(iii)Angle of declination: The angle between geographic and magnetic meridian is called angle of declination.
(iv)Angle of Dip: The angle between the horizontal and earth's magnetic field is known as angle of dip.
Question 2

Solution 2
(i) When a nylon shirt , blouse or stocking s are removed then they get rubbed with the hairs and due to friction between hairs and nylon , charges get induced on them and attractive force get induced between them.
(ii) The rubbed ebonite rod contains more electrons so it acquires the negative charge so a charged is acquired by it. But, in the rubbed metal rod , electrons are transferred but through hands and body they pass to the earth so no charges will be there while metal rod is held in hand.
(iii)Soft iron is used to make electromagnets because it has high susceptibility and low retentivity , it get magnetized very faster and loses magnetism as soon as the inducing magnet is removed.
(iv)Two steel needles hanging from the lower end of the vertical bar magnet do not hang vertical but will diverge because they got the like poles on it and like poles repel each other so they diverge.
(v)If magnetic material is brought near to the magnet then it get attracted although its not magnetized but the magnetic material will be repelled only in case it is magnetised. So repulsion is the sure test of magnetism.
(ii) The rubbed ebonite rod contains more electrons so it acquires the negative charge so a charged is acquired by it. But, in the rubbed metal rod , electrons are transferred but through hands and body they pass to the earth so no charges will be there while metal rod is held in hand.
(iii)Soft iron is used to make electromagnets because it has high susceptibility and low retentivity , it get magnetized very faster and loses magnetism as soon as the inducing magnet is removed.
(iv)Two steel needles hanging from the lower end of the vertical bar magnet do not hang vertical but will diverge because they got the like poles on it and like poles repel each other so they diverge.
(v)If magnetic material is brought near to the magnet then it get attracted although its not magnetized but the magnetic material will be repelled only in case it is magnetised. So repulsion is the sure test of magnetism.
Question 3
(a) What is a neutral point?
(b) Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet when a bar magnet is placed such that the N pole points North.
(b) Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet when a bar magnet is placed such that the N pole points North.
Solution 3

Question 4
State two disadvantages of setting up large dams for hydro-electricity power station.
Solution 4
Disadvantages of setting up large dams for hydro-electricity power station::
(1) It leads to large catchment area being submerged
(2) displacement of people from their places.
(1) It leads to large catchment area being submerged
(2) displacement of people from their places.
Question 5
State two particles in the use of energy those cut down energy consumption.
Solution 5
Improved practices in the use of energy :
(1) Use the improved cook stove which will save the bio-mass energy
(2) Use the improved solar panels and solar furnaces.
(1) Use the improved cook stove which will save the bio-mass energy
(2) Use the improved solar panels and solar furnaces.
Question 6
What are the functions of Bureau of energy efficiency set up by the government?
Solution 6
The functions of bureau of energy efficiency setup are :
(1) control and keep an eye on consumption pattern
(2) develop appliances suitable for the energy change
(3) organize posters and slogans for developing awareness in society.
(1) control and keep an eye on consumption pattern
(2) develop appliances suitable for the energy change
(3) organize posters and slogans for developing awareness in society.
Question 7
Suggest best particles in use of energy (a) at school (b) at home that save energy.
Solution 7
(a) At School : Use of solar cells to light up the electricity in schools and do rain water harvesting, keep the electrical appliances off after the needed period of time.
(b) At Home : Use of bio energy for cooking and lightening, use CFLs instead of filament bulbs, keep the electrical appliances off after the needed period of time.
(b) At Home : Use of bio energy for cooking and lightening, use CFLs instead of filament bulbs, keep the electrical appliances off after the needed period of time.
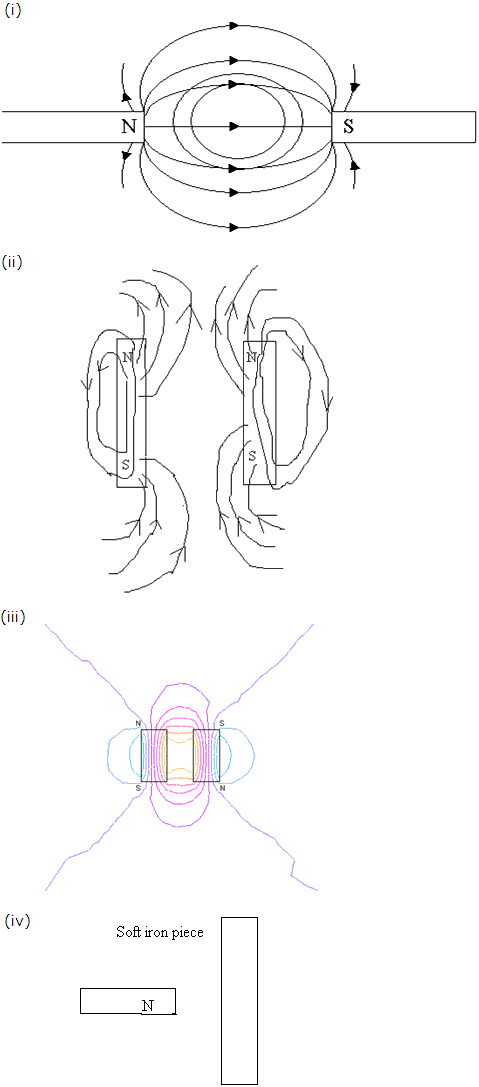
Question 8
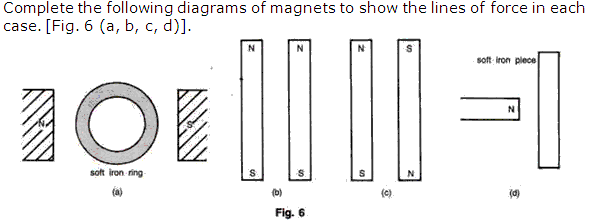
Solution 8

0 comments:
Post a Comment