Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 145
Question 1

Solution 1

Question 2
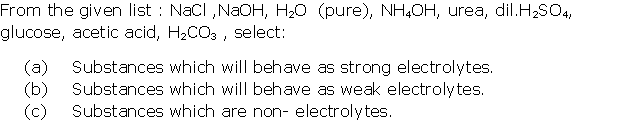
Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3
Question 4
Explain electrolysis of lead bromide.
Solution 4
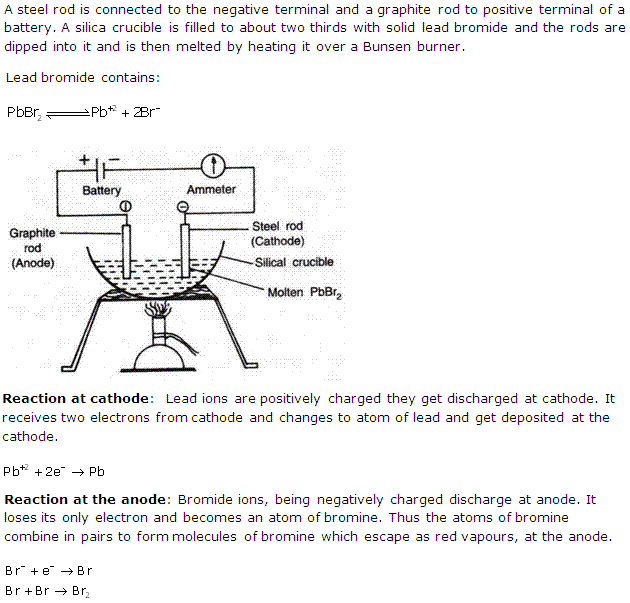
Question 5
Solution 5
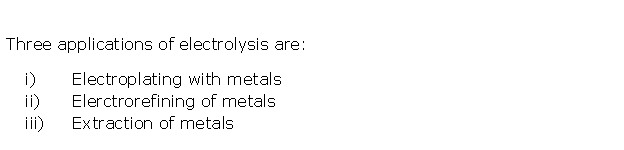
Question 6

