Chapter 24 - Perimeter and Area Exercise Ex. 24.1
Question 1
Find
the area of a triangle whose base is 3.8 cm and height is 2.8 cm.
Solution 1
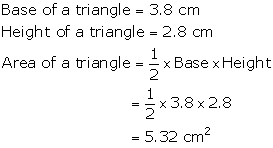
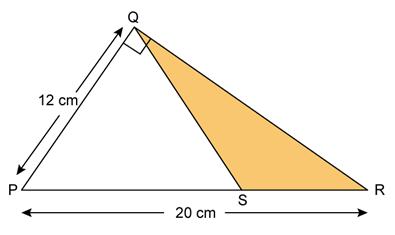
Question 2
Find
the area of the shaded region in the figure as shown, in which DPQS
is an equilateral triangle and ∠PQR = 90°.
Solution 2


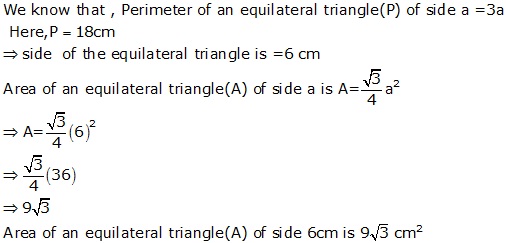
Question 3
The
area of an equilateral triangle is numerically equal to its perimeter. Find
the length of its sides, correct two decimal places.
Solution 3

Question 4
In
a right-angled triangle PQR right-angled at Q, QR = x cm, PQ = (x + 7) cm and
area = 30 cm2. Find the sides of the triangle.
Solution 4
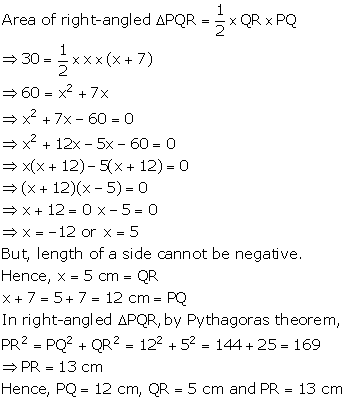
Question 5
In
a right-angled triangle ABC, if ∠B
= 90°, AB - BC = 2 cm; AC - BC = 4 and its perimeter is 24 cm, find the area
of the triangle.
Solution 5

Question 6
Find
the area of a triangle whose sides are 27 cm, 45 cm and 36 cm.
Solution 6
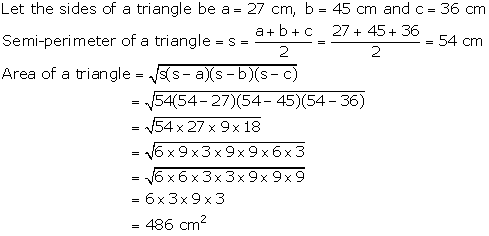
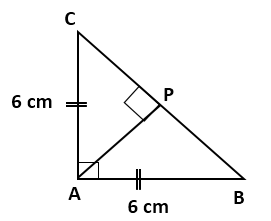
Question 7
Find
the area of an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC = 6 cm, ∠A
= 90°. Also, find the length of perpendicular from A to BC.
Solution 7
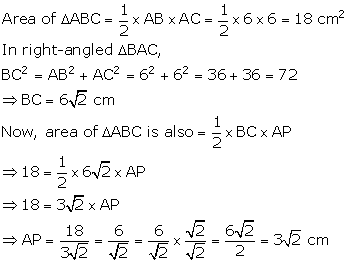
Question 8
Find
the area of an equilateral triangle of side 20 cm.
Solution 8
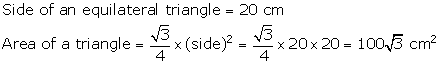
Question 9
Solution 9

