Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 307
Question 1
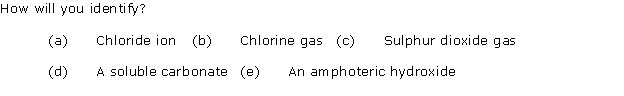
Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3
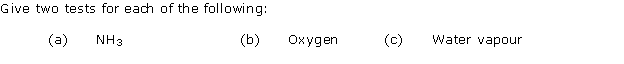
Solution 3

Question 4
Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5

Question 6
Write
sqauential observation for effect of heat on
(a) Copper nitrate
(b) Lead carbonate
(c) Ammonium chloride
Solution 6
(a) i) Bluish green
crystalline solid, on heating, melts to form a bluish green mass and gives
off steamy vapours which condense on the cooler part of the test tube.
ii) On further heating, the bluish green mass changes to a black
residue.
iii) It gives off a reddish brown gas and gives a gas which
rekindles a glowing splinter, i.e. oxygen.
(b) i) A white solid
turns yellow on heating.
ii) Gives off a gas which extinguishes a burning wooden
splinter.
iii) Gas evolved turns lime water milky.
(c) i) When ammonium chloride is heated in a test tube, the
lighter ammonia gas will emerge first and turn a piece of moist red litmus
paper blue.
ii) Hydrogen
chloride coming up next will change the
litmus
paper from blue back to red.
Question 7

Solution 7
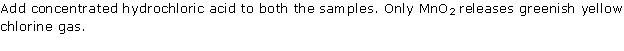
Question 8

Solution 8

Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 308
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5
Solution 5
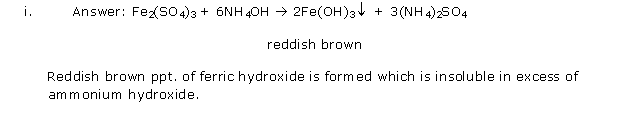
Question 6

Solution 6
Question 7


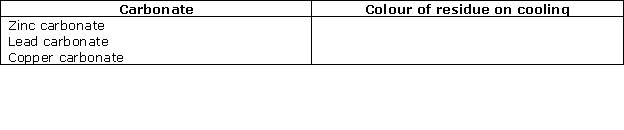
Solution 7
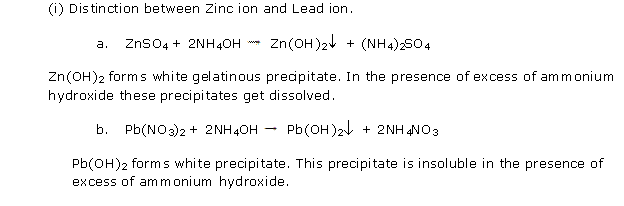
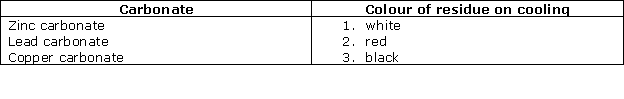
Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 309
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
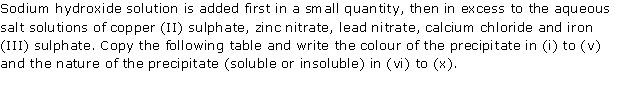

Solution 2

Question 3

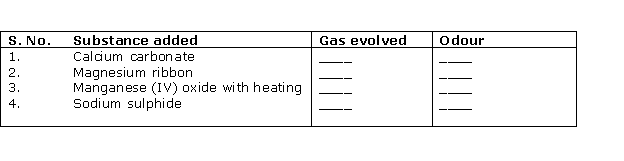
Solution 3
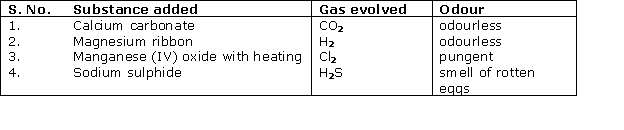
Question 4