Solution 6

Question 7
Solution 7

Question 8
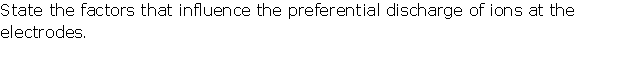
Solution 8

Question 9

Solution 9

Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 146
Question 1

Solution 1
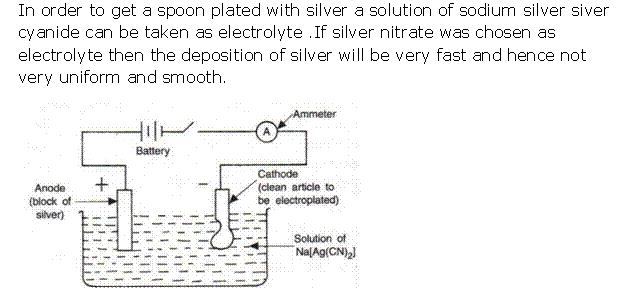
Question 2

Solution 2

Question 3

Solution 3
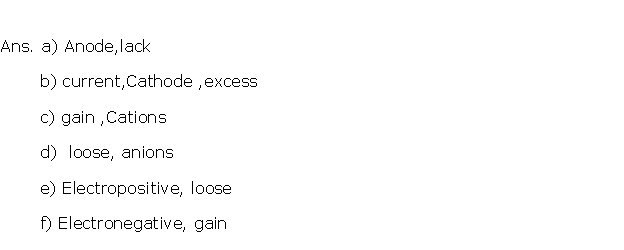
Question 4

Solution 4

Question 5

Solution 5

Question 6
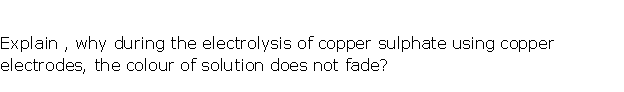
Solution 6

Question 7

Solution 7

Question 8
Solution 8
Question 9
Solution 9

Question 10
Solution 10

Question 11

Solution 11

Question 12
Choose
the correct answer from the options given below:
(i) Which one is weak electrolyte?
(a) HNO3
(b) KOH
(c) CuSO4
(d) Cu(OH)2
(ii) Which among the following cations will
discharge with ease
at cathode?
(a) Na+
(b) Au3+
(c) Cu2+
(d) H+
(iii) Which among the following anions will discharge with
ease at anode?
(a) Cl-
(b) I-
(c) OH-
(d) 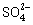
(iv) In electrolysis of molten lead bromine anode is made up
of
(a) Steel rod
(b) Platinum foil
(c) Glass rod
(d) Graphite rod
(v) Electrolysis of acidulated water is used in
the production of
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Hydrogen and oxygen
Solution 12
(i) CuSO4
(ii) Au3+
(iii) OH⁻
(iv) Graphite rod
(v) Hydrogen and oxygen
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 147
Question 1
The following questions relate to the electroplating of an article with silver.
(a) Name the electrode formed by the article which is to be plated.
(b) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(c) What should be the nature of the anode?
(a) Name the electrode formed by the article which is to be plated.
(b) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(c) What should be the nature of the anode?
Solution 1
(a) The article to be plated must be made Cathode.
(b) The ions of the metal which is to be electroplated must be present in the electrolyte.
(c) The metal to be plated on the article must be made anode. It needs to be periodically replaced.
(b) The ions of the metal which is to be electroplated must be present in the electrolyte.
(c) The metal to be plated on the article must be made anode. It needs to be periodically replaced.
Question 2
How is the passage of electricity through an electrolyte different from the passage of electricity through a copper wire?
Solution 2
The passage of electricity through an electrolyte occurs through ions furnished by the electrolyte where as the passage of electricity through a copper wire occurs through electrons.
Question 3
The following questions are about electroplating of copper wire with silver.
(a) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(b) Of what substance must the anode be made up of?
(c) What will the cathode be made up of?
(d) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
(a) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(b) Of what substance must the anode be made up of?
(c) What will the cathode be made up of?
(d) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
Solution 3

Question 4
Define or explain the term: Electrolysis.
Solution 4
It is the process of decomposition of an electrolyte in the molten or aqueous state by discharge of ions at the electrodes on the passage of an electric current.
Question 5
Why is it necessary to add acid to water before proceeding with electrolysis of 'water'?
Solution 5
Pure water does not conduct electricity because the degree of ionization is low. Thus to make it a good conductor of electricity acid is added to it which will increase the degree of ionization.
Question 6
Give one example of a substance which contains: (i) Ions only (ii) molecules only (iii) both ions and molecules.
Solution 6
Substance which contain
(i) Ions only:- HCl
(ii) Molecules only:- Petrol
(iii) Both ions and molecules:- CH3COOH
(i) Ions only:- HCl
(ii) Molecules only:- Petrol
(iii) Both ions and molecules:- CH3COOH
Question 7
(a) What is meant by the term 'electrolyte'?
(b) What are the particles present in a compound which is a non- electrolyte?
(c) If an electrolyte is described as a 'strong electrolyte' what does this mean?
(b) What are the particles present in a compound which is a non- electrolyte?
(c) If an electrolyte is described as a 'strong electrolyte' what does this mean?
Solution 7
(a) Electrolyte is a compound which either in aqueous solution or in molten state allows an electric current to pass through it and is accompanied by discharge of ions and finally into neutral atoms at the two electrodes.
(b) Non- electrolyte are substances which do not conduct electricity in fused or aqueous state. They contain only molecules and do not ionize. For example: petrol, alcohol.
(c) If the electrolyte is described as 'strong electrolyte' it means it completely dissociates into its constituting ions in aqueous solution.
(b) Non- electrolyte are substances which do not conduct electricity in fused or aqueous state. They contain only molecules and do not ionize. For example: petrol, alcohol.
(c) If the electrolyte is described as 'strong electrolyte' it means it completely dissociates into its constituting ions in aqueous solution.
Question 8
The following Question refer to the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution with copper electrodes:
(a) Compare the change in mass of the anode
(b) What is seen to happen to the colour of the copper sulphate solution if platinum electrodes are used? Explain the observation.
(c) What is the practical application of the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution? Briefly, describe one such application.
(a) Compare the change in mass of the anode
(b) What is seen to happen to the colour of the copper sulphate solution if platinum electrodes are used? Explain the observation.
(c) What is the practical application of the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution? Briefly, describe one such application.
Solution 8
(a) As for every copper ion discharged at the cathode, an ion of copper is formed at the anode which goes into the solution .Since atoms of copper are deposited at the cathode, the cathode becomesthicker and as the atoms of copper from the anode change into ions of copper, the anode becomes thinner.
(b) When platinum rods are used as electrodes, then x the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades and sulphuric acid is formed. This is because oxygen is liberated at anode and copper metal is deposited at cathode
(c) Practical application of electrolysis of copper sulphate solution: This is the basis for purification of copper.
Other metals like Zinc, Nickel, Silver .Lead can also be purified.
(b) When platinum rods are used as electrodes, then x the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades and sulphuric acid is formed. This is because oxygen is liberated at anode and copper metal is deposited at cathode
(c) Practical application of electrolysis of copper sulphate solution: This is the basis for purification of copper.
Other metals like Zinc, Nickel, Silver .Lead can also be purified.
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 148
Question 1
What should be the physical state of lead bromide if it is to conduct electricity?
Solution 1
Lead Bromide should be in the molten state if it has to conduct electricity.
Question 2
What particles are present in pure lead bromide?
Solution 2
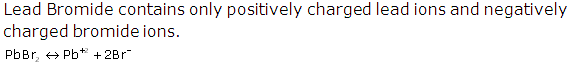
Question 3
Write the equations for the reactions, which takes place at the electrodes during the electrolysis of lead bromide?
Solution 3