Question 10
Solution 10
Question 11
Solution 11

Question 12
Solution 12


Question 13
Solution 13

Question 14
Solution 14
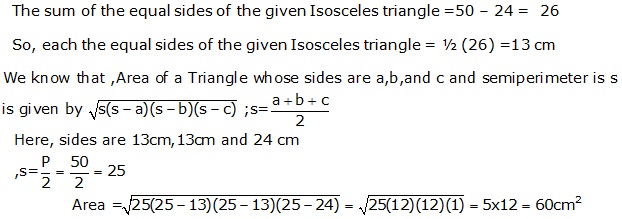
Question 15
Solution 15
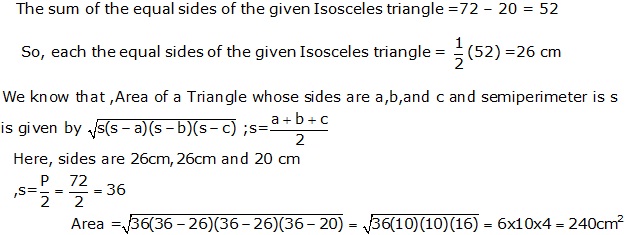
Question 16
Solution 16

Question 17
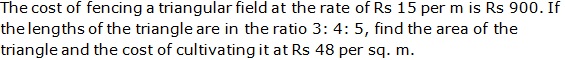
Solution 17

Question 18
Solution 18

Question 19
Solution 19
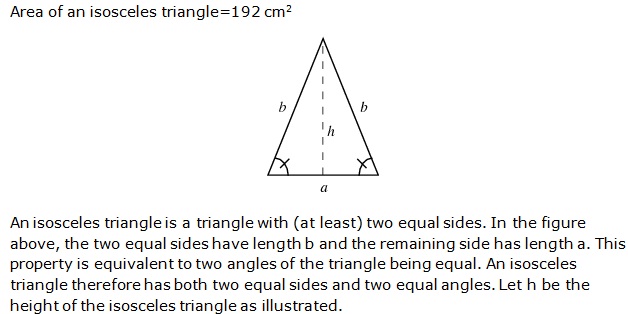

Question 20

Solution 20

Chapter 24 - Perimeter and Area Exercise Ex. 24.2
Question 1
The
side of a square is of length 20 mm. Find its perimeter in cm.
Solution 1
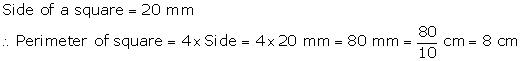
Question 2
In
a rectangle ABCD, AB = 7 cm and AD = 25 cm. Find the height of a triangle
whose base is AB and whose area is two times the area of the rectangle ABCD.
Solution 2

Question 3
Two
adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 34 cm and 20 cm. If one of its diagonal
is 42 cm, find:
a. area of
the parallelogram.
b. distance between its shorter
sides
Solution 3

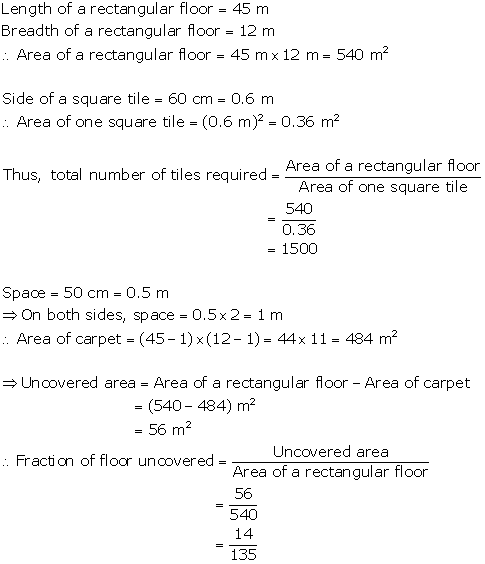
Question 4
A
rectangular floor 45 in long and 12 m broad is to be paved exactly with
square tiles, of side 60 cm. Find the total number of tiles required to pave
it.
If
a carpet is laid on the floor such as a space of 50 cm exists between its
edges and the edges of the floor, find what fraction of the floor is
uncovered.
Solution 4
Question 5
The
area of a square is 36 cm2. How long are its sides?
Solution 5

Question 6
Find
the perimeter and area of a square whose diagonal is 5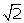 cm. Give your answer correct to two decimal places if
cm. Give your answer correct to two decimal places if 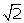 = 1.414.
= 1.414.
Solution 6
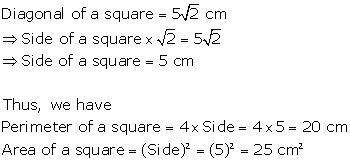
Question 7
The
sides of a rectangle are 5 cm and 3 cm respectively. Find its area in mm2.
Solution 7
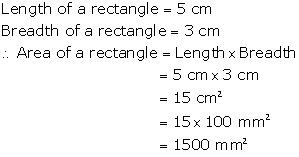
Question 8
The
area of a rhombus is 234 cm2. If its one
diagonal is 18 cm, find the lengths of its side and the other diagonal. Also,
find perimeter of the rhombus.
Solution 8