Solution 4
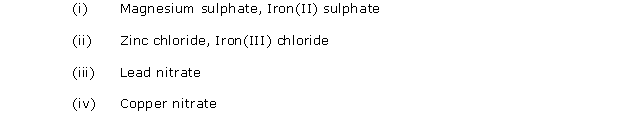
Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 310
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
Solution 2

Question 3

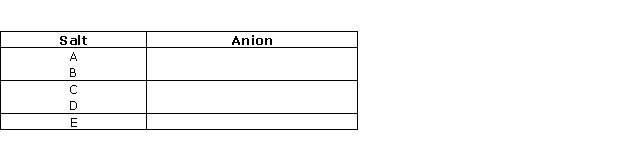
Solution 3

Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 311
Question 1

Solution 1

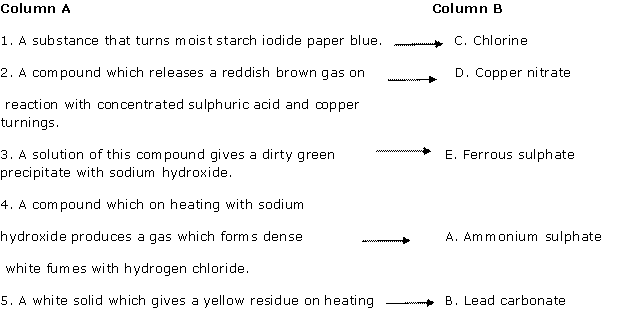
Question 2
Select
from the list given (a to e) one substances in each case which matches the
description given in parts (i) to (v). (Note : Each substance is used only
one in the answer)
(a) Nitroso Iron (II) Sulphate
(b) Iron (III) chloride
(c) Chromium sulphate
(d) Lead (II) chloride
(e) Sodium chloride
(i) A compound which is deliquescent
(ii) A compound which is insoluble in cold water, but
soluble in hot water
(iii) The compound responsible for the brown ring during the
brown ring test of nitrate iron
(iv) A compound whose aqueous solution is neutral in nature
(v) The compound which is responsible for the green
colouration when sulphur dioxide is passed through acidified potassium
dichromate solution
Solution 2
(i) Iron (III) chloride
(ii) Lead (II) chloride
(iii)Nitroso iron (II) sulphate
(iv)Sodium chloride
(v) Chromium sulphate
Question 3
What
would you observe in the following cases:
Ammonium
hydroxide is first added in a small quantity and then in excess to a solution
of copper sulphate.
Solution 3
On addition of ammonium hydroxide in a small
quantity, a blue-coloured copper hydroxide precipitate is formed. This copper
hydroxide of light blue colour dissolves in excess of ammonium hydroxide to
yield a deep blue solution.
Question 4
Sodium
hydroxide solution is added to the solutions containing the ions mentioned in
List X. List Y gives the details of the precipitate. Match the ions with
their coloured precipitates.
List X
|
List Y
|
(i) Pb2+
(ii) Fe2+
(iii) Zn2+
(iv) Fe3+
(v) Cu2+
(vi) Ca2+
|
(A) Reddish Brown
(B) White insoluble inexcess
(C) Dirty green
(D) White soluble in excess
(E) White soluble in excess
(F) Blue
|
Solution 4
(i) D
(ii) C
(iii) E
(iv) A
(v) F
(vi) B
Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 312
Question 1
State
two observations when
(i) Lead nitrate crystals are heated in a hard glass test
tube.
(ii) A few crystals of KNO3 are
heated in a hard glass tube
Solution 1
(i) Lead nitrate decrepitates on
heating; a yellow solid is formed and it fuses with glass. Lead nitrate
decomposes to lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
(ii) Oxygen is evolved.
2KNO3→ 2KNO2 + O2
Question 2
Give
a chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Sodium chloride solution and sodium nitrate solution
(ii) Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrogen sulphide gas
(iii) Calcium nitrate gas and sulphur diaoxide gas
(iv) Carbon dioxide gas and sulphur dioxide gas
Solution 2
(i) Add silver nitrate solution to both solutions. Sodium
chloride will form a curdy white ppt., whereas sodium nitrate will not
undergo any reaction.
(ii) Hydrogen chloride gas gives thick white fumes of
ammonium chloride when a glass rod dipped in ammonia solution is held near
the vapour of the acid, whereas no white fumes are observed in case of
hydrogen sulphide gas.
(iii) Calcium nitrate forms no ppt. even with addition of
excess of NH4OH, whereas zinc nitrate forms a white gelatinous
ppt. which dissolves in excess of NH4OH.
(iv) Carbon dioxide gas has no effect on acidified KMnO4
or K2Cr2O7, but sulphur dioxide turns
potassium permanganate from pink to colourless.
Question 3
Distinguish
between the following pairs of compounds using the test given with brackets :
Dilute
sulphuric acid and dilute hydrochloric acid (using barium chloride solution)
Solution 3
Sulphuric acid
precipitates the insoluble sulphate of barium from the solution of barium
chloride.
BaCl2 + H2SO4→
BaSO4 + 2HCl
Dilute HCl does not react with
barium chloride solution, and thus, no precipitate is produced in the
reaction.
Question 4
State
the inference drawn from the following observations :
(i) On Carrying out the flame test with a salt P a brick
red flame was obtained. What is the cation in P?
(ii) A gas Q turns moist lead acetate paper silvery black.
Identify the gas Q.
(iii) pH of liquid R is 10. What kind of substance is R?
(iv) Salt S is prepared by reacting dilute sulphuric acid
with copper oxide Identify S.
Solution 4
(i) On carrying out the flame test with a salt P, a
brick red flame is obtained. Hence, the cation P is Ca2+.
(ii) A gas Q turns moist lead acetate paper silvery
black. Hence, the gas is H2S.
(iii) pH of liquid R is 10. Hence, substance R is a base.
(iv) Salt S is prepared by reacting dilute sulphuric acid
with copper oxide. Hence, salt S is copper sulphate.
Question 5
State