Question 4
Choosing only words from the following list, write down the appropriate words to fill in the blanks (a) to (e) below: anions, anode, cathode, cations, electrode, electrolyte, nickel, voltameter.
To electroplate an article with nickel requires an (a) ________ which must be a solution containing (b) ________ions. The article to be plated is placed as the (c) _________of the cell in which the plating is carried out. The (d)________ of the cell is made from pure nickel. The ions that are attracted to the negative electrode and discharged are called (e)________.
To electroplate an article with nickel requires an (a) ________ which must be a solution containing (b) ________ions. The article to be plated is placed as the (c) _________of the cell in which the plating is carried out. The (d)________ of the cell is made from pure nickel. The ions that are attracted to the negative electrode and discharged are called (e)________.
Solution 4
(a) Electrolyte
(b) Nickel
(c) cathode
(d) anode
(e) Cations
(b) Nickel
(c) cathode
(d) anode
(e) Cations
Question 5
Correct the sentence by adding word(s)
The electrolysis of lead bromide liberates lead and bromine.
The electrolysis of lead bromide liberates lead and bromine.
Solution 5
The electrolysis of lead bromide liberates lead at cathode and bromine at anode.
Question 6
If a fused metallic chloride is electrolyzed, at which electrode would the metal be obtained?
Solution 6
When a fused metallic chloride is electrolyzed, the metal is obtained at cathode.
Question 7
Classify the following substances under three headings:
(a) Strong electrolytes (b) weak electrolytes ( c) non- electrolytes
Acetic acid, ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide, carbon tetrachloride, dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium acetate, dilute sulphuric acid.
(a) Strong electrolytes (b) weak electrolytes ( c) non- electrolytes
Acetic acid, ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide, carbon tetrachloride, dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium acetate, dilute sulphuric acid.
Solution 7
(a) Strong electrolytes - dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulphuric acid, Ammonium chloride
(b) Weak electrolyte - Acetic acid, Ammonium hydroxide
(c) Non-electrolytes - Carbon tetrachloride
(b) Weak electrolyte - Acetic acid, Ammonium hydroxide
(c) Non-electrolytes - Carbon tetrachloride
Question 8
(a) Write down the words or phrases from the brackets that will correctly fill in the blanks in the following sentences:
(i) Pure water consists entirely of ________ ( ions/ molecules).
(ii) We can expect that pure water _______ ( will / will not) normally conduct electricity.
(i) Pure water consists entirely of ________ ( ions/ molecules).
(ii) We can expect that pure water _______ ( will / will not) normally conduct electricity.
Solution 8
(i) molecules.
(ii) will not
(ii) will not
Question 9
(a) To carry out the so called "electrolysis of water", sulphuric acid is added to water. How does the addition of sulphuric acid produce a conducting solution?
(b) Copy and complete the following sentence :
With platinum electrodes, hydrogen is liberated at the ______and oxygen at the _________ during the electrolysis of acidified water.
(b) Copy and complete the following sentence :
With platinum electrodes, hydrogen is liberated at the ______and oxygen at the _________ during the electrolysis of acidified water.
Solution 9
(a) When sulphuric acid is added to water it becomes good conductor as addition of sulphuric acid causes dissociation of water molecules into H+ and OH- ions which are then responsible for conduction of electricity by pure water. The water thus obtained is called acidified water.
(b) Cathode, Anode
(b) Cathode, Anode
Question 10
Solution 10
Question 11
Complete the sentence by choosing correct words given in brackets.
Electrolysis is the passage of __________ (electricity/electrons) through a liquid or solution accompanied by a __________ ( physical/chemical ) change.
Electrolysis is the passage of __________ (electricity/electrons) through a liquid or solution accompanied by a __________ ( physical/chemical ) change.
Solution 11
electricity, chemical
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 149
Question 1
Element X is a metal with valency 2. Element Y is a non-metal with valency 3.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(b) If Y is diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
(c) Write two applications of electrolysis in which anode diminish in mass.
(d) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the _____ and the Y at the ________of the electrolytic cell. (Provide the missing words).