Question 9
The
floor of a room is of size 6 m x 5 m. Find the cost of covering the floor of
the room with 50 cm wide carpet at the rate of Rs.24.50 per metre. Also, find the cost of carpeting the same hall if
the carpet, 60 cm, wide, is at the rate of Rs.26 per metre.
Solution 9

Question 10
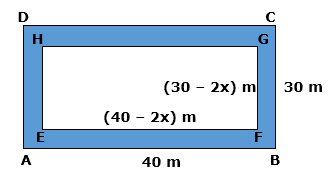
A
footpath of uniform width runs all around the inside of a rectangular garden
of 40 m x 30 m. If the path occupies 136 m2, find the width of the
path.
Solution 10

Question 11
Find
the area and perimeter of the given figure.
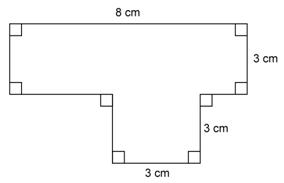
Solution 11
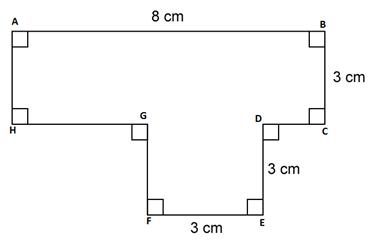
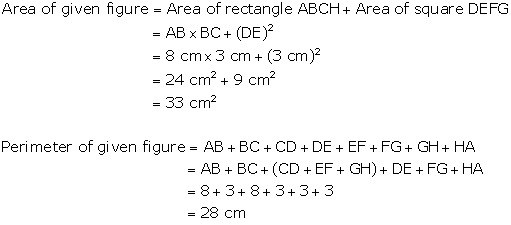
Question 12
How
many tiles, each of area 625 cm2, will be needed to pave a
footpath which is 1 m wide and surrounds a grass plot of size 38 m x 14 m?
Solution 12

Question 13

Solution 13
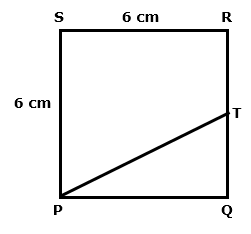
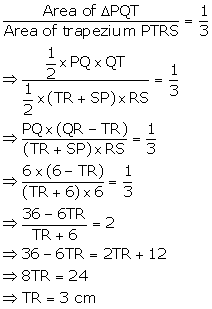
Question 14
A
wire when bent in the form of a square encloses an area of 16 cm2.
Find the area enclosed by it when the same wire is bent in the form of
a. a
rectangle whose sides are in the ratio of 1 : 3.
b. an equilateral triangle
Solution 14

Question 15
Find
the shaded area in the given figure.
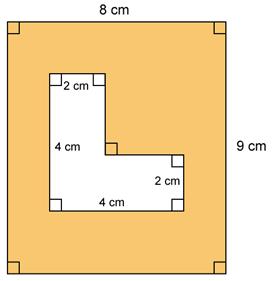
Solution 15
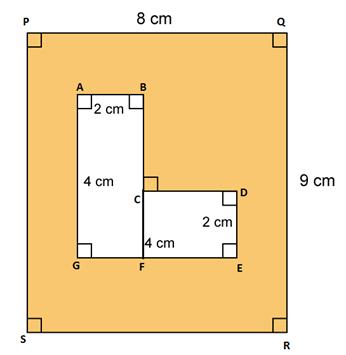

Question 16
Find
the area of each of the following figure:
Solution 16
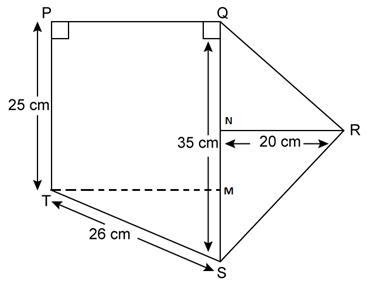