your observation in each of the following cases:
(i) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium
carbonate crystals
(ii) When excess sodium hydroxide is added to calcium
nitrate solution
(iii) At the cathode when acidified aqueous copper sulphate
solution is electrolyzed with copper electrodes
(iv) When calcium hydroxide is heated with ammonium chloride
crystals
(v) When moist starch iodide paper is introduced into
chlorine gas
Solution 5
(i) Sodium carbonate crystals on reaction with dilute HCl form
sodium chloride, water and carbon dioxide, which is evolved with brisk
effervescence. This is a neutralisation reaction as sodium carbonate is a
basic salt, while hydrochloric acid is an acid. The chemical equation for
this reaction is as follows:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl
+H2O + CO2
(ii) Calcium nitrate solution on reaction with excess of sodium
hydroxide produces calcium hydroxide and sodium nitrate. Calcium nitrate
reacts with excess of sodium hydroxide to form a white precipitate of calcium
hydroxide, which is sparingly soluble, and colourless sodium nitrate. The
reaction is as follows:
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaOH
→ Ca(OH)2 + 2NaNO3
(iii) Acidified aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed
with copper electrodes by electrolysis. The electrolysis of an aqueous
solution of copper sulphate using copper electrodes (i.e. using active
electrodes) results in the transfer of copper metal from the anode to the
cathode during electrolysis. Copper sulphate is ionised in aqueous solution.
Chemical equation:
CuSO4 → Cu2+
+ SO42-
The positively charged
copper ions migrate to the cathode, where each gains two electrons to become
copper atoms which are deposited on the cathode.
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Hence,
the colour of copper sulphate changes from blue to colourless.
(iv) When ammonium chloride is heated with
calcium hydroxide, ammonia gas is released.
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2→ CaCl2 + 2NH3 + 2H2O
The liberated gas turns red litmus
blue.
(v) When moist starch iodide paper
is introduced into chlorine gas, chlorine oxidises iodide to iodine, which shows up as blue when it forms
a complex with starch.
Question 6
The
following table shows the tests a student performed on four different aqueous
solutions which are X,Y,Z and W. Based on the observations provided, Identify
the cation present
Chemical Test
|
Observation
|
Conclusion
|
To Solution X, ammonium hydroxide is added in minium quantity first
and then in excess
|
A dirty white precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess to
form a clear solution
|
(i)
|
To Solution Y, ammonium hydroxide is added in minimum quantity first
and then in excess
|
A pale blue precipitate is formed which dissolves in excess to form
a clear inky blue solution
|
(ii)
|
To solution W, A small quantity of sodium hydroxide solution is
added and then in excess
|
A white precipitate is formed which remains insoluble
|
(iii)
|
To a salt Z, calcium hydroxide solution is added and then heated
|
A pungent smelling gas turning moist red litmus paper blue is
obtained
|
(iv)
|
Solution 6
(i) Zn2+
(ii) Cu2+
(iii) Ca2+
(iv) NH4+
Chapter 12 - Practical Work Exercise 313
Question 1
Identify
the anion present in each of the following compounds :
(i) A salt M on treatment with concentrated sulphuric acid
produces a gas which fumes in moist air and gives dense fumes with ammonia
(ii) A salt D on treatment with dilute sulphuric acid
produces a gas which turns lime water milky but has no effect on acidified
potassium dichromate solution
(iii) When barium chloride solution is added to salt solution
E a white precipitate insoluble in dilute hydrochloric acid is obtained
Solution 1
(i) Chloride ion (Cl-)
(ii) Carbonate (CO32-)
(iii) Sulphate (SO42-)
Question 2
From
the list of the following salts choose the salt that most appropriately fits
the description given in the following :
[AgCl,MgCl2,NaHSO4,PbCO3,ZnCO3,KNO3,Ca(NO3)2]
(i) A deliquescent salt
(ii) An insoluble chloride
(iii) On heating this salt gives a yellow residue when hot
and white when cold
(iv) On heating this salt, a brown coloured to prepare the
following salts:
Solution 2
(i) A deliquescent salt: MgCl2
(ii) An insoluble chloride: AgCl
(iii) On heating, this salt gives a
yellow residue when hot and a white residue when cold: ZnCO3
(iv) On heating this salt, a brown-coloured gas is evolved: Ca(NO3)2
Question 3
Give
balanced chemical equations to prepare the following salts:
(i) Lead sulphate from lead carbonate
(ii) Sodium sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid
(iii) Copper chloride using copper carbonate
Solution 3
(i) 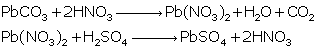