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
(b) If Y is diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
(c) Write two applications of electrolysis in which anode diminish in mass.
(d) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the _____ and the Y at the ________of the electrolytic cell. (Provide the missing words).
Solution 1
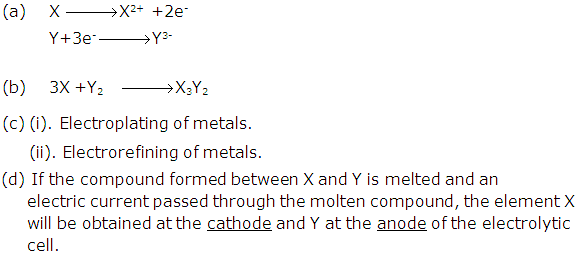
Question 2
(a) What kind of particles will be found in a liquid compound which is a non- electrolyte?
(b) If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be present in its dilute solution apart from those of water?
(c) Cations are formed by _______ (loss/ gain) of electrons and anions are formed by ________( loss/gain) of electrons.
(Choose the correct words to fill in the blanks.)
(d) What ions must be present in a solution used for electroplating a particular metal?
(e) Explain how electrolysis is an example of Redox reaction.
(b) If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be present in its dilute solution apart from those of water?
(c) Cations are formed by _______ (loss/ gain) of electrons and anions are formed by ________( loss/gain) of electrons.
(Choose the correct words to fill in the blanks.)
(d) What ions must be present in a solution used for electroplating a particular metal?
(e) Explain how electrolysis is an example of Redox reaction.
Solution 2
(a) Molecules are found in a liquid compound which is a non-electrolyte.
(b) Non ionized molecules; H+ and X- particles will be present in dilute solution.
(c) Loss, Gain
(d) The ions of the metal which is to be electroplated on the article must be present in a solution.
(e) Redox reaction is one in which oxidation and reduction occurs simultaneously.
Similarly in case of electrolysis:
At cathode: The cations gain electron and become neutral. As the electrons are gained the ion is said to be reduced.
At anode: The anions lose electron to form neutral atoms. As the electrons are lost the ion is said to be oxidized.
Hence in electrolysis also the oxidation and reduction occurs hence it is an example of Redox reaction.
(b) Non ionized molecules; H+ and X- particles will be present in dilute solution.
(c) Loss, Gain
(d) The ions of the metal which is to be electroplated on the article must be present in a solution.
(e) Redox reaction is one in which oxidation and reduction occurs simultaneously.
Similarly in case of electrolysis:
At cathode: The cations gain electron and become neutral. As the electrons are gained the ion is said to be reduced.
At anode: The anions lose electron to form neutral atoms. As the electrons are lost the ion is said to be oxidized.
Hence in electrolysis also the oxidation and reduction occurs hence it is an example of Redox reaction.
Question 3
(i) Explain, why copper though a good conductor of electricity is, a non- electrolyte.
(ii) Name the gas released at the cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
(iii) Explain, why solid sodium chloride does not allow electricity to pass through?
(iv) Fill in the blanks:
(a) As we descend the electrochemical series containing cations, the tendency of the cations to get ________ (oxidized/reduced) at the cathode increases.
(b) The (higher/lower) _______ the concentration of an ion in a solution, the greater is the probability of its being discharged at its appropriate electrode.
(ii) Name the gas released at the cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
(iii) Explain, why solid sodium chloride does not allow electricity to pass through?
(iv) Fill in the blanks:
(a) As we descend the electrochemical series containing cations, the tendency of the cations to get ________ (oxidized/reduced) at the cathode increases.
(b) The (higher/lower) _______ the concentration of an ion in a solution, the greater is the probability of its being discharged at its appropriate electrode.
Solution 3
(i) Copper metal is solid and has no mobile ions whereas an electrolyte should dissociate into oppositely charged ions to conduct the electric current.
(ii) Hydrogen is released at the cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
(iii) In sodium chloride, Na+ and Cl- ions are not free to carry the electric current.
(iv) (a) Reduced
(b) Higher
(ii) Hydrogen is released at the cathode when acidulated water is electrolyzed.
(iii) In sodium chloride, Na+ and Cl- ions are not free to carry the electric current.
(iv) (a) Reduced
(b) Higher
Question 4
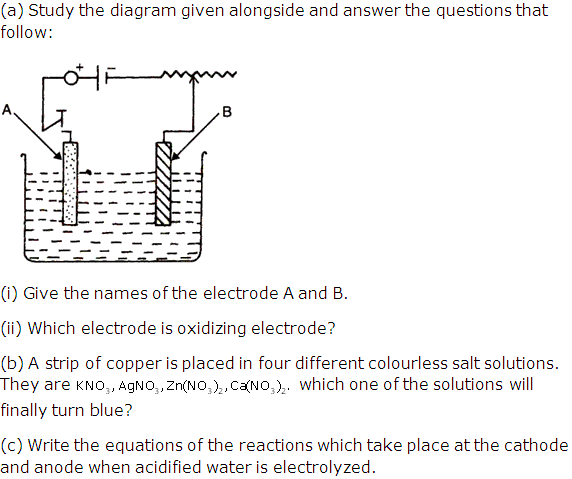
Solution 4
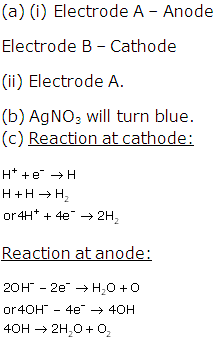
Question 5
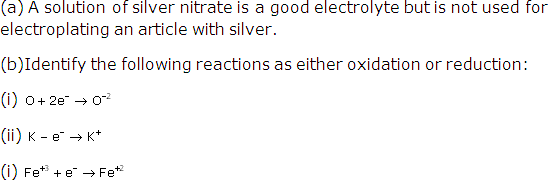
Solution 5