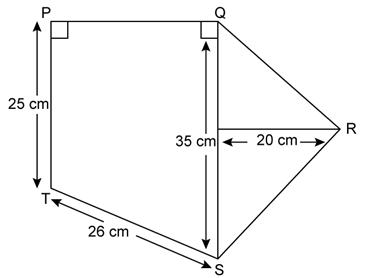
Question 17
Find
the area of each of the following figure:
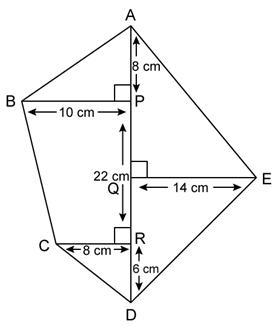
Solution 17
Question 18
Find
the area of each of the following figure:
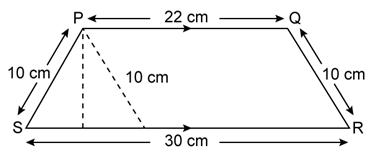
Solution 18

Question 19
Find
the area of each of the following figure:
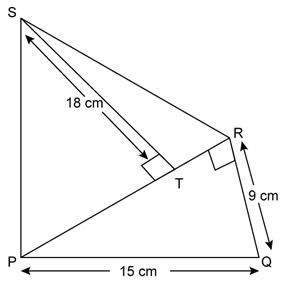
Solution 19

Question 20
Find
the area of quadrilateral, whose diagonals of lengths 18 cm and 13 cm
intersect each other at right angle.
Solution 20

Question 21
Solution 21
Question 22
Solution 22

Question 23

Solution 23

Question 24

Solution 24

Question 25
Solution 25
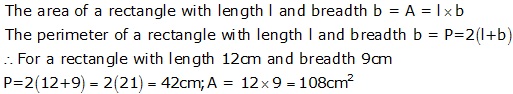
Question 26
Solution 26

Question 27
Solution 27

Question 28
Solution 28

Question 29
Solution 29
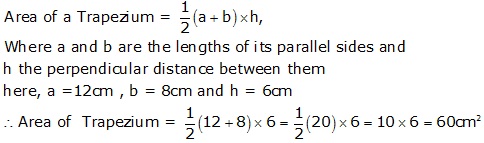
Question 30
Solution 30