(ii) 
(iii) 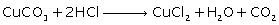
Question 4
Identify
the cations in each of the following case:
(i) NaOH solution when added to solution (A) gives a
reddish brown precipitate
(ii) NH4OH solution when added to solution (B)
gives white ppt. which does not dissolve in excess.
(iii) NaOH solution when added to solution (C) gives white
ppt. which insoluble in excess
Solution 4
(i) Fe3+ ion
(ii) Pb2+ ion
(iii) Ca2+ ion
Question 5
Identify
the gas evolved and give the chemical test in each of the following cases:
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium sulphite
(ii) Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron (II) sulphide
Solution 5
(i) Sulphur dioxide
Freshly
prepared K2Cr2O7 paper changes from orange
to green.
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide
The
gas released has a rotten egg smell.
Question 6
Identify
the salts P and Q from the observations given below:
(i) On performing the flame test salt P produces a lilac
coloured flame and its solution gives a white precipitate with silver nitrate
solution. Which is soluble in ammonium hydroxide solution.
(ii) When dilute HCl is added to a salt Q, a brisk effervescence
is produced and the gas turns lime water milky. When NH4OH soltion
is added to the above mixture (after adding dilute HCl), it produces a white
precipitate which is soluble in excess NH4OH solution.
Solution 6
(i) KCl
(ii) ZnCO3

0 comments:
Post a Comment