Question 6
Choose A, B, C or D to match the descriptions (i) to (v) below . Some alphabets may be repeated.
(A) Non-electrolyte, (B) Strong electrolyte, (C) Weak electrolyte, (D) Metallic conductor
(i) Molten ionic compound
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride
(iii) An aluminium wire
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules.
(A) Non-electrolyte, (B) Strong electrolyte, (C) Weak electrolyte, (D) Metallic conductor
(i) Molten ionic compound
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride
(iii) An aluminium wire
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules.
Solution 6
(i) Molten ionic compound - Strong electrolyte
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride- Non-electrolyte
(iii) An aluminium wire- Metallic conductor
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules- weak electrolyte
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules- Non-electrolyte
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride- Non-electrolyte
(iii) An aluminium wire- Metallic conductor
(iv) A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules- weak electrolyte
(v) A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules- Non-electrolyte
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 150
Question 1
The following is an extract from metals in the service of man, Alexander and street /Pelican 1976': Alumina (aluminium oxide) has a very high melting point over 2000oC, so that I cannot readily be liquefied. However, conversion of alumina to aluminium and oxygen, by electrolysis, an occur when it is dissolved in some other substance.
(a) Which solution is used to react with bauxite as first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide?
(b) The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the equation for this reaction.
(c) Name the element which serves both as the anode and the cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
(d) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium.
(e) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
(f) Give the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
(a) Which solution is used to react with bauxite as first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide?
(b) The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the equation for this reaction.
(c) Name the element which serves both as the anode and the cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
(d) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium.
(e) Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
(f) Give the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
Solution 1