Question 31

Solution 31
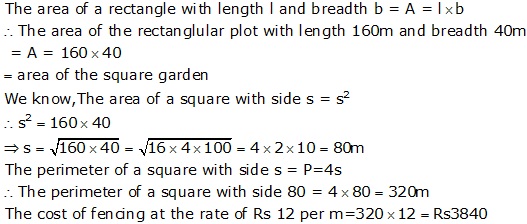
Question 32
Solution 32

Question 33
Solution 33
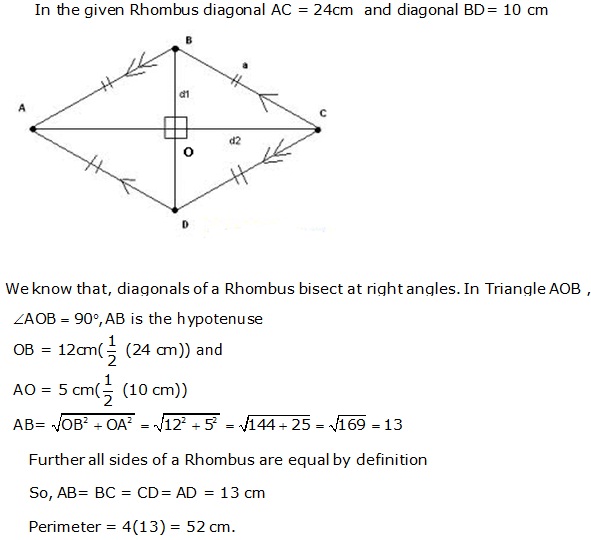
Question 34

Solution 34

Question 35

Solution 35

Question 36
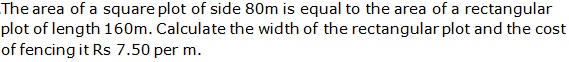
Solution 36

Question 37

Solution 37

Question 38
Solution 38
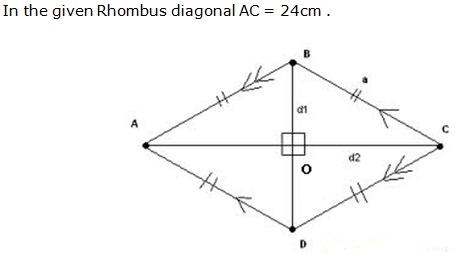

Question 39
Solution 39
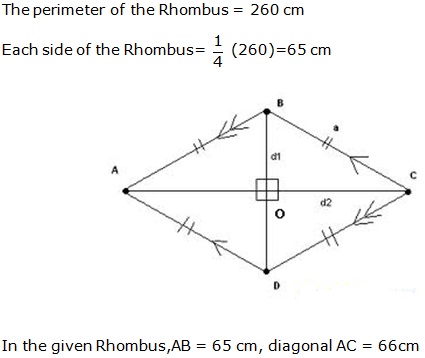
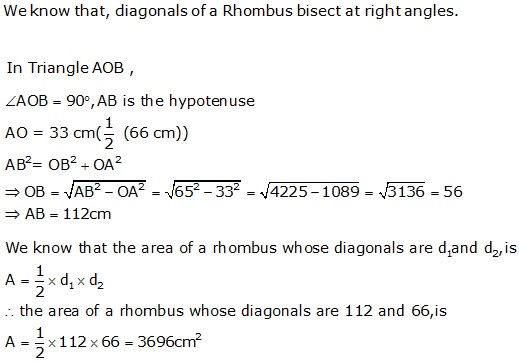
Question 40