Question 2
Choose the correct answer:
During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, which of the following takes place?
(a) Bromine is released at the cathode
(b) Lead is deposited at the anode
(c) Bromine ions gain electrons
(d) Lead is deposited at the cathode
During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, which of the following takes place?
(a) Bromine is released at the cathode
(b) Lead is deposited at the anode
(c) Bromine ions gain electrons
(d) Lead is deposited at the cathode
Solution 2
(d) Lead is deposited at the cathode
Question 3

Solution 3

Question 4
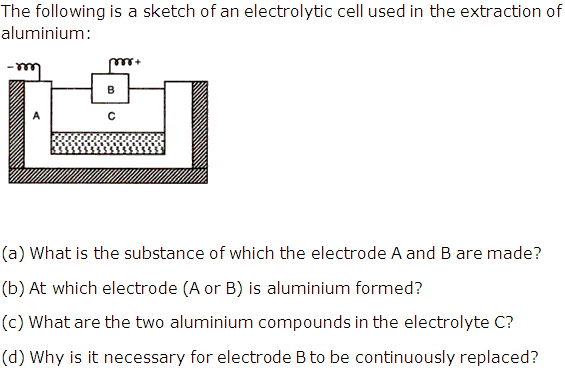
Solution 4
(a) Electrode A is made of gas carbon and electrode B is made of Carbon rods.
(b) At electrode A.
(c) Two compounds in the electrolyte are Al2O3 and Na3AlF6
(d) As at electrode B the oxygen is liberated during the process. The oxygen liberated oxidizes the carbon anode producing CO and CO2.Thus electrode B is to be replaced continuously.
(b) At electrode A.
(c) Two compounds in the electrolyte are Al2O3 and Na3AlF6
(d) As at electrode B the oxygen is liberated during the process. The oxygen liberated oxidizes the carbon anode producing CO and CO2.Thus electrode B is to be replaced continuously.
Question 5
A metal article is to be electroplated with silver. The electrolyte selected is sodium argentocyanide.
(a) What kind of salt is sodium argento cyanide?
(b) Why is it preferred to silver nitrate as an electrolyte?
(c) State one condition to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and long lasting.
(d) Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
(e) Write the reaction taking place at the anode.
(a) What kind of salt is sodium argento cyanide?
(b) Why is it preferred to silver nitrate as an electrolyte?
(c) State one condition to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and long lasting.
(d) Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
(e) Write the reaction taking place at the anode.
Solution 5

Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 151
Question 1
Find the odd one out from the following and explain your choice:
Al(OH)3, Pb(OH)2,Mg(OH)2,Zn(OH)2
Al(OH)3, Pb(OH)2,Mg(OH)2,Zn(OH)2
Solution 1
Mg(OH)2 as it is basic while rest are amphoteric.
Question 2
Correct the following statement:
Lead bromide conducts electricity.
Lead bromide conducts electricity.
Solution 2
Molten Lead bromide conducts electricity.
Question 3
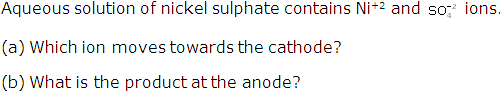
Solution 3
(a) Nickel ions move towards cathode.
(b) Nickel ions.
(b) Nickel ions.
Question 4
Select
the correct answer from the choices a,b,c
and d which are given. Write only the letter corresponding to the correct
answer.
(i) A compound which liberates reddish brown gas around the
anode during the electrolysis in its molten state is :
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Copper (II) oxide
(c) Copper (II) sulphate
(d) Lead (II) bromide
(ii) During ionization metals lose electrons, this change
can be called
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
(c) Redox
(d) Displacement
Solution 4
(i) Lead (II) bromide
(ii) Oxidation
Question 5
Mr Ramu wants
electrolyte his key chain with nickel to prevent rusting. For this
electroplating
(i) Name the electrolyte
(ii) Name the cathode
(iii) Name the anode
(iv) Give the reaction at the cathode
(v) Give the reaction at the anode
Solution 5
(i) Aqueous solution of nickel sulphate with few drops of
dil. sulphuric acid
(ii) Article (e.g. key chain)
(iii) Pure nickel
(iv) Ni2+ + 2e-→ Ni
(v) Ni → Ni2+
+ 2e-
Question 6
Three
different electrolytic cells, A,B, and C are conncted in separate circuits. Electrolytic cell A
contains sodium chloride solution. When the circuit is completed a bulb in
the circuit glows brightly. Electrolytic cell B contains acetic acid solution
and in this case the bulb in the circuit glows dimly. The electrolytic cell C
contains sugar solution and the bulb does not glow. Give a reason for each of
these observations
Solution 6
Cell
A contains sodium chloride solution which is a strong
electrolyte and contains only ions. So, it conducts electricity
and the bulb glows brightly.
Cell
B contains both ions and molecules. So, there are few
ions to conduct electricity and the bulb glows dimly.
Cell
C contains sugar solution which is a non-electrolyte and
does not contain ions. So, it is a bad conductor of
electricity
and the bulb does not glow.
Question 7
Give
reasons as to why - the electrolysis of acidulated water is considered to be
an example of catalysis.
Solution 7
Dilute
sulphuric acid catalyses dissociation, so electrolysis of acidified water is
considered an example of catalysis.
Question 8
Fill
in the blanks from the choices given below :
(i) In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to the
______ (sharing/transfer) of electrons.
(ii) Electro covalent compounds have a _____ (low/high)
boiling point
(iii) A molecule of _____ contains a triple bond (hydrogen,
ammonia, nitrogen).
Solution 8
(i) In covalent compounds, the bond is formed due to the sharing of electrons.
(ii) Electro covalent compounds have a high
boiling point.
(iii) A molecule of nitrogen
contains a triple bond.
Question 9
Differentiate
between electrical conductivity of copper sulphate solution and copper metal
Solution 9
Copper sulphate solution
|
Copper metal
|
Conduction of electricity is
due to the flow of ions.
|
Conduction of electricity is
due to the flow of electrons.
|
It is an aqueous solution of
an ionic compound.
|
It is a metal in the solid
state.
|
It undergoes a chemical
change.
|
It remains unchanged
chemically.
|
Question 10
During
the electrolysis of copper (II) sulphate solution using platinum as cathode
and carbon an anode:
(i) What do you observe at the cathode and at the anode?
(ii) What change is noticed in the electrolyte?
(iii) Write the reactions at the cathode and at the anode.
Solution 10
(i) Red shiny metal is deposited at the cathode.
(ii) The colour of the electrolytes changes gradually from
blue to colourless.
(iii) At the cathode:
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Reaction at the anode:
OH- → OH + e-
4OH → 2H2O + O2
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 152
Question 1
Copper
sulphate solution is electrolyzed using copper electrodes
Study
the diagram given alongside and answer the questions that
follows.
(i) Which electrode to your left or right is known as the
oxidizing electrode and why?
(ii) Write the equation representing the reaction that
occurs
(iii) State two appropriate observations for the above
electrolysis reactions.
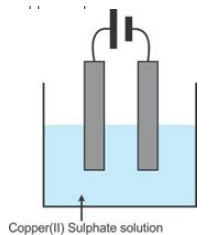
Solution 1
(i) The right electrode is the anode and oxidising electrode Cu → Cu2+
+ 2e- losing electrode.
(ii) Reaction at the anode: Cu → Cu2+
+ 2e-
Reaction at the cathode: Cu2+
+ 2e- → Cu
(iii) The anode dissolves and anode mud containing precious
metal is recovered.
Question 2
Which
of these will act as a non-electrolyte?
(i) Liquid carbon tetrachloride
(ii) Acetic acid
(iii) Sodium hydroxide aqueous solution acid
(iv) Potassium chloride aqueous solution
Solution 2
(i) Liquid carbon tetrachloride
Question 3
State
one observation when electricity is passed through molten lead bromide.
Solution 3
Dark reddish brown fumes of
bromine evolve at the anode and greyish white metal
lead is formed on the cathode.
Question 4
When
fused lead bromide is electrolyzed we observe
(i) A silver grey deposit at anode and a reddish brown
deposit at cathode
(ii) A silver grey deposit at cathode and reddish brown
deposit at anode
(iii) A silver grey
deposit at cathode and reddish brown fumes at anode
(iv) Silver grey fumes at anode and reddish brown fumes at
cathode
Solution 4
(iii) A silver grey deposit at the
cathode and reddish brown fumes at the anode.
Question 5
The
electrolyte used for electroplating an article with silver is:
(i) Silver nitrate solution
(ii) Silver cynide solution
(iii) Sodium argentocyanide
solution
(iv) Nickel sulphate solution
Solution 5
(iii) Sodium argentocyanide solution
Question 6
M
is a metal above hydrogen in the activity series and its oxide has the
formula M2O. The oxide when dissolved in water forms the
corresponding hydroxide which is a good conductor of electricity. In the