Solution 40
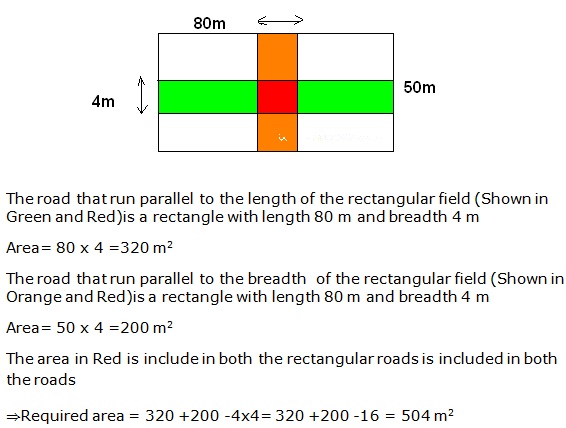
Question 41

Solution 41
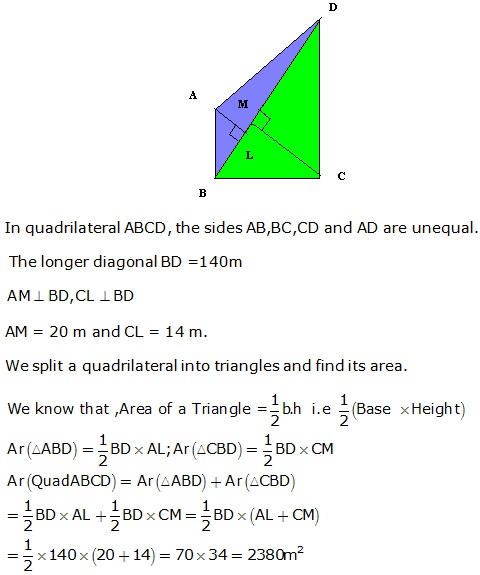
Question 42

Solution 42
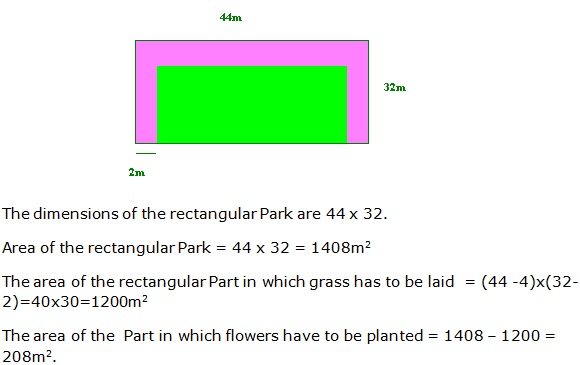
Question 43

Solution 43
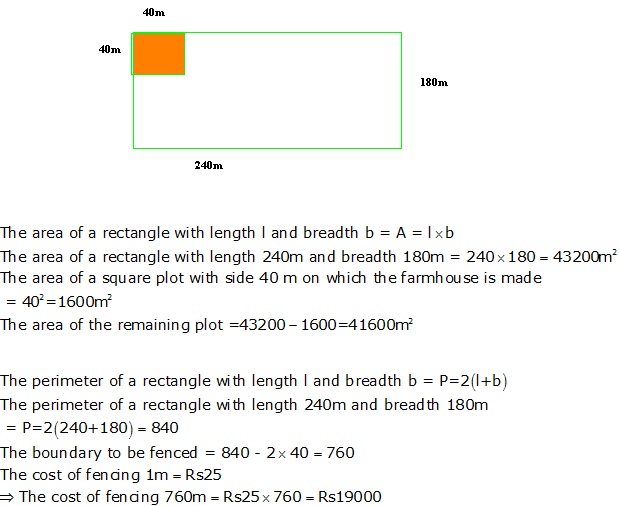
Question 44

Solution 44
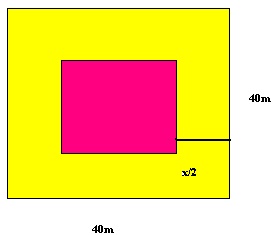

Question 45

Solution 45

Question 46
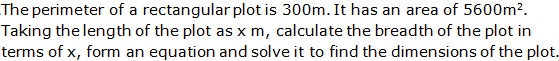
Solution 46

Question 47

Solution 47
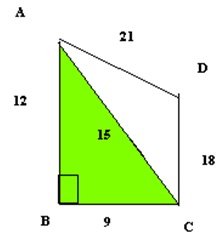

Question 48
Solution 48
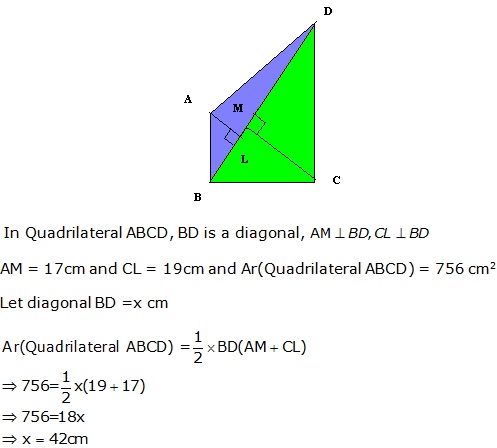
Question 49

Solution 49

Question 50

Solution 50
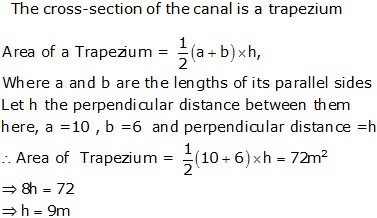
Chapter 24 - Perimeter and Area Exercise Ex. 24.3
Question 1
The
diameter of two circles are 28 cm and 24 cm. Find the circumference of the
circle having its area equal to sum of the areas of the two circles.
Solution 1

Question 2
The
radii of two circles are in the ratio 5 : 8. If the
difference between their areas is 156p
cm2, find the area of the bigger circle.
Solution 2
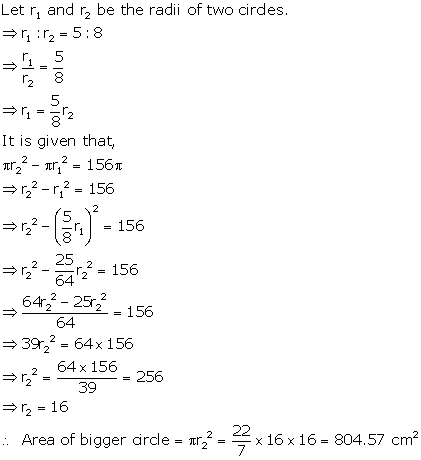
Question 3
The
diameters of three wheels are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 8.
If the sum of the circumferences of these circles be 132 cm, find the
difference between the areas of the largest and the smallest of these wheels.
Solution 3