above context answer the following:
(i) What kind of combination exists between M and O?
(ii) How many electrons and there in the outermost shell of
M?
(iii) Name the group to which M belongs
(iv) State the reaction taking place in the cathode
(v) Name the product at the anode
Solution 6
(i) Electrovalent or ionic compounds
(ii) One electron
(iii) Since it has valency 1, M belongs to Group 1.
(iv) At the cathode: M+ + 1e- → M
(v) At the anode: Oxygen gas
Question 7
Give
appropriate scientific reasons for the following statements:
(i) Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc by using carbon
monoxide, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity.
(iii) During electrolysis of molten lead bromide graphite
anode is preferred to other electrodes
(iv) The electrical conductivity of acetic acid is less in comparision to the electrical conductivity of dilute
sulphuric acid at a given concentration
(v) Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be
a redox reaction
Solution 7
(i) Zinc is lower in the reactivity series, so it is
comparatively less reactive. Hence, it is reduced by using carbon monoxide.
But aluminium is very reactive; hence, it cannot be reduced by using a reducing
agent and it can be reduced only by electrolytic reduction.
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride is a liquid and does not conduct
electricity because it is a covalent compound and there are no free ions
present and it contains only molecules.
(iii) In electrolysis of molten lead bromide, reactive bromine
is liberated at the anode. As bromine is very reactive, an inert electrode
like graphite is preferred in the electrolysis of molten lead bromide.
(iv) Acetic acid is a weak acid and has fewer ions, so
conductivity is less, whereas dilute sulphuric acid is a strong acid and has
more ions, and therefore, its electrical conductivity is more.
(v) During electrolysis of lead bromide, there is loss of
electrons at the anode by bromine and gain of electrons at the cathode by
lead. Thus, oxidation and reduction occur side by side. So, it is a redox reaction.
PbBr2 ⇌ Pb+2 + 2Br-
Question 8
Differentiate
between the terms strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte (stating any two
differences)
Solution 8
Strong Electrolytes
|
Weak Electrolytes
|
Electrolytes which allow a large
amount of electricity to flow through them.
|
Electrolytes which allow small
amounts of electricity to flow through them.
|
These are good conductors of
electricity.
|
These are poor
conductors of electricity.
|
These almost completely dissociate in
the fused or aqueous solution state.
|
These are partially dissociated in
the fused or aqueous solution state.
|
These solutions contain only free
mobile ions.
|
These solutions contain ions as well
as molecules.
|
Chapter 6 - Electrolysis Exercise 153
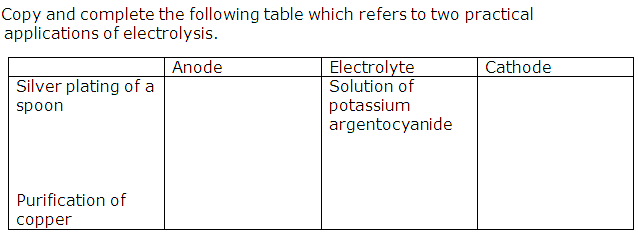
Question 1
(i) Copy and complete the following table :
Anode
|
Electrolyte
|
|
Purification of copper
|
(ii) Write the equation taking place at the
anode.
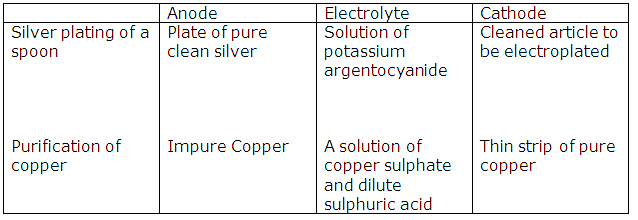
Solution 1
Anode
|
Electrolyte
|
|
Purification of copper
|
Impure copper
|
Solution of
copper sulphate
and dilute
sulphuric acid
|
(i)
(ii) Ag - e- → Ag+
Cu - e- → Cu2+
Cl⁻ ‒ e- → Cl
Cl + Cl → Cl2
Question 2
Give
reasons why:
(i) Sodium chloride will conduct electricity only in fused
or aqueous solution state
(ii) In the electroplating of an article with silver, the
electrolyte sodium argento-cynide solution is
preferred over silver nitrate solution
(iii) Although copper is a good conductor of electricity, it
is a non-electrolyte.
Solution 2
(i) Electrostatic forces of attraction between ions in the
solid state are very strong. These forces weaken in the fused state or in the
solution state. Hence, ions become mobile.
(ii) If silver nitrate solution is used directly instead of
double cyanide of silver and sodium, the deposition of silver will be very
fast and hence not very smooth and uniform.
(iii) Copper has no mobile electrons in the solid state and
an electrolyte should dissociate into oppositely charged ions to conduct
electricity.
Hence, copper is a non-electrolyte.
Question 3
(i) Name the product formed at the anode during the
electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrodes
(ii) Name the metallic ions that should be
present in the electrolyte when an article made copper is to be electroplated
with silver
Solution 3
(i) Oxygen is the product formed at the anode.
(ii) Ag+ and Na+
Question 4
Write
equations for the reactions taking place at the two electrodes (mentioning
clearly the name of the electrodes) during the electrolysis of
(i) Acidified copper sulphate solution with copper
electrodes
(ii) Molten lead bromide with inert electrodes
Solution 4
(i) Electrodes:
Cathode:
Copper
Anode: Platinum
Reaction at the cathode: Cu2+ +
2e-→
Cu
Reaction at the anode: 4OH- - 4e-→
4OH
2OH + 2OH →2H2O + O2
(ii) The cathode and anode are both made of
graphite plates.
Reaction at the cathode: Pb2+ +
2e-→Pb
Reaction at the anode: Br- - e-→Br
Br + Br →Br2
Question 5
Identify
the substance underlined in each of the following cases:
(a) The electrolyte used for electroplating an
article with silver.
(b) The particles present in a liquid such as kerosene, that is non-electrolyte.
Solution 5
(i) The electrolyte used for electroplating an article with
silver: Sodium argentocyanide or potassium argentocyanide
(ii) The particles present in a liquid such as
kerosene that is a non-electrolyte: Molecules
Question 6
State
the observations at the anode and at the cathode during the electrolysis of :
(a) Fused lead bromide using graphite
electrodes
(b) Copper sulphate solution using copper
electrodes
Solution 6
(i) Observations:
Anode: Dark reddish brown fumes of bromine
evolve at the anode.
Cathode: Greyish
white metal lead is formed on the cathode.
(ii) Observations:
Anode: Nothing gets deposited on the anode
because the copper anode dissolves during the reaction as Cu2+
ions are formed.
Cathode: Reddish brown Cu is deposited.
Question 7
Select
the ion in each case, that would get selectively discharge from the aqueous
mixture of the ions listed below :
Solution 7
(a) OH-
(b) Ag+

0 comments:
Post a Comment