Question 4
The
area of the circular ring enclosed between two concentric circles is 88 cm2.
Find the radii of the two circles, if their difference is 1 cm.
Solution 4
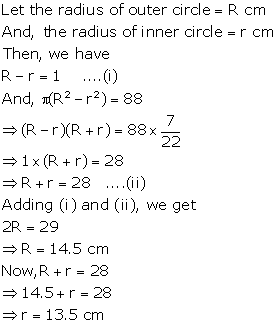
Question 5
The
sum of the radii of two circles is 10.5 cm and the difference of their
circumferences is 13.2 cm. Find the radii of the two circles.
Solution 5
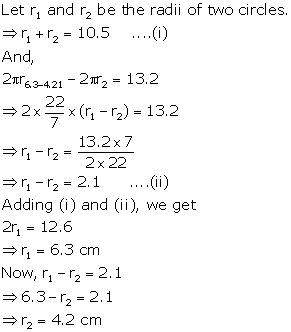
Question 6
A
square is inscribed in a circle of radius 6 cm. Find the area of the square.
Give your answer correct to two decimal places if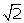 = 1.414.
= 1.414.
Solution 6

Question 7
The
cost of fencing a circular field at the rate of Rs.250 per metre is Rs.55000.
The field is to be ploughing at the rate of Rs.15 per m2.
Find the cost of ploughing the field.
Solution 7

Question 8
The
circumference of a circle exceeds its diameter by 450 cm. Find the area of
the circle.
Solution 8
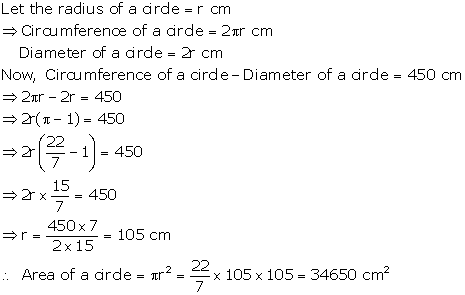
Question 9
The
circumference of a circle is numerically equal to its area. Find the area and
circumference of the circle.
Solution 9

Question 10
The
sum of the circumference and diameter of a circle is 176 cm. Find the area of
the circle.
Solution 10

Question 11
Find
the radius and area of the circle which has circumference equal to the sum of
circumferences of the two circles of radii 3 cm and 4 cm respectively.
Solution 11
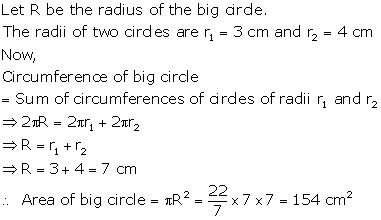
Question 12
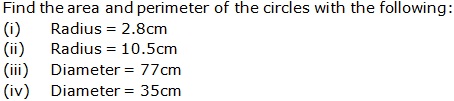
Solution 12


Question 13

Solution 13


Question 14
Solution 14
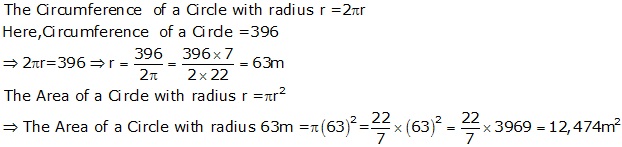
Question 15
Solution 15

Question 16
Solution 16

Question 17
Solution 17

Question 18
Solution 18

Question 19
Solution 19

Question 20
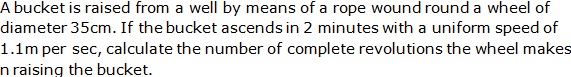
Solution 20

Question 21
Solution 21
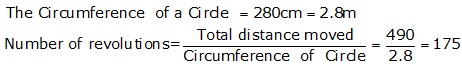
Question 22
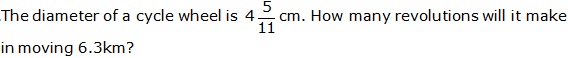
Solution 22

Question 23
Solution 23
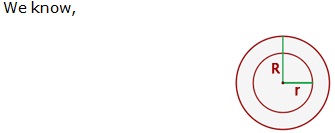

Question 24
Solution 24

Question 25
Solution 25

Question 26

Solution 26
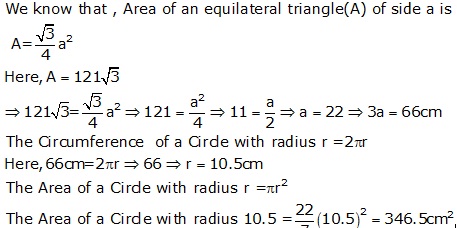
Question 27
Solution 27

Question 28
Solution 28

Question 29

Solution 29

Question 30
Solution 30
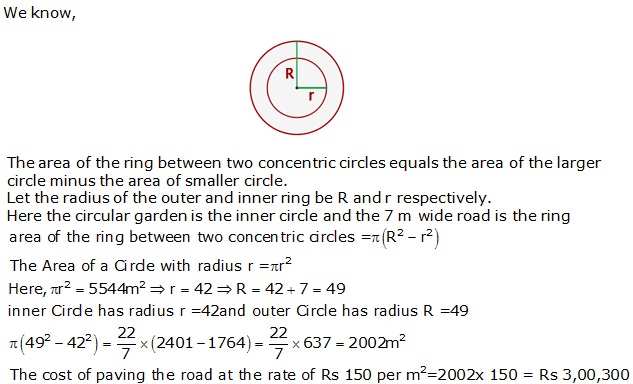
Question 31
Solution 31
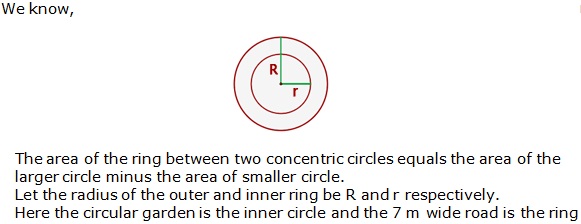
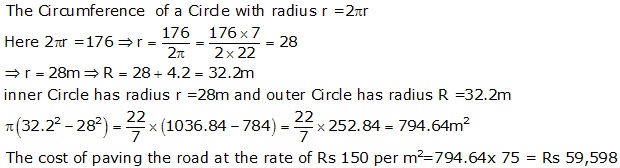
Question 32
Solution 32
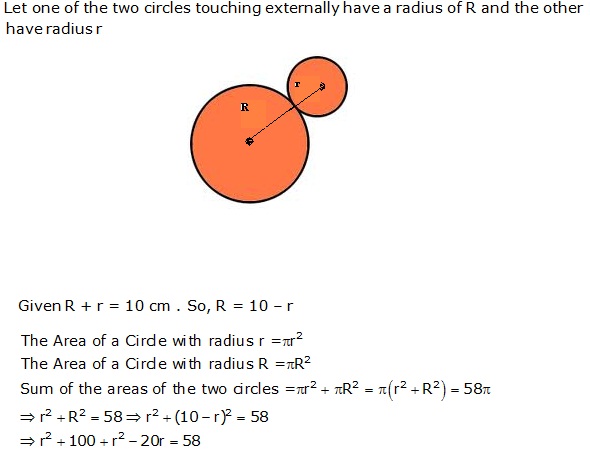

Question 33
Solution 33
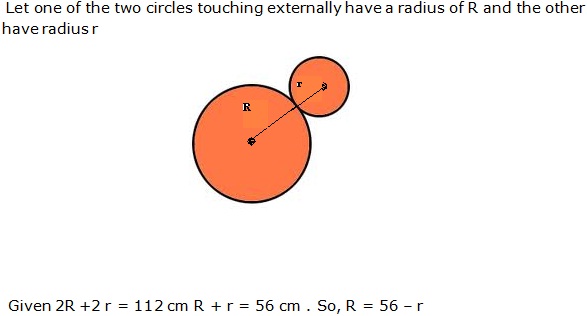

Question 34

Solution 34
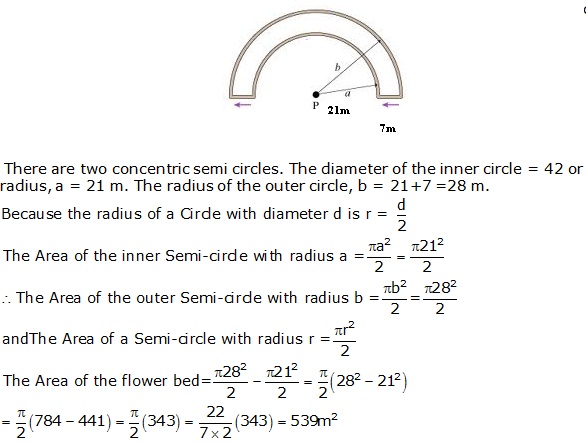
Question 35

Solution 35

Question 36
Solution 36


0 comments:
Post a Comment